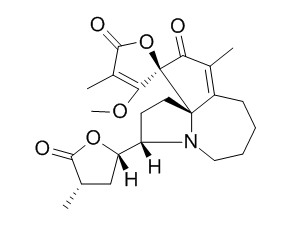
Protostemotinine
Protostemotinine is a natural product from Stemona japonica.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Cell Mol Med.2021, 25(5):2645-2654.
J Cell Mol Med.2018, 22(9):4236-4242
J of Food Quality2020, 8851285.
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety2019, 34(5):413-420
Biochemical Systematics and Ecology2018, 81
Nat Commun.2023, 14(1):8142.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2023, 31(6):388-395.
Molecules.2016, 21(6)
Journal of Research in Pharmacy.2022, 26(6):p1752-1757.
Biomed Pharmacother.2021, 137:111362.
Related and Featured Products
Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 2007,38 (6):499-501.
Chemical constituents of the roots of wild Stemona sessilifolia.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the chemical constituents of the roots of wild Stemona sessilifolia (Miq.) Miq. collected in Baohua Mountain, Jurong City, Jiangsu Province.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The roots of wild S. sessilifolia were extracted with 75 % EtOH and partitioned by CHCl3 and n-BuOH. The compounds were separated and purified by column chromatography with silica gel and macroporous resin, and their structures were identified by spectroscopic analyses. Ten compounds were isolated from the root of S. sessilifolia in this study, i. e., one new dihydrophenanthrene named 7-methoxy-3-methyl-2,5-dihydroxy- 9, 10-dihydrophenanthrene (1), and 9 of known compounds: stilbostemin D (2), protostemonine (3), Protostemotinine (4), stemospironine (5), (-)-syringaresinol-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), benzoic acid (7), vanillic acid (8), daucosterol (9), and stigmasterol (10).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 1 is a new compound, compound 6 is isolated from the genus for the first time, and compounds 7 - 10 are isolated from the species for the first time.