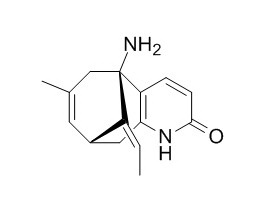
Huperzine A
Huperzine A is a potent, selective and reversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor and has been widely used in China for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD).Huperzine A induces CYP3A4 expression and activation via PXR dependent pathways, may contribute to drug-drug interactions with ligustrazine and oridonin.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Vietnam J. Chemistry2022, 60(2):211-222
Nutrients.2021, 13(3):978.
Molecules.2020, 25(15):3353.
Oncol Rep.2016, 35(3):1356-64
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176749.
Biomolecules.2019, 9(11):E696
Molecules.2016, 21(10)
Molecules2020, 25(4):892
Industrial Crops and Products2024, 129:119014
Food Chem.2023, 424:136383.
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Res. 2015 Jun;29(11):1035-41.
Huperzine A production by Paecilomyces tenuis YS-13, an endophytic fungus isolated from Huperzia serrata.[Pubmed:
25427833]
Huperzine A (HupA), a naturally occurring alkaloid in the plant family Huperziaceae, has drawn great interest for its potential application in Alzheimer disease therapy. Our primary objective was to identify alkaloid- and HupA-producing fungi from the Chinese folk herb, Huperzia serrata.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We established a rapid and efficient model for screening HupA-producing endophytic fungal strains. The presence of HupA in Paecilomyces tenuis YS-13 was analysed by thin-layer chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. The fermentation yield of HupA was 21.0 μg/L, and the IC50 of the crude extract of YS-13 fermentation broth was 1.27 ± 0.04 mg/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of P. tenuis as a HupA-producing endophyte isolated from Huperziaceae.
Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Aug 19;6:216.
Huperzine A: Is it an Effective Disease-Modifying Drug for Alzheimer's Disease?[Pubmed:
25191267]
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder for which there is no cure. Huperzine A (HupA) is a natural inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) derived from the Chinese folk medicine Huperzia serrata (Qian Ceng Ta). It is a licensed anti-AD drug in China and is available as a nutraceutical in the US.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A growing body of evidence has demonstrated that HupA has multifaceted pharmacological effects. In addition to the symptomatic, cognitive-enhancing effect via inhibition of AChE, a number of recent studies have reported that this drug has "non-cholinergic" effects on AD. Most important among these is the protective effect of HupA on neurons against amyloid beta-induced oxidative injury and mitochondrial dysfunction as well as via the up-regulation of nerve growth factor and antagonizing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most recent discovery that HupA may reduce brain iron accumulation lends further support to the argument that HupA could serve as a potential disease-modifying agent for AD and also other neurodegenerative disorders by significantly slowing down the course of neuronal death.
Neurosignals, 2005, 14(1-2):71-82.
Neuroprotective Effects of Huperzine A.[Reference:
WebLink]
Huperzine A (HupA), isolated from Chinese herb Huperzia serrata, is a potent, highly specific and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. It has been found to reverse or attenuate cognitive deficits in a broad range of animal models.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Clinical trials in China have demonstrated that HupA significantly relieves memory deficits in aged subjects, patients with benign senescent forgetfulness, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VD), with minimal peripheral cholinergic side effects compared with other AChEIs in use. HupA possesses the ability to protect cells against hydrogen peroxide, beta-amyloid protein (or peptide), glutamate, ischemia and staurosporine-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis. These protective effects are related to its ability to attenuate oxidative stress, regulate the expression of apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Bax, P53 and caspase-3, protect mitochondria, and interfere with APP metabolism. Antagonizing effects on NMDA receptors and potassium currents may contribute to the neuroprotection as well.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is also possible that the non-catalytic function of AChE is involved in neuroprotective effects of HupA. The therapeutic effects of HupA on AD or VD are probably exerted via a multi-target mechanism.
Pharmazie. 2014 Jul;69(7):532-6.
Induction of human CYP3A4 by huperzine A, ligustrazine and oridonin through pregnane X receptor-mediated pathways.[Pubmed:
25073399 ]
The pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a key regulator of CYP3A4, which is involved in catalyzing the metabolic conversion of a number of endogenous substrates.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we screened 22 compounds isolated from traditional Chinese herbal medicines using luciferase reporter gene assays for inspecting their capabilities in inducing PXR-mediated transactivation of CYP3A4 expression. In addition, the mRNA and protein expressions of CYP3A4 and PXR as well as the enzymatic activites of CYP3A4 were analyzed by real-time PCR, Western blot analysis and UPLC-MS/MS-based metabolite assay in LS174T cells. Huperzine A, ligustrazine and oridonin were identified to be the inducers of CYP3A4. These compounds induced the CYP3A4 reporter luciferase activity, and up-regulated CYP3A4 mRNA and protein levels significantly. Besides, Huperzine A, ligustrazine and oridonin significantly up-regulated enzymatic activities of CYP3A4. However, the three compounds showed no effects on PXR mRNA and protein expression. To our knowledge, it is the first identification of these three compounds as PXR activators to induce CYP3A4.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Huperzine A, ligustrazine and oridonin induced CYP3A4 expression and activation via PXR dependent pathways, and might contribute to drug-drug interactions.
PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0120809.
De Novo RNA Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides ES026 Reveal Genes Related to Biosynthesis of Huperzine A.[Pubmed:
25799531]
Huperzine A is important in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. There are major challenges for the mass production of Huperzine A from plants due to the limited number of Huperzine A-producing plants, as well as the low content of Huperzine A in these plants. Various endophytic fungi produce Huperzine A. Colletotrichum gloeosporioides ES026 was previously isolated from a Huperzine A-producing plant Huperzia serrata, and this fungus also produces Huperzine A.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, de novo RNA sequencing of C. gloeosporioides ES026 was carried out with an Illumina HiSeq2000. A total of 4,324,299,051 bp from 50,442,617 high-quality sequence reads of ES026 were obtained. These raw data were assembled into 24,998 unigenes, 40,536,684 residues and 19,790 genes. The majority of the unique sequences were assigned to corresponding putative functions based on BLAST searches of public databases. The molecular functions, biological processes and biochemical pathways of these unique sequences were determined using gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) assignments. A gene encoding copper amine oxidase (CAO) (unigene 9322) was annotated for the conversion of cadaverine to 5-aminopentanal in the biosynthesis of Huperzine A. This gene was also detected in the root, stem and leaf of H. serrata. Furthermore, a close relationship was observed between expression of the CAO gene (unigene 9322) and quantity of crude Huperzine A extracted from ES026.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, CAO might be involved in the biosynthesis of Huperzine A and it most likely plays a key role in regulating the content of Huperzine A in ES026.