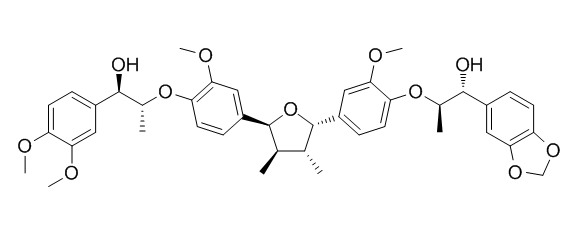
Manassantin B
Manassantin B is a potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation by the suppression of transciptional activity of RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB. It also possesses anti-EBV lytic replication activity. Manassantin B inhibits interleukin-6-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation in Hep3B cells, it has potential as a potent anti-inflammatory drug for use in pathological processes such as sepsis or acute lung injury. Manassantin B exerts antifibrotic activity in HSC-T6 cells, in part, via inhibition of cell proliferation and decrease of collagen production.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Res Int.2018, 106:909-919
Environ Toxicol.2024, 39(4):2417-2428.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(21):11836.
Mol Plant Pathol.2022, 10.1111:mpp.13280.
Org Biomol Chem.2017, 15(31):6483-6492
Universiti Tunku Aboul Rahman2023, 6263.
LWT2021, 138:110630.
Cell Physiol Biochem.2017, 43(4):1425-1435
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 960:176121.
Drug Des Devel Ther.2023, 17:2461-2479.
Related and Featured Products
Journal of Natural Products,2013, 77(1):100-110.
Potential antiviral lignans from the roots of Saururus chinensis with activity against Epstein-Barr virus lytic replication.[Reference:
WebLink]
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a member of the γ-herpes virus subfamily and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several human malignancies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided fractionation was conducted on an EtOAc-soluble extract of the roots of Saururus chinensis and monitored using an EBV lytic replication assay. This led to the isolation of 19 new (1-19) and nine known (20-28) lignans. The absolute configurations of the new lignans were established by Mosher's ester, ECD, and computational methods. Eight lignans, including three sesquineolignans (19, 23, and 24) and five dineolignans (3, 4, 26, 27, and 28), exhibited inhibitory effects toward EBV lytic replication with EC50 values from 1.09 to 7.55 μM and SI values from 3.3 to 116.4. In particular, Manassantin B (27) exhibited the most promising inhibition, with an EC50 of 1.72 μM, low cytotoxicity, CC50 > 200 μM, and SI > 116.4.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first study demonstrating that lignans possess anti-EBV lytic replication activity.
Natural Product Sciences, 2008, 14(2):118-121.
Antifibrotic activity of manassantin B from Saururus chinensis in HSC-T6 hepatic stellate cells.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Manassantin B, a dilignan isolated from Saururus chinensis, significantly inhibited proliferation in HSC-T6 cells in concentration- and time-dependent manners. In addition, treatment of HSC-T6 cells with Manassantin B changed cell morphology from flattened myofibroblastic membranous morphology, representing activation state, to slender shape, representing quiescent state. Furthermore, Manassantin B effectively reduced collagen content in HSC-T6 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggested that Manassantin B exerted antifibrotic activity in HSC-T6 cells, in part, via inhibition of cell proliferation and decrease of collagen production.
Biochemical Pharmacology, 2003, 66(10):1925-1933.
Suppression of RelA/p65 transactivation activity by a lignoid manassantin isolated from Saururus chinensis.[Reference:
WebLink]
In our search for NF-κB inhibitors from natural resources, we have previously identified two structurally related dilignans, manassantin A and Manassantin B as specific inhibitors of NF-κB activation from Saururus chinensis. However, their molecular mechanism of action remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We here demonstrate that manassantin A and Manassantin B are potent inhibitors of NF-κB activation by the suppression of transciptional activity of RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB. These compounds significantly inhibited the induced expression of NF-κB reporter gene by LPS or TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner. However, these compounds did not prevent the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay as well as the induced-degradation of IκB-α protein by LPS or TNF-α. Further analysis revealed that manassantin A and Manassantin B dose-dependently suppressed not only the induced NF-κB activation by overexpression of RelA/p65, but also transactivation activity of RelA/p65. Furthermore, treatment of cells with these compounds prevented the TNF-α-induced expression of anti-apoptotic NF-κB target genes Bfl-1/A1, a prosurvival Bcl-2 homologue, and resulted in sensitizing HT-1080 cells to TNF-α-induced cell death. Similarly, these compounds also suppressed the LPS-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide production.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, manassantin A and Manassantin B could be valuable candidate for the intervention of NF-κB-dependent pathological condition such as inflammation and cancer.
Korean Journal of Anesthesiology, 2012, 62(2):161-5.
Effect of manassantin B, a lignan isolated from Saururus chinensis, on lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1β in RAW 264.7 cells.[Reference:
WebLink]
Elevated systemic levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines cause hypotension during septic shock and induce capillary leakage in acute lung injury. Manassantin B has anti-inflammatory and anti-plasmoidal properties. This study examined the effects of Manassantin B on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
RAW 264.7 macrophage cells were incubated without or with (1, 3 and 10 µM) Manassantin B and without or with (100 ng/ml) LPS. Manassantin B dissolved in phosphate buffered saline was added to the medium 1 h prior to the addition of LPS. The degree of activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) including extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun amino terminal kinases (JNK) and p38 MAPK, and the level of interleukin (IL)-1β were determined 30 min and 24 h after the addition of LPS respectively. Manassantin B inhibited the production of IL-1β and attenuated the phosphorylations of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK, but not that of JNK, in RAW 264.7 cells treated with LPS. Manassantin B reduces LPS-induced IL-1β expression through effects on ERK1/2- and p38 MAPK-mediated pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
Manassantin B has potential as a potent anti-inflammatory drug for use in pathological processes such as sepsis or acute lung injury.