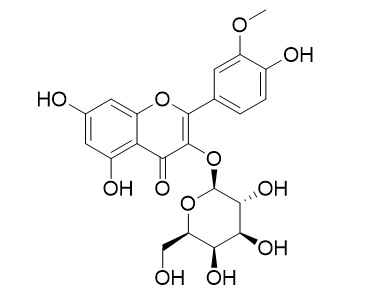
Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside
Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside shows antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective,and barrier protective activities, it could be used as a candidate therapeutic for treatment of severe vascular inflammatory diseases.It has potential anticoagulant activity, it possesses antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activity and offers bases for development of a novel anticoagulant. Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside is also a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, it may have therapeutic potential in skin inflammatory disorders in traditional medicine.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Korean. J. Pestic. Sci.2024, 28(3):241-248.
Phytomedicine.2016, 23(4):331-9
J Cell Biochem.2018, 119(2):2231-2239
J Physiol Biochem.2024, 80(2):421-437.
Research Square2022, rs.3.rs-1948239
J Integr Plant Biol.2023, 13564.
Nutrients.2021, 13(8):2901.
Food Research International2020, 108987
J Appl Biol Chem.2024, V67:46-53
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(7):1376.
Related and Featured Products
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Mar;53:197-204.
Antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activities of isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside and hyperoside.[Pubmed:
23220618]
The potential anticoagulant activities of two single compounds, Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside (IMG) and hyperoside, from Oenanthe javanica, were tested.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anticoagulant activities were investigated by measuring activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and prothrombin time (PT), and the ability to inhibit production of thrombin and activated factor X (FXa) was investigated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). And, the effects of the compounds on expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) and tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) were tested in tumor necrosis factor-(TNF)-α activated HUVECs. Treatment with IMG and hyperoside resulted in significantly prolonged aPTT and PT and inhibition of the activities of thrombin and FXa, and IMG or hyperoside inhibited production of thrombin and FXa in HUVECs. In accordance with these anticoagulant activities, both agents elicited anticoagulant effects in mouse. In addition, treatment with IMG and hyperoside resulted in inhibition of TNF-α-induced production of PAI-1, and treatment with IMG resulted in significant reduction of the PAI-1 to t-PA ratio.
CONCLUSIONS:
The anticoagulant and profibrinolytic effects of IMG were greater than those of hyperoside, indicating positive regulation of its anticoagulant function by the methoxy group of IMG. IMG and hyperoside possess antithrombotic activities and offer bases for development of a novel anticoagulant.
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2012, 114(2):336-345.
Anti-inflammatory activities of isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside against HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in both HUVECs and CLP-induced septic mice.[Pubmed:
22930571]
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein is a crucial nuclear cytokine that elicits severe vascular inflammatory diseases. Oenanthe javanica (water dropwort) extract has anti-arrhythmic, neuroprotective and anti-diabetic activity. However, Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside (I3G), an active compound from O. javanica, is not researched well for its biological activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated the anti-inflammatory activities of I3G by monitoring the effects of I3G on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-mediated release of HMGB1 and HMGB1 or CLP-mediated modulation of inflammatory responses. I3G potently inhibited the release of HMGB1 and down-regulated HMGB1-dependent inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells. I3G also inhibited HMGB1-mediated hyperpermeability and leukocyte migration in mice. Further studies revealed that I3G suppressed the production of tumor necrosis factor-α and activation of nuclear factor-κB by HMGB1. In addition, I3G reduced CLP-induced HMGB1 release and sepsis-related mortality.
CONCLUSIONS:
Given these results, I3G should be viewed as a candidate therapeutic agent for the treatment of severe vascular inflammatory diseases such as sepsis or septic shock via inhibition of the HMGB1 signaling pathway.
Thromb Res. 2013 Jul;132(1):e58-63.
Down-regulation of endothelial protein C receptor shedding by persicarin and isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside.[Pubmed:
23726966 ]
Increasing evidence has shown that beyond its role in coagulation, endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) plays an important role in the cytoprotective pathway.
