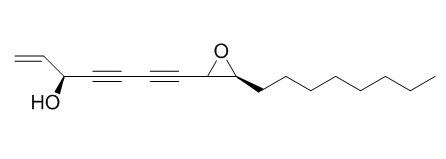
Panaxydol
Panaxydol has anti-cancer activity, can inhibit the growth and apoptosis of cancer cells, the signaling mechanisms involve a [Ca(2+)](i) increase, JNK and p38 MAPK activation, cAMP, MAP kinase and ROS generation through NADPH oxidase and mitochondria. It induces the differentiation in C6 cells, may through a PI 3-K-dependent pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Arch Biochem Biophys.2020, 687:108363.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 241:115990.
Institut Pasteur Korea2020, doi: 10.21203.
Hortic Res.2023, 10(9):uhad154.
Am J Chin Med.2016, 44(6):1255-1271
Sci Rep.2020, 10:4495(2020)
Pharmacol Res.2022, 182:106346.
Plants2022, 11(3),294.
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2093.
Food Chem Toxicol.2024, 186:114589.
Related and Featured Products
11-Hydroxyjasmonic acid
Catalog No: CFN99457
CAS No: 140447-14-9
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
12-Hydroxyjasmonic acid
Catalog No: CFN99460
CAS No: 140631-27-2
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
(S,E)-Deca-2,9-diene-4,6-diyne-1,8-diol
Catalog No: CFN97501
CAS No: 931114-98-6
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
(R,E)-Deca-2-ene-4,6-diyne-1,8-diol
Catalog No: CFN97502
CAS No: 931116-24-4
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Panaxydol
Catalog No: CFN92797
CAS No: 72800-72-7
Price: $448/20mg
Panaxydiol
Catalog No: CFN92798
CAS No: 63910-76-9
Price: $368/10 mg
Panaxytriol
Catalog No: CFN95665
CAS No: 87005-03-6
Price: $368/10mg
Panaxyne
Catalog No: CFN96202
CAS No: 122855-49-6
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
8-Acetoxypentadeca-1,9Z-diene-4,6-diyn-3-ol
Catalog No: CFN97743
CAS No: 41682-30-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
9,17-Octadecadiene-12,14-diyne-1,11,16-triol
Catalog No: CFN98061
CAS No: 211238-60-7
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Molecules. 2011 Jun 29;16(7):5561-73.
Induction of apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells by panaxynol and panaxydol.[Pubmed:
21716177]
Panaxynol and Panaxydol are naturally occurring polyacetylenes, isolated from the lipophilic fractions of Panax notoginseng, that exert anti-proliferative effects against malignant cells. However, to the best of our knowledge, no study concerning the inhibitory effects of the two polyacetylenes on cell growth of human promyelocytic leukemia cells has been reported. In this paper, we examined the antiproliferation and proapoptotic effects of panaxynol and Panaxydol on HL60 cells and investigated their mechanism of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cell growth inhibition of panaxynol and Panaxydol were determined by trypan blue dye exclusion assays. Apoptosis of cells was revealed by morphological observation, analysis for nuclear DNA distribution and by annexin V-FITC/ PI staining using flow cytometry. It was found that panaxynol and Panaxydol markedly inhibited proliferation of HL60 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner via an apoptotic pathway. In concern with these findings, Western blot analysis showed proteolytic activation of PKCδ, caspase-3 activation and cleavage of poly (ADP [adenosine diphosphate]-ribose) polymerase in HL60 cells treated by panaxynol and Panaxydol.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, panaxynol and Panaxydol have profound effects on growth and apoptosis of HL60 cells, suggesting those substances are worthy of further exploration as potential anti-cancer agents.
Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011;131(6):993-1000.
Induction of differentiation by panaxydol in human hepatocarcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via cAMP and MAP kinase dependent mechanism.[Pubmed:
21628989]
Panaxydol (PND) is one of the main non-peptidyl small molecules isolated from the lipophilic fractions of Panax notoginseng.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was carried out to demonstrate the potential effects of Panaxydol on the induction of differentiation of human liver carcinoma cell lines SMMC-7721. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT method and Trypan blue exclusion assay respectively. The changes of morphology were detected by transmission electron microscope. Inhibitors were applied to detect the signaling pathway of differentiation. The level of intracellular cyclic AMP was determined by radioimmunoassay. The expression of p-ERK, Id1, and p21 were determined by Western blot. We found that Panaxydol inhibit the proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells and caused the morphology and ultrastructure changes of SMMC-7721. Moreover, Panaxydol dose-dependently increased the secretion of albumin and alkaline phosphatase activity, and decreased the secretion of AFP correspondingly. These changes of differentiation markers in SMMC-7721 can be reversed by the protein kinase A inhibitor RpcAMPS and by MAP kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor U0126 or sorafenib. Intracellular cAMP was elevated by Panaxydol in SMMC-7721 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Panaxydol dose-dependently decreased the expression of regulatory factors Id1 and increased the protein levels of p21 and p-ERK1/2 correspondingly. It suggested Panaxydol might be of value for further exploration as a potential anti-cancer agent via cAMP and MAP kinase-dependent mechanism.
