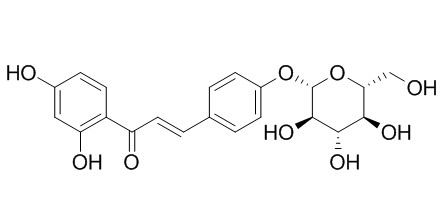
Isoliquiritin
Isoliquiritin has significant antidepressant-like, antifungal and anti-cancer activities. It induces apoptotic cell death through upregulating p53 and p21 in the A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells and inhibit the p53-dependent pathway and showed crosstalk between Akt activities.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Acta Pharm Sin B.2024, 14(4):1772-1786.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(2):764.
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 12(1):189.
Journal of Mushroom2024, 22(4):192-198
Front Pharmacol.2018, 9:756
Eur J Pharmacol.2021, 906:174220.
Food Funct.2020, 11(2):1322-1333.
Antioxidants (Basel).2022, 11(12):2411.
Metab Eng.2022, 75:143-152.
Toxicol In Vitro.2023, 93:105667.
Related and Featured Products
Oncol Rep. 2014 Jan;31(1):298-304.
Combination of liquiritin, isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin induce apoptotic cell death through upregulating p53 and p21 in the A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:
24247527]
Liquiritin, Isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin are the active polyphenols present in Glycyrrhiza uralensis which has been used for the treatment of cancer and its complications.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was conducted to evaluate the cytotoxicity and antitumor activity of liquiritin, Isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin on human non-small lung cancer cells including apoptosis-induction, inhibition of apoptotic pathways and to explore the underlying mechanism. Lactate dehydrogenase assays, FITC Annexin V staining assay were performed to evaluate cellular cytotoxicity and apoptosis activity. The results showed that pretreatment with these polyphenols induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Liquiritin, Isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin significantly increased cytotoxicity of, and upregulated p53 and p21 and downregulated the apoptotic pathways. Furthermore, it inhibited cell cycle at the G2/M phase. Western blot analysis showed it significantly decreased the protein expression of PCNA, MDM2, p-GSK-3β, p-Akt, p-c-Raf, p-PTEN, caspase-3, pro-caspase-8, pro-caspase-9 and PARP, Bcl-2 in a concentration-dependent manner while the protein expression of p53, p21 and Bax was increased. In addition, Akt pathway was downregulated.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that liquiritin, Isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin inhibited the p53-dependent pathway and showed crosstalk between Akt activities. These active polyphenols can be an alternative agent for the treatment of lung cancer.
Molecules. 2016 Feb 19;21(2):237.
Antifungal Activity of Isoliquiritin and Its Inhibitory Effect against Peronophythora litchi Chen through a Membrane Damage Mechanism.[Pubmed:
26907232 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study investigated the antifungal activity and potential antifungal mechanism(s) of Isoliquiritin against P. litchi Chen, one of the main litchi pathogens. The antifungal activity of Isoliquiritin against P. litchi Chen had been proven in a dose-dependent manner through in vitro (mycelial growth and sporangia germination) and in vivo (detached leaf) tests. Results revealed that Isoliquiritin exhibited significant antifungal activity against the tested pathogens, especially, P. litchi Chen, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 27.33 mg/L. The morphology of P. litchi Chen was apparently changed by Isoliquiritin through cytoplasm leakage and distortion of mycelia. The cell membrane permeability of the P. litchi Chen increased with the increasing concentration of Isoliquiritin, as evidenced by a rise in relative electric conductivity and a decrease in reducing sugar contents. These results indicated that the antifungal effects of Isoliquiritin could be explained by a membrane lesion mechanism causing damage to the cell membrane integrity leading to the death of mycelial cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, Isoliquiritin may be used as a natural alternative to commercial fungicides or a lead compound to develop new fungicides for the control of litchi downy blight.
Biol Pharm Bull. 1995 Oct;18(10):1382-6.
