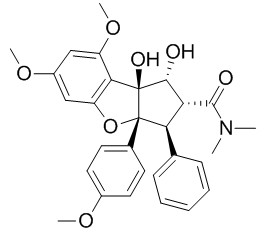
Rocaglamide
Rocaglamides are potent natural anticancer products that inhibit proliferation of various cancer cells at nanomolar concentrations, it prevents tumor growth and sensitize resistant cancer cells to apoptosis by blocking the MEK-ERK-eIF4 pathway. Rocaglamides can suppress the PMA-induced expression of NF-kappaB target genes and sensitize leukemic T cells to apoptosis induced by TNFalpha, cisplatin, and gamma-irradiation, suggests that rocaglamide derivatives could serve as lead structures in the development of anti-inflammatory and tumoricidal drugs. Rocaglamide and a XIAP inhibitor cooperatively sensitize TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Industrial Crops and Products2020, 146:112186
Nutrients.2024, 16(22):3805.
Appl. Sci.2023, 13(2), 860.
Br J Pharmacol.2024, 181(24):5009-5027.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:806869.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):303
Agriculture.2024, 69(3):140-148.
Arch Biochem Biophys.2018, 644:93-99
VNU J Science: Med.&Pharm. Sci.2024.2588-1132
Toxicol In Vitro.2019, 59:161-178
Related and Featured Products
Int J Cancer. 2014 Apr 15;134(8):1991-2002.
The natural anticancer compound rocaglamide selectively inhibits the G1-S-phase transition in cancer cells through the ATM/ATR-mediated Chk1/2 cell cycle checkpoints.[Pubmed:
24150948]
Targeting the cancer cell cycle machinery is an important strategy for cancer treatment. Cdc25A is an essential regulator of cycle progression and checkpoint response. Over-expression of Cdc25A occurs often in human cancers.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we show that Rocaglamide-A (Roc-A), a natural anticancer compound isolated from the medicinal plant Aglaia, induces a rapid phosphorylation of Cdc25A and its subsequent degradation and, thereby, blocks cell cycle progression of tumor cells at the G1-S phase. Roc-A has previously been shown to inhibit tumor proliferation by blocking protein synthesis. In this study, we demonstrate that besides the translation inhibition Roc-A can induce a rapid degradation of Cdc25A by activation of the ATM/ATR-Chk1/Chk2 checkpoint pathway. However, Roc-A has no influence on cell cycle progression in proliferating normal T lymphocytes. Investigation of the molecular basis of tumor selectivity of Roc-A by a time-resolved microarray analysis of leukemic vs. proliferating normal T lymphocytes revealed that Roc-A activates different sets of genes in tumor cells compared with normal cells. In particular, Roc-A selectively stimulates a set of genes responsive to DNA replication stress in leukemic but not in normal T lymphocytes.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings further support the development of Rocaglamide for antitumor therapy.
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jan;11(1):203-11.
Rocaglamide overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by attenuating the inhibition of caspase-8 through cellular FLICE-like-inhibitory protein downregulation.[Pubmed:
25333816]
The enhancement of apoptosis is a therapeutic strategy used in the treatment of cancer. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising antitumor agent. However, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells exhibit marked resistance to the induction of cell death by TRAIL.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study investigated whether Rocaglamide, a naturally occurring product isolated from the genus Aglaia, is able to sensitize resistant HCC cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Two HCC cell lines, HepG2 and Huh-7, were treated with Rocaglamide and/or TRAIL and the induction of apoptosis and effects on the TRAIL signaling pathway were investigated. The in vivo efficacy of Rocaglamide was determined in TRAIL-resistant Huh-7-derived tumor xenografts. Rocaglamide significantly sensitized the TRAIL-resistant HCC cells to apoptosis by TRAIL, which resulted from the Rocaglamide-mediated downregulation of cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein and subsequent caspase-8 activation. Furthermore, Rocaglamide markedly inhibited tumor growth from Huh-7 cells propagated in severe combined immunodeficient mice, suggesting that chemosentization also occurred in vivo. These data suggest that Rocaglamide acted synergistically with TRAIL against the TRAIL-resistant HCC cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, it is concluded that Rocaglamide as an adjuvant to TRAIL-based therapy may present a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of HCC.
Int J Cancer. 2012 Aug 15;131(4):1003-8.
