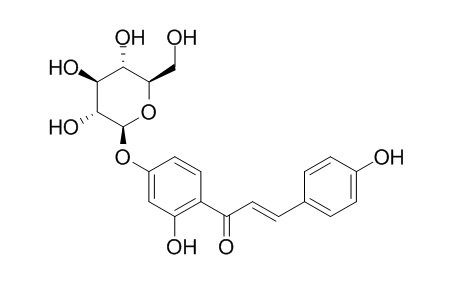
Neoisoliquiritin
Neoisoliquiritin is a natural product from Glycyrrhiza uralensis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Chem.2020, 332:127412
Pharmacia2022, 69(3): 883-890.
Cell Chem Biol.2019, 26(1):27-34
Food Bioscience2024, 57:103518.
Pathogens.2018, 7(3):E62
Fitoterapia.2024, 106006.
Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine2022, 345930.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8847358.
Vietnam J. Chem.2023, 61(3),308-317
Chem Biol Interact.2019, 315:108910
Related and Featured Products
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2017 Mar;64(2):211-7.
Assessment of genetic fidelity and composition: Mixed elicitors enhance triterpenoid and flavonoid biosynthesis of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. tissue cultures.[Pubmed:
26872048 ]
Glycyrrhiza uralensis has acquired significant importance due to its medicinal properties and health function.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the quality of G. uralensis adventitious roots was evaluated in terms of genetic stability, active compounds, and anti-inflammatory activity. Monomorphic banding pattern obtained from the mother plant and tissue cultures of G. uralensis with randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers confirmed the genetic stability of adventitious roots. Neoliquiritin (Neoisoliquiritin), ononin, liquiritin, and glycyrrhizic acid were identified from G. uralensis adventitious roots on the basis of high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. This study also revealed that adventitious roots possessed a better anti-inflammatory effect than native roots. To increase the contents of G. uralensis active components, elicitors were used in the adventitious roots culture. The combination of methyl jasmonate and phenylalanine synergistically stimulated the accumulation of glycyrrhetinic acid (0.22 mg/g) and total flavonoid (5.43 mg/g) compared with single treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, G. uralensis adventitious roots can be an exploitable system for the production of licorice.
J Sep Sci. 2015 Dec;38(24):4180-6.
Combination of the advantages of chromatographic methods based on active components for the quality evaluation of licorice.[Pubmed:
26472171 ]
A rapid, improved and comprehensive method including high-performance thin-layer chromatography, fingerprint technology and single standard to determine multiple components was developed and validated for the quality evaluation of licorice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, a newly developed high-performance thin-layer chromatography method was first used for authentication of licorice, which achieved simultaneous identification of multiple bands including five bands for known bioactive components by comparing their retention factor values and colors with the standards. For fingerprint analysis, 8 of 16 common peaks were identified. Simultaneously, similarity analysis which showed very similar patterns and hierarchical clustering analysis were performed to discriminate and classify the 27 batches of samples. Additionally, the single standard to determine multiple components method was first successfully achieved to quantify the eight important active markers in licorice including liquiritin apioside, liquiritin, isoliquiritin apioside, isoliquritin, Neoisoliquiritin, liquiritigenin, isoliquiritigenin and glycyrrhizic acid. The easily available glycyrrhizic acid was selected as the reference substance to calculate relative response factors.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compared with the normal external standard method, this alternative method can be used to determine the multiple indices effectively and accurately. The validation result showed that the developed method was specific, accurate, precise, robust and reliable for the overall quality assessment of licorice.