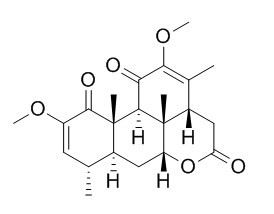
Quassin
Quassin has female anti-fertility properties, possibly acting via inhibition of estrogen secretion. Quassin alters the immunological patterns of murine macrophages through generation of nitric oxide to exert antileishmanial activity. It also exhibits P. falciparum inhibitory activity (IC50=0.06 micro g/ml, 0.15 micro M). Quassin possesses anti-anaemic property, it can significantly increase red blood cell count, pack cell volume and haemoglobin concentration.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Tradit Chin Med.2023, 43(6):1081-1091.
Asian J Beauty Cosmetol2020, 18(3): 265-272.
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 19(1)
Int J Vitam Nutr Res.2022, doi: 10.1024.
J Separation Science & Technology2016, 51:1579-1588
Natural Product Communications2022, 7(3):1-7.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10,1304
Phytochem Anal.2024, pca.3319.
J Cell Biochem.2022, 123(7):1222-1236.
Food Sci Nutr.2023, 00:1-10.
Related and Featured Products
Exp Parasitol. 2010 Apr;124(4):421-7.
Plasmodium falciparum: in vitro interaction of quassin and neo-quassin with artesunate, a hemisuccinate derivative of artemisinin.[Pubmed:
20036657]
Quassia amara L. (Family Simaroubaceae) is known to have several medicinal properties including the activity against malaria.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An HPLC method was employed for purification of the biologically active Quassinoids; Quassin (Q) and neo-Quassin (NQ), further characterized by MALDI-TOF analyses. Purified Q, NQ and the crude bark extract (S1) along with artesunate (AS) were studied for their in vitro anti-plasmodial activity. The in vivo toxicity studies at intraperitoneal doses with higher concentrations of the crude bark extract (S1) in Balb/C mice ruled out the apprehension of toxicity. Interaction studies between the test compounds among themselves (Q+NQ) and individually with artesunate (AS+Q, AS+NQ), were carried out in vitro at four ratios (1:5, 1:2, 2:1 and 5:1) on chloroquine sensitive (MRC-pf-20) and resistant (MRC-pf-303) strains of Plasmodium falciparum. The crude bark extracts of Q. amara exhibited higher P. falciparum inhibitory activity (IC(50)=0.0025 microg/ml) as compared to that of the isolated compounds, Quassin (IC(50)=0.06 microg/ml, 0.15 microM), neo-Quassin (IC(50)=0.04 microg/ml, 0.1 microM) and also to the positive control, artesunate (IC(50)=0.02 microg/ml, 0.05 microM).
CONCLUSIONS:
The in vitro drug interaction study revealed the compounds, Quassin and neo-Quassin to be additive to each other. At lower ratios, artesunate was found to be a potential combination partner with both the compounds. It was interesting to note that none of the combinations exhibited antagonistic interactions. This phenomenon offers the opportunity for further exploration of novel therapeutic concentrations and combinations.
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 Feb;63(2):317-24.
Quassin alters the immunological patterns of murine macrophages through generation of nitric oxide to exert antileishmanial activity.[Pubmed:
19036753]
The aim of this study was to characterize the in vitro antileishmanial activity of Quassin, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The cytotoxic effect of Quassin was studied in murine peritoneal macrophages at various concentrations using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide method. The role of Quassin as an antileishmanial agent was evaluated by microscopic counting of intracellular amastigotes in macrophages stained with Giemsa. To understand the effector mechanism of Quassin-treated macrophages against leishmanial parasites, western blot and real-time PCR analysis of inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase 2 (iNOS2) were done followed by measurement of NO generation by Griess reaction. The effect of Quassin on the production of Th1 cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-12 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and Th2 cytokines such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta was measured by ELISA, and the mRNA expression of these cytokines was analysed by real-time PCR. Quassin at a dose of 25 microg/mL (64.36 microM) showed less cytotoxicity to the host murine peritoneal macrophages but at the same dose was effective enough to control the intracellular parasitic load compared with higher doses of Quassin. Leishmania donovani is known to exert its pathogenic effects mainly by the suppression of NO generation and subversion of the cellular inflammatory responses in the macrophages. Quassin was found to induce a potent host-protective immune response by enhancing NO generation and iNOS2 expression both at a protein and mRNA level and by up-regulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-12 in L. donovani-infected macrophages with concurrent inhibition of anti-inflammatory responses.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings strongly support the effectiveness of Quassin as a potent immunomodulatory tool for controlling the establishment of leishmanial parasite within the host macrophages.
Niger J Physiol Sci. 2010 Nov 28;25(2):103-6.
Effects of bioactive principles from stem bark extract of Quassia amara, Quassin and 2-methoxycanthine-6-one, on haematological parameters in albino rats.[Pubmed:
22314946]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of Quassia amara extract and two isolated compounds from the extract, Quassin and 2-methoxycathine-6-one on haematological parameters was studied in rats. All doses of the extract and those of the Quassin significantly increased red blood cell count, packed cell volume and haemoglobin concentration.However, there was no significant increase in the total white blood cell count.There was also no significant change in all parameters studied with 2-methoxycanthine-6-one.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that quassia extract possesses antianaemic property.
Niger J Physiol Sci. 2010 Nov 24;25(2):95-102.
Reproductive activities of female albino rats treated with quassin, a bioactive triterpenoid from stem bark extract of Quassia amara.[Pubmed:
22314945]
To evaluate the effect of Quassin on female reproductive functions, 42 albino rats (35 females and 7 males) were used.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The female albino rats were divided into seven groups of five rats each. Group I served as the control group and received distilled water while Groups II, III and IV rats were treatedorally with 0.1mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg and 2.0 mg/kg body weight of Quassin for 60 days respectively. Groups V, VI and VII rats were also treated orally with 0.1 mg/kg, 1.0mg/kg and 2.0 mg/kg body weight of Quassin for 60 days but were left untreated for another 30 days, to serve as the recovery groups. At the end of each experimental period, blood samples were collected from each rat. Fertility study was done by cohabiting one untreated male with the five female rats in each group for 10 days. Quassin did not adversely affect the weight of the kidney, heart, liver and the body of the rats. However there was a significant decrease in the weight of the ovary and uterus in all the groups relative to the control. There was also a significant decrease in serum estrogen levels in Quassin treated rats. The Quassin treated rats had a significantly decreased mean litter number and weight. Histological studies show a disorganization and degeneration in the ovary while the uterus showed signs of vacuolation and disorganization. However, these effects were ameliorated after Quassin was withdrawn from the rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that Quassin has female anti-fertility properties, possibly acting via inhibition of estrogen secretion.