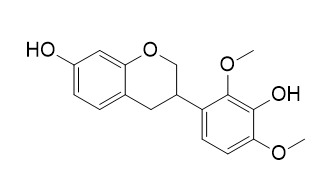
Mucronulatol
Mucronulatol has anticancer,antiangiogenic activity. Mucronulatol exhibits markedly potent inhibition of yeast α-glucosidase.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Anat Rec2018, 24264
Int J Vitam Nutr Res.2022, doi: 10.1024.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 2022:3483511
Food Sci Nutr.2019, 8(1):246-256
Phytofrontiers2024, 2690-5442.
Oxid Med Cell Longev2019, 9056845:13
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(11): 1802.
Analytical Methods2018, 10(27)
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography 2017, 30(4)
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 18(12)
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Res . 2021 Dec;35(24):5879-5882.
Exploring natural compounds for the management of non-small cell lung cancer[Pubmed:
32722994]
A growing incidence of drug resistance and tumour proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer escalates the urge for potential lead molecules. The plant-derived natural compounds have played a pivotal role in potential therapeutic agents owing to its versatility and low toxicity over the past decades. In this study, we have executed an in-silico based screening of 1574 natural compounds against the β-catenin via an integrated pharmacophore approach. Further investigation revealed that Mucronulatol and 7,4'-dihydroxyhomoisoflavanone possess a higher Glide score (-4.748 and -3.943 kcal/mol), binding affinity (-44.763 and -41.883 kcal/mol) alongside drug-likeness property than the iCRT5. Moreover, these compounds are reported to have cytotoxicity against lung cancer cell lines with an IC50 value of 6.74 μM and 8.99 μM respectively. Furthermore, dynamic studies were employed to determine the structural stability and we hope that the lead molecules proposed in this study could effectively inhibit the β-catenin pathway associated with NSCLC.
Bioinformation . 2015 Feb 28;11(2):73-84.
In silico pharmacokinetic and molecular docking studies of small molecules derived from Indigofera aspalathoides Vahl targeting receptor tyrosine kinases[Pubmed:
25848167]
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from preexisting vascular network that plays an important role in the tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. Anti-angiogenesis targeting tyrosine kinases such as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and platelet derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ) constitutes a successful target for the treatment of cancer. In this work, molecular docking studies of three bioflavanoid such as indigocarpan, Mucronulatol, indigocarpan diacetate and two diterpenes namely erythroxydiol X and Y derived from Indigofera aspalathoides as PDGFRβ and VEGFR2 inhibitors were performed using computational tools. The crystal structures of two target proteins were retrieved from PDB website. Among the five compounds investigated, indigocarpan exhibited potent binding energy ΔG = -7.04 kcal/mol with VEGFR2 and ΔG = -4.82 with PDGFRβ compared to commercially available anti-angiogenic drug sorafenib (positive control). Our results strongly suggested that indigocarpan is a potent angiogenesis inhibitor as ascertained by its potential interaction with VEGFR2 and PDGFRβ. This hypothesis provides a better insight to control metastasis by blocking angiogenesis.
J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Sep 22;58(18):9988-9993.
Yeast alpha-glucosidase inhibition by isoflavones from plants of Leguminosae as an in vitro alternative to acarbose[Pubmed:
20734984]
In the course of searching for new classes of α-glucosidase inhibitors originated from natural resources, 11 kinds of isoflavones, i.e., medicarpin (1), formononetin (2), Mucronulatol (3), (3R)-calussequinone (5), (3R)-5'-methoxyvestitol (6), tectorigenin (7), biochanin A (8), tuberosin (9), calycosin (10), daidzein (11), and genistein (12), as well as a flavone, liquritigenin (4), were isolated as active principles responsible for the yeast α-glucosidase inhibitory activity from two leguminous plant extracts, i.e., the heartwood extract of Dalbergia odorifera and the roots extract of Pueraria thunbergiana. Each components (1-12) demonstrated a significantly potent inhibition on yeast α-glucosidase in a dose dependent manner when the p-nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside was used as a substrate in vitro. The concentration required for 50% enzyme inhibition (IC50) were calculated as 2.93 mM (1), 0.51 mM (2), 3.52 mM (7) 0.35 mM (8), 3.52 mM (9), 0.85 mM (11), and 0.15 mM (12) when that of reference drug acarbose was evaluated as 9.11 mM, in vitro. However, isoflavone glycosides, i.e., puerarin (13), daidzin (14), formononetin-7-O-β-glucopyranoside (15), and genistin (16), exhibited a relatively poor inhibitory activity on yeast α-glucosidase as compared with the corresponding isoflavone (2, 11, 12), respectively.
Bioorg Med Chem . 2008 May 15;16(10):5434-5440
Cytotoxic constituents from Brazilian red propolis and their structure-activity relationship[Pubmed:
18440233]
Several classes of flavonoids [flavanoids (1-10), flavonol (11), isoflavones (12-18), isoflavanones (19-22), isoflavans (23-26), chalcones (27-30), auronol (31), pterocarpans (32-37), 2-arylbenzofuran (38), and neoflavonoid (39)] and lignans (40-42) isolated from the MeOH extract of Brazilian red propolis were investigated for their cytotoxic activity against a panel of six different cancer cell lines including murine colon 26-L5 carcinoma, murine B16-BL6 melanoma, murine Lewis lung carcinoma, human lung A549 adenocarcinoma, human cervix HeLa adenocarcinoma, and human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell lines. Based on the observed results, structure-activity relationships were discussed. Among the tested compounds, 7-hydroxy-6-methoxyflavanone (3) exhibited the most potent activity against B16-BL6 (IC(50), 6.66microM), LLC (IC(50), 9.29microM), A549 (IC(50), 8.63microM), and HT-1080 (IC(50), 7.94microM) cancer cell lines, and Mucronulatol (26) against LLC (IC(50), 8.38microM) and A549 (IC(50), 9.9microM) cancer cell lines. These activity data were comparable to those of the clinically used anticancer drugs, 5-fluorouracil and doxorubicin, against the tested cell lines, suggesting that 3 and 26 are the good candidates for future anticancer drug development.
Pharm Biol . 2000;38(3):229-234.
Bioactive flavonoids from the black locust tree, robinia pseudoacacia[Pubmed:
21214467]
Five flavonoids, acacetin ( 1 ), secundiflorol I ( 2 ), Mucronulatol ( 3 ), isoMucronulatol ( 4 ), and isovestitol ( 5 ) were isolated, with the fractionation being guided by the brine shrimp lethality test (BST), from the ethanolic extract of the whole plant of Robinia pseudoacacia (Fabaceae). The structures of 1 - 5 were identified by spectral analyses. Compounds 2 - 5 are, for the first time, reported from this species. Corrections have been made for the previous literature assignments of the 13 C NMR resonances of compounds 1 - 3 . Bioactivities in BST and cytotoxicities against a panel of six solid human tumor cell lines were determined, and 1 was significantly cytotoxic in the prostate cell line (PC-3).
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 May;46(5):226-235.
Mucronulatol from Caribbean propolis exerts cytotoxic effects on human tumor cell lines[Pubmed:
18538108]
Objective: Mucronulatol is one of the most cytotoxic substances present in Caribbean propolis. This work aimed at initially characterizing the biological effects of Mucronulatol in cancer cell lines comprehending both wildtype and resistant sublines.
Materials and methods: An RP-HPLC technique was employed to separate and purify Mucronulatol. IC(50) values were determined using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) proliferation assay. FACS-based cell cycle studies were carried out combining propidium iodide staining and 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation. Cell cycle regulator proteins were detected by Western blotting. The transcription of genes of interest was analyzed using RT-PCR.
Results: In MDR1-/MDR3+ cells, Mucronulatol exhibited cytotoxicity in the range of 2.7 - 10.2 microg/ml, while no cytotoxic effects were observed in MDR1+ systems at up to 100 microg/ml. Cytometric studies revealed that Mucronulatol promoted a global reduction in all cell cycle phases, with a remarkable increase of the apoptotic sub-G1 population. Immunoblotting showed that Mucronulatol induced an up-regulation of p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) while down-regulating cyclin E and CDK4 in a drug concentration-dependent manner. No effect on topoisomerase I was observed, while we detected an altered expression of topoisomerases II-I+/-/I(2). RT-PCR studies showed that 2-fold the IC(50) in HCT8 colon carcinoma cells was sufficient for altering the expression pattern of genes in this cell line, including topoisomerase I, thymidilate synthase, EGF receptor and c-myc, amongst others.
Conclusion: Here, we demonstrate for the first time that Mucronulatol exerts cytotoxicity in cancer cell lines by targeting the control of cell cycle progression, indicating that the mechanism of action of this compound involves interference with the cell cycle machinery.