Previous reports have shown that EPCR can be shed from the cell surface, and that this is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme (TACE) and that sEPCR levels are increased in patients with systemic inflammatory diseases. Persicarin and Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside (I3G) are active compounds from Oenanthe javanica, which has been widely studied for its neuroprotective, antioxidant, and barrier protective activities. However, little is known of the effects of persicarin on EPCR shedding.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated this issue by monitoring the effects of persicarin and I3G on phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-mediated EPCR shedding and underlying mechanisms. According to the results, persicarin and I3G induced potent inhibition of PMA and CLP-induced EPCR shedding by suppressing expression of TACE. In addition, persicarin and I3G reduced PMA-stimulated phosphorylation of p38MAPK, extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK).
CONCLUSIONS:
Given these results, persicarin and I3G could be used as a candidate therapeutic for treatment of severe vascular inflammatory diseases.
Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Sep;34(9):1561-9.
Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and skin inflammation by the aerial parts of Artemisia capillaris and its constituents.[Pubmed:
21975819]
The aerial parts of Artemisia capillaris Thunberg (Compositae) have been used in Chinese medicine as a liver protective agent, diuretic, and for amelioration of skin inflammatory conditions. This study was conducted to establish the scientific rationale for treating skin inflammation and to find active principles from A. capillaris.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To accomplish these goals, the 70% ethanol extract of the aerial parts of A. capillaris (AR) was prepared and its 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitory action was studied since 5-LOX products are known to be involved in several allergic and skin inflammatory disorders. AR showed potent inhibitory activity against 5-LOX-catalyzed leukotriene production by ionophore-induced rat basophilic leukemia-1 cells, with an IC(50) of < 1.0 μg/mL. Nine major compounds, scopoletin, scopolin, scoparone, esculetin, quercetin, capillarisin, isorhamnetin, 3-O-robinobioside, Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside and chlorogenic acid, were isolated from A. capillaris, and their effects were examined to identify the active principle(s). Several coumarin and flavonoid derivatives were found to be 5-LOX inhibitors. In particular, esculetin and quercetin were potent inhibitors, with IC(50) values of 6.6 and 0.7 μM, respectively. Against arachidonic acid-induced ear edema in mice, AR, and esculetin strongly inhibited edematic response. AR and esculetin also inhibited delayed-type hypersensitivity response in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, AR and some of their major constituents are 5-LOX inhibitors, and these in vitro and in vivo activities may contribute to the therapeutic potential of AR in skin inflammatory disorders in traditional medicine.
Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013 Nov 2;11(1):67-72.
The flavonoid constitunts of Leucaena leucocephala. Growing in Egypt, and their biological activity.[Pubmed:
24653555]
Leucaena leucocephala is native to Southern Mexico and Northern Central America, but is now naturalized throughout the tropics. The phyto-chemical data of L. leucocephala revealed the presence of terpenes, flavonoids, coumarins and sterols. Various parts of L. leucocephala have been reported to have medicinal properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Flavonoids were isolated from the aerial parts of L. leucocephala. Antioxidant activity of the extracts and the isolated compounds was evaluated using (DPPH), as well as their cytotoxic activity using a single tumor [Ehrlish ascites carcinoma cells].
The flavonoidal constituents isolated from chloroform, ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of the aqueous alcoholic extract of aerial parts of Leucaena leucocephala were identified as Caffeic acid, Isorhamnetin, Chrysoeriol, Isorhamnetin 3-O-galactoside, Kaempferol-3-O-rubinoside, Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside and Luteolin-7-glucoside. Chemical structures of the isolated compounds were identified by TLC, PC and spectral techniques (UV, (1)H-NMR and MS). The ethyl acetate fraction and the isolated flavonoidal compounds showed high antioxidant activity compared to Trolox (standard antioxidant compound). The different fractions and isolated compounds of Leucaena leucocephala exhibited no cytotoxic activity against Ehrlich-ascitis carcinoma cell line at the tested concentrations.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first record of the flavonoids in the aerial parts of Leucaena leucocephala (L.) except Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside.