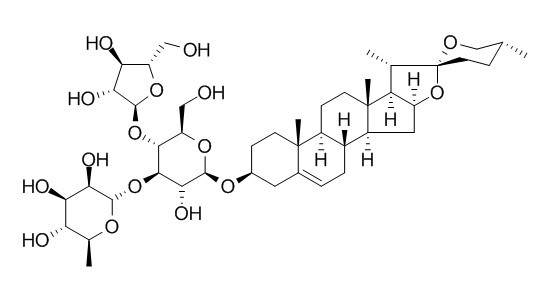
Polyphyllin II
Polyphyllin II has hemolytic effect, the hemolytic mechanism in vitro may be related to the increase in intracellular osmotic pressure and rupture of erythrocytes by changing the anion channel transport activity, with glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) as the major competitive interaction site.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Enzyme Microb Technol.2019, 122:64-73
J Chem Inf Model.2021, 61(11):5708-5718.
Microb Pathog.2019, 131:128-134
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 324:117775.
Int J Mol Med.2015, 35(5):1237-45
J Nat Med.2021, doi: 10.1007.
Sage Journals2024, v20:4,1350-1358
Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2024, e0031424.
J Appl Biol Chem.2021, 64(3),263?268
Exp Neurobiol.2018, 27(3):200-209
Related and Featured Products
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Sep;40(18):3623-9.
Study on hemolytic mechanism of polyphyllin II.[Pubmed:
26983211]
To study the hemolytic effect of Polyphyllin II (PP II) mediated by anion channel protein and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), in order to initially reveal its hemolytic mechanism in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the experiment, the spectrophotometric method was adopted to detect the hemolysis of PP II in vitro and the effect of anion channel-related solution and blocker, glucose channel-related inhibitor and multi-target drugs dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and diazepam on the hemolysis of PP II. The scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope were used to observe the effect of PP II on erythrocyte (RBC) morphology. The results showed that PP II -processed blood cells were severely deformed into spherocytes, acanthocyturia and vesicae. According to the results of the PP II hemolysis experiment in vitro, the anion hypertonic solution LiCl, NaHCO3, Na2SO4 and PBS significantly inhibited the hemolysis induced by PP II (P < 0.05), while blockers NPPB and DIDS remarkably promoted it (P < 0.01). Hyperosmotic sodium chloride, fructose and glucose at specific concentrations notably antagonized the hemolysis induced by PP II (P < 0.05). The glucose channel inhibitor Cytochalasin B and verapamil remarkably antagonized the hemolysis induced by PP II (P < 0.01). The hemolysis induced by PP II could also be antagonized by 1 gmol x L(1) diazepam and 100 μmol x L(-1) DHEA pretreated for 1 min (P < 0.01).
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the hemolytic mechanism of PP II in vitro may be related to the increase in intracellular osmotic pressure and rupture of erythrocytes by changing the anion channel transport activity, with GLUT1 as the major competitive interaction site.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2013 Mar;27(3):343-8.
Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII in beagle dog plasma after oral administration of Rhizoma Paridis extracts by LC-MS-MS.[Pubmed:
22903625]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
For the first time, a rapid and specific LC-MS-MS method has been developed for the analysis of polyphyllin I, Polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII in beagle dog plasma. The method was applied to study the pharmacokinetics of Rhizoma Paridis extracts containing polyphyllin I, Polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII. The analysis was carried out on an Agilent Zorbax XDB-C(18) reversed-phase column (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm) by isocratic elution with acetonitrile and water (50:50, v/v). The flow rate was 0.25 mL/min. All analytes including internal standards were monitored by selected reaction monitoring with an electrospray ionization source. Linear responses were obtained for polyphyllin I, Polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII ranging from 10 to 5000 ng/mL. The intra-and inter-day precisions (RSDs) were less than 6.66 and 9.15%. The extraction recovery ranged from 95.53 to 104.21% with RSD less than 8.69%. Stability studies showed that polyphyllin I, Polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII were stable in preparation and analytical process.
CONCLUSIONS:
The validated method was successfully used to determine the concentration-time profiles of polyphyllin I, Polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VI and polyphyllin VII.