Inhibitory effect of isoliquiritin, a compound in licorice root, on angiogenesis in vivo and tube formation in vitro.[Pubmed:
8593441]
A water extract of licorice root inhibits granuloma angiogenesis in adjuvant-induced chronic inflammation (Phytother. Res., 5, 195. 1991).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study has investigated the effects of licorice-derived compounds on granuloma angiogenesis. Isoliquiritin (0.31-3.1 mg/kg), a licorice-derived flavonoid, inhibited the carmine content of granuloma tissue 50-fold greater than licorice extract. Glyeyrrhizin (20-80 mg/kg), a licorice-derived saponin, inhibited carmine content with a weak potency. The licorice extract (0.01-1 mg/ml) also inhibited tube formation from vascular endothelial cells in a concentration-dependent manner. From the chemical structure-activities of used licorice-derived flavonoids (0.1-100 microM), their potencies for anti-tube formation were in the order isoliquiritigenin > Isoliquiritin > liquiritigenin >> Isoliquiritin-apioside. Glycyrrhizin (0.1-100 microM) and glycyrrhetinic acid (0.1-10 microM) increased tube formation. A glycyrrhizin (82 micrograms/ml)-induced increase in tube formation was inhibited by Isoliquiritin. The combined effect of a mixture of 82 micrograms/ml glycyrrhizin and 4.2 micrograms/ml Isoliquiritin, a similar concentration ratio to their yield ratio in the licorice extract, corresponded to the effect of 100 micrograms/ml extract.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the anti-angiogenic effect of licorice extract depended on the anti-tube formation effect of Isoliquiritin.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Jul 1;32(5):1179-84.
Antidepressant-like effects of liquiritin and isoliquiritin from Glycyrrhiza uralensis in the forced swimming test and tail suspension test in mice.[Pubmed:
18289754]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two classic animal behavior despair tests--the Forced Swimming Test (FST) and the Tail Suspension Test (TST) were used to evaluate the antidepressant activity of liquiritin and Isoliquiritin from Glycyrrhiza uralensis in mice. It was observed that both liquiritin and Isoliquiritin at doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg significantly reduced the immobility time in the FST and TST in mice 30 min after treatment. Measurement of locomotor activity indicated that liquiritin and Isoliquiritin had no central nervous system (CNS)-stimulating effects. The main monoamine neurotransmitters and their metabolites in mouse brain regions were also simultaneously determined by HPLC-ECD. It was found that these two compounds significantly increased the concentrations of the main neurotransmitters 5-HT and NE in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and cortex. Liquiritin and Isoliquiritin also significantly reduced the ratio of 5-HIAA/5-HT in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and cortex, slowing down 5-HT metabolism compared with mice treated with vehicle+stress.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, liquiritin and Isoliquiritin produced significant antidepressant-like effects, and their mechanism of action may be due to increased 5-HT and NE in the mouse hippocampus, hypothalamus and cortex..
Asian J. Chem., 2014,26(8):24-5.
Analysis of isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin from insampaedoksan fermented by lactobacillus plantarum 144 Using RP-HPLC[Reference:
WebLink]
Insampaedoksan is a traditional herbal medicine used for antipyretic and antiinflammatory diseases. Thus isoliquiritigenin have bioactivity effects such as antioxidant, estrogenic and anticancer. The level of Isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin in insampaedoksan were investigated before and after fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum 144, along with Isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin extraction efficiency with 100 % water, 60 % aqueous MeOH and 100 % MeOH. The characterization of Isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin were achieved by comparing its retention time (tR), molecular weight and UV absorption with those of the standard compound. The extraction efficiency of Isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin were the highest with 100 % MeOH. After fermentation, the amount of 100 % MeOH extract isoliquiritigenin was selectively increased (202.73 %) and Isoliquiritin was selectively decreased (82.57 %). The bioconversion rate of Isoliquiritin to isoliquritigenin was 39.93 %. Also, the molecular mass of the fermented insampaedoksan fraction (#1) were shown via LC-MS and, its high purity was shown to be above > 95 %. Thus, qualitative and quantitative analyses of Isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin in insampaedoksan and fermented insampaedoksan were conducted.