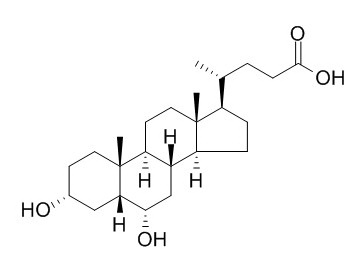
Hyodeoxycholic acid
Hyodeoxycholic acid is a secondary bile acid formed in the small intestine by the gut flora, and acts as a TGR5 (GPCR19) agonist, with an EC50 of 31.6 µM in CHO cells. Hyodeoxycholic acid has hypolipidemic effect through regulation of FXR activation, it is a candidate for antiatherosclerotic drug, by significantly increasing the expression of genes involved in cholesterol efflux, such as Abca1, Abcg1,and Apoe,in a macrophage cell line.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Foods.2024, 13(11):1739.
Trop J Nat Prod Res2023, 7(12):5611-5615.
Journal of Mushroom2023, 21(4):215-221.
Chem Biol Interact.2024, 403:111249.
Biomed Pharmacother.2020, 125:109784.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2023, 45(3):2136-2156.
Anal Chim Acta.2021, 1180:338874.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol.2018, 8:292
Int J Vitam Nutr Res.2022, doi: 10.1024.
Preprints2022, 202211.0388.v1.
Related and Featured Products
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006 Sep 14;842(1):22-7.
Simultaneous determination of geniposide, baicalin, cholic acid and hyodeoxycholic acid in rat serum for the pharmacokinetic investigations by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:
16750434]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A simple, rapid, and specific analytical method for simultaneous determination of geniposide, baicalin, cholic acid and Hyodeoxycholic acid in 50 microL samples of rat serum was developed by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The quantification of the target compounds was determined by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode using electrospray ionization (ESI). The correlation coefficients of the calibration curves were better than 0.997. The intra- and inter-day accuracy, precision, and linear range had been investigated in detail.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method was subsequently applied to pharmacokinetic studies of geniposide, baicalin, cholic acid and Hyodeoxycholic acid in rats successfully.
Lipids. 2014 Oct;49(10):963-73.
Dietary hyodeoxycholic acid exerts hypolipidemic effects by reducing farnesoid X receptor antagonist bile acids in mouse enterohepatic tissues.[Pubmed:
25189147]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Mice were fed a control diet or a diet supplemented with Hyodeoxycholic acid, the most abundant bile acid contained in pig bile, for 4 weeks, after which their serum and livers were collected. The contents of total fatty acids of serum and liver cholesteryl esters, and of liver triglycerides, were reduced following the administration of the Hyodeoxycholic acid-supplemented diet, which was mainly due to the reductions in the contents of monounsaturated fatty acids. Free cholesterol contents in the serum and liver were not changed by Hyodeoxycholic acid administration. Hyodeoxycholic acid administration reduced the gene expression levels of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, fatty acid synthase, and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1. Hyodeoxycholic acid administration markedly changes the ratio of FXR-antagonist/FXR-agonist bile acids in the enterohepatic tissues of the mice (1.13 and 7.60 in Hyodeoxycholic acid and control diet groups, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings demonstrate that Hyodeoxycholic acid administration exerts the hypolipidemic effect in mice, in which downregulations of de novo lipogenesis and desaturation of saturated fatty acids are suggested to play important roles. In addition, regulation of FXR activation through the selective modification of the enterohepatic bile acid pool may be involved in the hypolipidemic effect of Hyodeoxycholic acid administration.
FASEB J. 2013 Sep;27(9):3805-17.
Hyodeoxycholic acid improves HDL function and inhibits atherosclerotic lesion formation in LDLR-knockout mice.[Pubmed:
23752203]
We examined the effects of a natural secondary bile acid, Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA), on lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-null (LDLRKO) mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Female LDLRKO mice were maintained on a Western diet for 8 wk and then divided into 2 groups that received chow, or chow + 1.25% HDCA, diets for 15 wk. We observed that mice fed the HDCA diet were leaner and exhibited a 37% (P<0.05) decrease in fasting plasma glucose level. HDCA supplementation significantly decreased atherosclerotic lesion size at the aortic root region, the entire aorta, and the innominate artery by 44% (P<0.0001), 48% (P<0.01), and 94% (P<0.01), respectively, as compared with the chow group. Plasma VLDL/IDL/LDL cholesterol levels were significantly decreased, by 61% (P<0.05), in the HDCA group as compared with the chow diet group. HDCA supplementation decreased intestinal cholesterol absorption by 76% (P<0.0001) as compared with the chow group. Furthermore, HDL isolated from the HDCA group exhibited significantly increased ability to mediate cholesterol efflux ex vivo as compared with HDL of the chow diet group. In addition, HDCA significantly increased the expression of genes involved in cholesterol efflux, such as Abca1, Abcg1, and Apoe, in a macrophage cell line.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, HDCA is a candidate for antiatherosclerotic drug therapy.
Molecules. 2013 Aug 30;18(9):10497-513.
Synthesis and quantitative structure-property relationships of side chain-modified hyodeoxycholic acid derivatives.[Pubmed:
23999724]
Bile acids have emerged as versatile signalling compounds of a complex network of nuclear and membrane receptors regulating various endocrine and paracrine functions. The elucidation of the interconnection between the biological pathways under the bile acid control and manifestations of hepatic and metabolic diseases have extended the scope of this class of steroids for in vivo investigations.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this framework, the design and synthesis of novel biliary derivatives able to modulate a specific receptor requires a deep understanding of both structure-activity and structure-property relationships of bile acids. In this paper, we report the preparation and the critical micellization concentration evaluation of a series of Hyodeoxycholic acid derivatives characterized by a diverse side chain length and by the presence of a methyl group at the alpha position with respect to the terminal carboxylic acid moiety.
CONCLUSIONS:
The data collected are instrumental to extend on a quantitative basis, the knowledge of the current structure-property relationships of bile acids and will be fruitful, in combination with models of receptor activity, to design and prioritize the synthesis of novel pharmacokinetically suitable ligands useful in the validation of bile acid-responsive receptors as therapeutic targets.