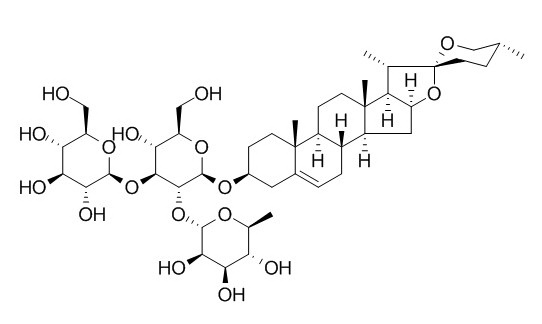
Gracillin
Gracillin has anti-tumor activity, can induce cell cycle arrest, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in HL60 cells, and has the potential to be developed as an antitumor agent.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Med Assoc Thai2024, P-04.
Nat Commun.2023, 14(1):5075.
Inflammation.2021, doi: 10.1007
Chem. of Vegetable Raw Materials2020, 97-105
J Ethnopharmacol.2017, 198:205-213
Food Addit Contam Part A.2021, 38(12):1985-1994.
J Ethnopharmacol.2019, 228:132-141
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(2):770.
Neuropharmacology2019, 151437
Am J Chin Med.2016, 44(6):1255-1271
Related and Featured Products
Pharmazie. 2015 Mar;70(3):199-204.
Gracillin induces apoptosis in HL60 human leukemic cell line via oxidative stress and cell cycle arrest of G1.[Pubmed:
25980181]
Gracillin, a kind of steroidal saponin isolated from the root bark of wild yam Dioscorea nipponica has been reported to exert antitumor activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated the anticancer activity of Gracillin against HL60 cells, and evaluated the possible mechanism involved in its antineoplastic action. The cell proliferation was evaluated by cell counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, Gracillin inhibited the growth of HL60 cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Flow cytometry was used to analyze the cell cycle distribution whereas Annexin V-FITC/PI flow cytometry analysis was carried out to confirm apoptosis induced by Gracillin, Our results demonstrated that Gracillin could induce cell cycle arrest of G1 and apoptosis in HL60 cells. Furthermore, based on the biochemical methods, induction of oxidative stress by Gracillin was indicated by increased the content of malondialdehyde (MDA), and decreased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. In addition, real time-PCR verified the expression of apoptosis-related genes, the mRNA level of Bcl-2 was decreased dramatically, while Bax was remarkably increased by Gracillin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, Gracillin could induce cell cycle arrest, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in HL60 cells, and has the potential to be developed as an antitumor agent.
Phytother Res. 2003 Jun;17(6):620-6.
The cytotoxicity of methyl protoneogracillin (NSC-698793) and gracillin (NSC-698787), two steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii var. hypoglauca, against human cancer cells in vitro.[Pubmed:
12820229]
In our continuous studies of anticancer activity of steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii var. hypoglauca (Dioscoreaceae), methyl protoneoGracillin (NSC-698793) and Gracillin (NSC-698787) were tested for cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines from leukemia and eight solid tumor diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
As a result, methyl protoneoGracillin was cytotoxic against all the test cell lines with GI(50) < 100 micro M, especially selectively against two leukemia lines (CCRF-CEM and RPMT-8226), one colon cancer line (KM12), two central nervous system (CNS) cancer lines (SF-539 and U251), one melanoma line (M14), one renal cancer line (786-0), one prostate cancer line (DU-145), and one breast cancer line (MDA-MB-435), with GI(50) < or = 2.0 micro M. Leukemia, CNS cancer, and prostate cancer were the most sensitive subpanels, while ovarian cancer was the least sensitive subpanels. The preliminary toxicity studies showed that the maximum tolerant dose was 600 mg/kg for methyl protoneoGracillin to mice. Gracillin was cytotoxic against most cell lines with GI(50), TGI and LC(50) at micromolar levels, but no activity against EKVX (non-small cell lung cancer), HT29 (colon cancer), OVCAR-5 (ovarian cancer), and SN12C (renal cancer). Based on structure-activity relationship, C-25 R/S con fi guration was critical for leukemia selectivity between methyl protoneoGracillin and methyl protoGracillin. F-ring was critical to selectivity between furostanol (methyl protoneoGracillin and methyl protoGracillin) and spirostanol (Gracillin) saponins in this study. By an analysis of COMPARE software, no compounds in the NCI's database had similar mean graphs to those of methyl protoneoGracillin and Gracillin, respectively, indicating potential novel mechanism(s) of action involved.
CONCLUSIONS:
Put all in together, methyl protoneoGracillin has been selected as a potential anticancer candidate for hollow fi ber assay to nude mice, but Gracillin will not be pursued due to lack of selectivity against human cancer diseases.
Parasitology. 2015 Mar;142(3):473-9.
Antiparasitic efficacy of Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin from Costus speciosus (Koen ex. Retz) Sm. against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis.[Pubmed:
25140457]
The present study aims to evaluate the antiparasitic activity of active components from Costus speciosus against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Bioassay-guided fractionation was employed to identify active compounds from C. speciosus yielding 2 bioactive compounds: Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In-vitro assays revealed that Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin could be 100% effective against I. multifiliis at concentrations of 0.8 and 4.5 mg L(-1), with median effective concentration (EC50) values of 0.53 and 3.2 mg L(-1), respectively. All protomonts and encysted tomonts were killed when the concentrations of Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin were 1.0 and 5.0 mg L(-1). In-vivo experiments demonstrated that fish treated with Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin at concentrations of 1.0 and 5.0 mg L(-1) carried significantly fewer parasites than the control (P<0.05). Mortality of fish did not occur in the treatment group (Zingibernsis newsaponin at 5.0 mg L(-1)) during the trial, although 100% of untreated fish died. Acute toxicities (LD50) of Gracillin and Zingibernsis newsaponin for grass carp were 1.64 and 20.7 mg L(-1), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results provided evidence that the 2 compounds can be selected as lead compounds for the development of new drugs against I. multifiliis.