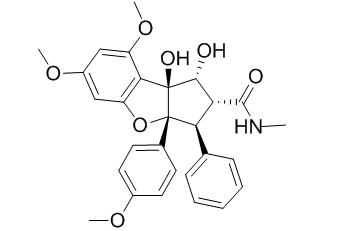
Desmethylrocaglamide
Desmethylrocaglamide is a novel inducer of cellular differentiation using HL-60 promyelocytic cells, it may be a drug for the prevention and therapy of cancer. It also has insecticidal activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Natural Product Sciences2023, 29(4):276-280.
World J Mens Health.2019, 10.5534
Nutrients.2022, 14(16):3393.
Phytomedicine.2018, 38:45-56
Molecules.2021, 26(9):2765.
J Phys Chem Lett.2021, 12(7):1793-1802.
Foods.2021, 10(12):2929.
J Nat Prod.2022, doi: 10.1021
LWT2020, 124:109163
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2019, 1113:1-13
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry. 2001 May;57(1):57-64.
Insecticidal flavaglines and other compounds from Fijian Aglaia species.[Pubmed:
11336261]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassays with lipophilic crude extracts of four Fijian Aglaia species against Spodoptera littoralis displayed strong insecticidal activity for A. basiphylla and A. gracilis, whereas A. archboldiana and A. vitiensis did not have any significant effects. The insect toxicity of A. basiphylla was caused by the well known benzofuran flavaglines rocaglamide, Desmethylrocaglamide and aglafoline. In contrast, A. gracilis contained four related pyrimidinone derivatives in the root and stem bark, including two new congeners named marikarin and 3'-hydroxymarikarin. Moreover, two new putrescine bisamides, secoodorine and secopiriferine, a new benzopyran flavagline. desacetylaglain A. and a new norsesquiterpene were isolated from the leaves together with three known bisamides and 3-hydroxy-5,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. Comparative feeding assays within the active pyrimidinone flavaglines showed that the free hydroxy group in aromatic ring A of marikarin diminishes insecticidal activity.
Anticancer Res. 2001 May-Jun;21(3B):1763-70.
Discovery of novel inducers of cellular differentiation using HL-60 promyelocytic cells.[Pubmed:
11497257]
Non-physiological inducers of terminal differentiation have been used as novel therapies for the prevention and therapy of cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We have used cultured HL-60 promyelocytic cells to monitor differentiation, proliferation and cell death events as induced by a large set of extracts derived from plants. Screening of more than 1400 extracts led to the discovery of 34 with potent activity (ED50 <8 mg/ml). Bioassay-guided fractionation led to the isolation of zapotin and 2',5,6-trimethoxyflavone as active principles from Casimiroa edulis, dibenzyltrisulfide and 2-[(phenylmethyl)dithio]ethanol as active principles from Petiveria alliacea, and Desmethylrocaglamide from Aglaia ponapensis. Zapotin demonstrated the most favorable biological profile in that induction of differentiation correlated with proliferation arrest, and a lack of cytotoxicity.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that the HL-60 cell model is a useful system for the discovery of novel pharmacophores with potential to suppress the process of carcinogenesis, and that flavonoids may be especially useful in this capacity.
Carasinol D
Catalog No: CFN95044
CAS No: 1072797-66-0
Price: $333/5mg
Cyclocurcumin
Catalog No: CFN95103
CAS No: 153127-42-5
Price: $338/10mg
New compound 3
Catalog No: CFN95184
CAS No: N/A
Price: $368/5mg
(3S,5S,E)-1,7-Diphenylhept-1-ene-3,5-diol
Catalog No: CFN95195
CAS No: 87095-75-8
Price: $318/5mg
Methyl neochebulinate
Catalog No: CFN95201
CAS No: 1236310-34-1
Price: $318/10mg
5-Hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy (2R)-flavanone-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No: CFN95209
CAS No: 942626-74-6
Price: $318/10mg
Perlolyrine
Catalog No: CFN95291
CAS No: 29700-20-7
Price: $413/5mg
trans-Psoralenoside
Catalog No: CFN95349
CAS No: N/A
Price: $318/5mg
2,3-Dehydrosilychristin
Catalog No: CFN95370
CAS No: 57499-41-9
Price: $318/5mg
5,6,7,3',4'-Pentamethoxyflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95394
CAS No: 104193-93-3
Price: $318/5mg