Apoptosis. 2011 Apr;16(4):347-58.
Panaxydol induces apoptosis through an increased intracellular calcium level, activation of JNK and p38 MAPK and NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species.[Pubmed:
21190085 ]
Panaxydol, a polyacetylenic compound derived from Panax ginseng roots, has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we demonstrated that Panaxydol induced apoptosis preferentially in transformed cells with a minimal effect on non-transformed cells. Furthermore, Panaxydol was shown to induce apoptosis through an increase in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)), activation of JNK and p38 MAPK, and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) initially by NADPH oxidase and then by mitochondria. Panaxydol-induced apoptosis was caspase-dependent and occurred through a mitochondrial pathway. ROS generation by NADPH oxidase was critical for Panaxydol-induced apoptosis. Mitochondrial ROS production was also required, however, it appeared to be secondary to the ROS generation by NADPH oxidase. Activation of NADPH oxidase was demonstrated by the membrane translocation of regulatory p47(phox) and p67(phox) subunits and shown to be necessary for ROS generation by Panaxydol treatment. Panaxydol triggered a rapid and sustained increase of [Ca(2+)](i), which resulted in activation of JNK and p38 MAPK. JNK and p38 MAPK play a key role in activation of NADPH oxidase, since inhibition of their expression or activity abrogated membrane translocation of p47(phox) and p67(phox) subunits and ROS generation.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, these data indicate that Panaxydol induces apoptosis preferentially in cancer cells, and the signaling mechanisms involve a [Ca(2+)](i) increase, JNK and p38 MAPK activation, and ROS generation through NADPH oxidase and mitochondria.
J Clin Neurosci. 2009 Mar;16(3):444-8.
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is required for the induction of differentiation in C6 glioma cells by panaxydol.[Pubmed:
19179079]
Panaxydol isolated from the lipophilic fractions of Tienchi ginseng (Panax notoginseng) induces growth inhibition and differentiation of rat C6 glioma cells. The underlying molecular mechanisms are not completely understood.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we identified phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) as a necessary enzyme for the differentiation of C6 cells treated with Panaxydol. The specific PI 3-K inhibitor wortmannin resulted in attenuated differentiation of C6 cells induced by Panaxydol, and was associated with perinuclear localization of glial fibrillary acidic protein expression and a diminished process formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that induction of differentiation in C6 cells by Panaxydol could be mediated through a PI 3-K-dependent pathway.
Chem Biol Interact. 2009 Sep 14;181(1):138-43.
Panaxydol inhibits the proliferation and induces the differentiation of human hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2.[Pubmed:
19450571]
Panaxydol, a polyacetylene compound isolated from Panax ginseng, exerts anti-proliferative effects against malignant cells. No previous study, however, has been reported on its effects on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated the effects of Panaxydol on the proliferation and differentiation of human hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2. We studied by electronic microscopy of morphological and ultrastructural changes induced by Panaxydol. We also examined the cytotoxicities of Panaxydol against HepG2 cells using the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay and the effect of Panaxydol on cell cycle distributions by flow cytometry. We investigated the production of liver proteins in Panaxydol-treated cells including alpha-fetoprotein and albumin and measured the specific activity of alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transferase. We further investigated the effects of Panaxydol on the expression of Id-1, Id-2, p21 and pRb by RT-PCR or immunoblotting analysis. We found that Panaxydol inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 cells and caused morphological and ultrastructural changes in HepG2 cells resembling more mature forms of hepatocytes. Moreover, Panaxydol induced a cell cycle arrest at the G(1) to S transition in HepG2 cells. It also significantly decreased the secretion of alpha-fetoprotein and the activity of gamma-glutamyl transferase. By contrast, Panaxydol remarkably increased the secretion of albumin and the alkaline phosphatase activity. Furthermore, Panaxydol increased the mRNA content of p21 while reducing that of Id-1 and Id-2. Panaxydol also increased the protein levels of p21, pRb and the hypophosphorylated pRb in a dose-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Panaxydol is of value for further exploration as a potential anti-cancer agent.