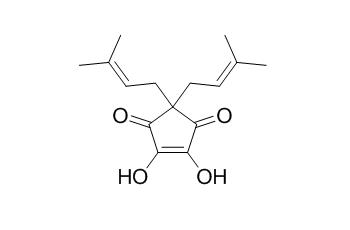
Hulupinic acid
Hulupinic acid may show inhibitory activities on the production of NO in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Mol Pharm.2017, 14(9):3164-3177
Oxid Med Cell Longev.2022, 2022:5888636.
Korean J Pain.2021, 34(4):405-416.
Journal of Ginseng Research2024, 03.005.
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(15):8784-8797.
Mol Immunol. 2016, 78:121-132
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 19(1)
Phytomedicine.2024, 122:155065.
Int. J. Mol. Sci.2022, 23(14),7699;
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2022, 15(8):982.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2005 Jan;68(1):43-9.
Prenylflavonoids and phloroglucinol derivatives from hops (Humulus lupulus).[Pubmed:
15679315 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The ethyl acetate soluble fraction of hops (Humulus lupulus) showed potent inhibitory activity on the production of nitric oxide (NO) induced by a combination of LPS and IFN-gamma. Four known prenylflavonoids (1-4) and a new prenylflavonoid (5), Hulupinic acid (6), lupulone (7), and its six new derivatives (8-13) were isolated from the active fraction. The structures were determined on the basis of physiochemical properties and spectroscopic analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their inhibitory activities on the production of NO in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells were examined.
J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Aug 26;57(16):7480-9.
Identification and RP-HPLC-ESI-MS/MS quantitation of bitter-tasting beta-acid transformation products in beer.[Pubmed:
19627140 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Thermal treatment of the hop beta-acid colupulone under wort boiling conditions, followed by LC-TOF-MS and 1D/2D NMR spectroscopy, revealed cohulupone, Hulupinic acid, nortricyclocolupone, two tricyclocolupone epimers, two dehydrotricyclocolupone epimers, two hydroxytricyclocolupone epimers, and two hydroperoxytricyclocolupone epimers as the major bitter-tasting beta-acid transformation products. Among these compounds, the chemical structures of the hydroxy- as well as the hydroperoxytricyclocolupone epimers have not previously been confirmed by 1D/2D NMR experiments. Depending on their chemical structure, these compounds showed rather low recognition thresholds ranging from 7.9 to 90.3 micromol/L.
The lowest thresholds of 7.9 and 14.7 micromol/L were found for cohulupone, imparting a short-lasting, iso-alpha-acid-like bitter impression, and for hydroxytricyclocolupone, exhibiting a long-lasting, lingering, and harsh bitterness perceived on the posterior tongue and throat. Furthermore, HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis allowed for the first time a simultaneous detection and quantitation of these bitter-tasting beta-acid transformation products in a range of commercial beer samples without any sample cleanup.
CONCLUSIONS:
Depending on the type of beer, these studies revealed remarkable differences in the concentrations of the individual beta-acid transformation products.