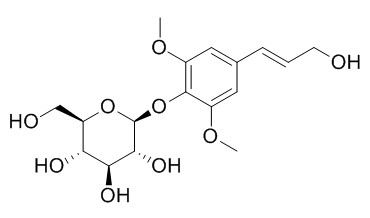
Syringin
Syringin (Eleutheroside B) has neuroprotective, tonic, adaptogenic, antitumour, anti- platelet aggregation, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive ,and immune-modulating properties. It reduced the expression levels of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) ,COX,TNF-α, Beta Amyloid, and Caspase.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Korean Med Obes Res.2023, 23:10-7
Metabolites2023, 13(1), 3.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2019, 19(1):11
Mol Med Rep.2022, 26(4):299.
Molecules.2023, 28(8):3503.
Academic J of Second Military Medical University2018, 39(11)
J Food Biochem.2019, 43(9):e12970
Int J Mol Med.2019, 43(6):2516-2522
HortTechnology2016, 26(6):816-819
Integrative Medicine Research2024, 13(1):101025.
Related and Featured Products
Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Apr;33(4):531-8.
Syringin from stem bark of Fraxinus rhynchophylla protects Abeta(25-35)-induced toxicity in neuronal cells.[Pubmed:
20422361]
The medicinal herb Jinpi, derived from the dried stem barks of Fraxinus rhynchophylla belonging to Oleaceae is widely used as a variety of Korean folk remedies for anti-inflammatory, febricide, antidiarrhea, and antileukorrhea diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the course of screening antidementia agents from natural products, F. rhynchophylla showed significant inhibitory activity toward Abeta(25-35)-induced neuronal cell death. An active principle was isolated and identified as Syringin.When the neuroblastoma cells were exposed to 50 microM Abeta(25-35), 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction rate (survival rate) decreased to 60.21 +/- 2.16% over control while Syringin treated ones recovered cell viability up to 79.12 +/- 1.39% at 20 microM. In addition, 20 microM Syringin almost completely removed Abeta(25-35)-induced reactive oxygen species. The neuroprotective effect of Syringin seemed to be originated from the reduction of apoptosis since decrease in caspase-3 activity and expression, reduction in cleaved PARP, and DNA fragmentation were observed.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that F. rhynchophylla and Syringin are expected to be useful for preventing Abeta(25-35)-induced neuronal cell damage.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;29(2):178-84.
Syringin may exert sleep-potentiating effects through the NOS/NO pathway.[Pubmed:
25377727]
Sleep is essential for basic survival as well as for optimal physical and cognitive performance in both human beings and animals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the effect of Syringin on sleep of anesthetized mice and the potential mechanisms, 35 male Kunming mice were randomly divided into six experimental groups (n = 5) and one control group (n = 5). Sleep latency and sleep duration, as well as nitric oxide (NO) content and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity, were determined after Syringin administration. The NO precursor l-Arginine (l-Arg) or NOS inhibitor NG-Nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) was administered alone or in combination with Syringin, and time for sleep latency and duration was recorded. After intragastric administration of Syringin, sleep latency decreased in a dose- and time-dependent manner, concomitant with increased sleep duration. The optimal sleep performance was obtained when Syringin was given at a dose of 80 mg/kg for eight consecutive days. Syringin significantly reduced NO concentration and NOS activity. Administration of l-Arg prolonged sleep latency and shortened sleep duration, and the effects were fully reversed by Syringin coadministration. Administration of L-NAME induced a significant reduction in sleep latency and a corresponding increase in sleep duration, and coadministration of Syringin further enhanced the effects.
CONCLUSIONS:
The finding of our study demonstrated that Syringin could exert sleep-potentiating effects on anesthetized mice in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and these effects may be intimately correlated with the NO/NOS pathway.
Planta Med. 2004 Nov;70(11):1027-32.
Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of sinapyl alcohol and its glucoside syringin.[Pubmed:
15549657]
In the present study, Syringin, isolated by activity-guided fractionation of the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts of the stem bark of Magnolia sieboldii, and sinapyl alcohol, the hydrolysate of Syringin, were evaluated for anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sinapyl alcohol (20, 30 mg/kg/day, p. o.) inhibited increased vascular permeability by acetic acid in mice and reduced acute paw edema by carrageenan in rats more so than Syringin. When analgesic activity was measured using the acetic acid-induced writhing test and the hot plate test, sinapyl alcohol was much more potent than Syringin in a mouse model. In addition, sinapyl alcohol more potently inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production by macrophages than Syringin. Consistent with these observations, the expression levels of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 was reduced by sinapyl alcohol in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of Syringin after oral administration may be attributed to its in vivo transformation to sinapyl alcohol.
J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Mar;34(3):265-71.
Hepatoprotective effects of syringin on fulminant hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide in mice.[Pubmed:
23620140]
Animal Models: BALB/c mice
Formulation: ---
Dosages:10, 30 and 100 mg/kg
Administration: i.p.