Rocaglamide and a XIAP inhibitor cooperatively sensitize TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in Hodgkin's lymphomas.[Pubmed:
21952919]
Although most of the patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) can be cured by the current regimen of high-dose multiagent chemotherapy, the treatment causes high risks of later toxicities including secondary malignancies.
Therefore, new rational strategies are needed for HL treatment. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising anticancer agent due to its tumor selectivity and its lack of toxicity for normal cells. Unfortunately, many cancers remain resistant to TRAIL including HL. HL is characterized by enhanced expression of cellular caspase-8 (FLICE)-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP), which block receptor-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-8 and caspase-3, respectively.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We have recently discovered the herbal compound Rocaglamide, which breaks TRAIL-resistance in acute T cell leukemia through inhibition of c-FLIP expression. We have also shown that small molecule XIAP inhibitors can sensitize TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in several resistant tumors. However, whether targeting XIAP or c-FLIP is also a suitable strategy to prime HL cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis has not yet been investigated. In our study, we show that Rocaglamide suppresses c-FLIP expression in HL cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. However, downregulation of c-FLIP alone was not sufficient to sensitize TRAIL-induced apoptosis in HL cells. Similarly, treatment of HL cells with a small molecule XIAP inhibitor resulted in a moderate induction of apoptosis. However, inhibition of XIAP alone was also not sufficient to enhance TRAIL-induced cell death. Synergistic increase in TRAIL-mediated killing of HL cells was only obtained by combination of Rocaglamide and XIAP inhibitors.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our study demonstrates that targeting both c-FLIP and XIAP are necessary for an efficient treatment of HL.
J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):44791-800.
Rocaglamide derivatives are potent inhibitors of NF-kappa B activation in T-cells.[Pubmed:
12237314 ]
Crude extracts from different Aglaia species are used as anti-inflammatory remedies in the traditional medicine of several countries from Southeast Asia.
Because NF-kappaB transcription factors represent key regulators of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, we supposed that the anti-inflammatory effects of Aglaia extracts are mediated by the inhibition of NF-kappaB activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Purified compounds of Aglaia species, namely 1H-cyclopenta[b]benzofuran lignans of the Rocaglamide type as well as one aglain congener were tested for their ability to inhibit NF-kappaB activity. We show that a group of Rocaglamides represent highly potent and specific inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene activity in Jurkat T cells with IC(50) values in the nanomolar range. Some derivatives are less effective, and others are completely inactive. Rocaglamides are able to suppress the PMA-induced expression of NF-kappaB target genes and sensitize leukemic T cells to apoptosis induced by TNFalpha, cisplatin, and gamma-irradiation. The suppression of NF-kappaB activation correlated with the inhibition of induced IkappaB(alpha) degradation and IkappaB(alpha) kinase activation. The level of interference was determined and found to be localized upstream of the IkappaB kinase complex but downstream of the TNF receptor-associated protein 2.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggest that Rocaglamide derivatives could serve as lead structures in the development of anti-inflammatory and tumoricidal drugs.
Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jan 16;5:e1000.
The traditional Chinese medical compound Rocaglamide protects nonmalignant primary cells from DNA damage-induced toxicity by inhibition of p53 expression.[Pubmed:
24434508]
Targeting the cancer cell cycle machinery is an important strategy for cancer treatment. Cdc25A is an essential regulator of cycle progression and checkpoint response. Over-expression of Cdc25A occurs often in human cancers.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we show that Rocaglamide-A (Roc-A), a natural anticancer compound isolated from the medicinal plant Aglaia, induces a rapid phosphorylation of Cdc25A and its subsequent degradation and, thereby, blocks cell cycle progression of tumor cells at the G1-S phase. Roc-A has previously been shown to inhibit tumor proliferation by blocking protein synthesis. In this study, we demonstrate that besides the translation inhibition Roc-A can induce a rapid degradation of Cdc25A by activation of the ATM/ATR-Chk1/Chk2 checkpoint pathway. However, Roc-A has no influence on cell cycle progression in proliferating normal T lymphocytes. Investigation of the molecular basis of tumor selectivity of Roc-A by a time-resolved microarray analysis of leukemic vs. proliferating normal T lymphocytes revealed that Roc-A activates different sets of genes in tumor cells compared with normal cells. In particular, Roc-A selectively stimulates a set of genes responsive to DNA replication stress in leukemic but not in normal T lymphocytes.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings further support the development of Rocaglamide for antitumor therapy.