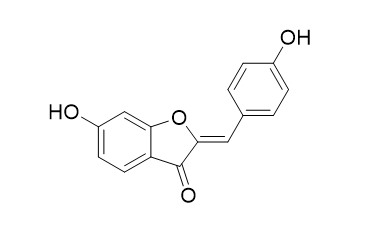
Hispidol
Hispidol ((Z)-Hispidol) is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease; inhibits TNF-α induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells with an IC50 of 0.50 μM.
Hispidol was found to potently and selectively inhibit an isoform of recombinant human monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), with an IC50 value of 0.26 μM, and to inhibit MAO-B, but with lower potency (IC50 = 2.45 μM). Hispidol has antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antidepressant effects.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Enzyme Microb Technol.2019, 122:64-73
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 963:176280.
Molecules.2021, 26(9):2765.
Food Chem.2019, 279:80-87
Front Plant Sci.2022, 13:982771.
Appl Biol Chem2019, 62:46
Current Topics in Nutraceutical Research2021, 19(1),p90-105.
J Pharm Pharmacol.2022, rgac033.
Biol Pharm Bull.2017, 40(6):797-806
J. Essential Oil Research2024, 6:36:554-565.
Related and Featured Products
Eur J Med Chem . 2017 Sep 8;137:575-597
Discovery and structure-activity relationship studies of 2-benzylidene-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one and benzofuran-3(2H)-one derivatives as a novel class of potential therapeutics for inflammatory bowel disease[Pubmed:
28646757]
To develop effective therapeutics for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), 2-benzylidene-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one and benzofuran-3(2H)-one derivatives, were designed and synthesized and their structure-activity relationships (SAR) were investigated. Compounds 7, 25, 26, 32, 39, 41, 52, 54, and 55 showed potent inhibitory effect (>70%) on the TNF-α-induced adhesion of monocytes to colon epithelial cells, which is one of the hallmark events leading to IBD. Such inhibitory activity of the compounds correlated with their suppressive activities against the TNF-α-induced production of ROS; ICAM-1 and MCP-1 expression, critical molecules involved in monocyte-epithelial adhesion; and NF-κB transcriptional activity. In addition, compounds 41 and 55 significantly suppressed the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of the TNF-α gene, with compound 55 showing better efficacy. This inhibition of TNF-α expression by compounds 41 and 55 corresponded to their additional inhibitory activity against AP-1 transcriptional activity, which is another transcription factor required for high level TNF-α expression. The strong inhibitory activity of compound 55 against an in vivo colitis model was confirmed by its dose-dependent inhibitory activity in a rat model of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis, demonstrating compound 55 as a new potential candidate for the development of therapeutics against IBD.
Neurochem Res . 2020 Aug;45(8):1930-1940
Antidepressant-Like Activities of Hispidol and Decursin in Mice and Analysis of Neurotransmitter Monoamines[Pubmed:
32440903]
The antidepressant activities of Hispidol and decursin (both potent monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) inhibitors) were evaluated using the forced swimming test (FST) and the tail suspension test (TST) in mice, and thereafter, levels of neurotransmitter monoamines and metabolites in brain tissues were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Hispidol (15 mg/kg) caused less or comparable immobility than fluoxetine (15 mg/kg; the positive control) in immobility time, as determined by FST (9.6 vs 32.0 s) and TST (53.1 vs 48.7 s), respectively, and its effects were dose-dependent and significant. Decursin (15 mg/kg) also produced immobility comparable to that of fluoxetine as determined by FST (47.0 vs 43.4 s) and TST (55.6 vs 63.4 s), and its effects were also dose-dependent and significant. LC-MS/MS analysis after FST showed that Hispidol (15 mg/kg) greatly increased dopamine (DA) and serotonin levels dose-dependently in brain tissues as compared with the positive control. Decursin (15 mg/kg) dose-dependently increased DA level after TST. Slight changes in norepinephrine and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid levels were observed after FST and TST in Hispidol- or decursin-treated animals. It was observed that Hispidol and decursin were effective and comparable to fluoxetine in immobility tests. These immobility and monoamine level results suggest that Hispidol and decursin are potential antidepressant agents for the treatment of depression, and that they act mainly through serotonergic and/or dopaminergic systems.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett . 2018 Feb 15;28(4):584-588
Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by hispidol[Pubmed:
29395970]
Hispidol, an aurone, isolated from Glycine max Merrill, was found to potently and selectively inhibit an isoform of recombinant human monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), with an IC50 value of 0.26 μM, and to inhibit MAO-B, but with lower potency (IC50 = 2.45 μM). Hispidol reversibly and competitively inhibited MAO-A with a Ki value of 0.10 μM with a potency much greater than toloxatone (IC50 = 1.10 μM), a marketed drug. It also reversibly and competitively inhibited MAO-B (Ki = 0.51 μM). Sulfuretin, an analog of Hispidol, effectively inhibited MAO-A (IC50 = 4.16 μM) but not MAO-B (IC50 > 80 μM). A comparison of their chemical structures showed that the 3'-hydroxyl group of sulfuretin might reduce its inhibitory activities against MAO-A and MAO-B. Flexible docking simulation revealed that the binding affinity of Hispidol for MAO-A (-9.1 kcal/mol) was greater than its affinity for MAO-B (-8.7 kcal/mol). The docking simulation showed Hispidol binds to the major pocket of MAO-A or MAO-B. The findings suggest Hispidol is a potent, selective, reversible inhibitor of MAO-A, and that it be considered a novel lead compound for development of novel reversible inhibitors of MAO-A.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett . 2018 Feb 15;28(4):584-588.
Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by hispidol[Pubmed:
29395970]
Hispidol, an aurone, isolated from Glycine max Merrill, was found to potently and selectively inhibit an isoform of recombinant human monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), with an IC50 value of 0.26 μM, and to inhibit MAO-B, but with lower potency (IC50 = 2.45 μM). Hispidol reversibly and competitively inhibited MAO-A with a Ki value of 0.10 μM with a potency much greater than toloxatone (IC50 = 1.10 μM), a marketed drug. It also reversibly and competitively inhibited MAO-B (Ki = 0.51 μM). Sulfuretin, an analog of Hispidol, effectively inhibited MAO-A (IC50 = 4.16 μM) but not MAO-B (IC50 > 80 μM). A comparison of their chemical structures showed that the 3'-hydroxyl group of sulfuretin might reduce its inhibitory activities against MAO-A and MAO-B. Flexible docking simulation revealed that the binding affinity of Hispidol for MAO-A (-9.1 kcal/mol) was greater than its affinity for MAO-B (-8.7 kcal/mol). The docking simulation showed Hispidol binds to the major pocket of MAO-A or MAO-B. The findings suggest Hispidol is a potent, selective, reversible inhibitor of MAO-A, and that it be considered a novel lead compound for development of novel reversible inhibitors of MAO-A.
Plant Physiol . 2009 Nov;151(3):1096-1113.
Integrated metabolite and transcript profiling identify a biosynthetic mechanism for hispidol in Medicago truncatula cell cultures[Pubmed:
19571306]
Metabolic profiling of elicited barrel medic (Medicago truncatula) cell cultures using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to photodiode and mass spectrometry detection revealed the accumulation of the aurone Hispidol (6-hydroxy-2-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-1-benzofuran-3-one) as a major response to yeast elicitor. Parallel, large-scale transcriptome profiling indicated that three peroxidases, MtPRX1, MtPRX2, and MtPRX3, were coordinately induced with the accumulation of Hispidol. MtPRX1 and MtPRX2 exhibited aurone synthase activity based upon in vitro substrate specificity and product profiles of recombinant proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. Hispidol possessed significant antifungal activity relative to other M. truncatula phenylpropanoids tested but has not been reported in this species before and was not found in differentiated roots in which high levels of the peroxidase transcripts accumulated. We propose that Hispidol is formed in cell cultures by metabolic spillover when the pool of its precursor, isoliquiritigenin, builds up as a result of an imbalance between the upstream and downstream segments of the phenylpropanoid pathway, reflecting the plasticity of plant secondary metabolism. The results illustrate that integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics in genetically reprogrammed plant cell cultures is a powerful approach for the discovery of novel bioactive secondary metabolites and the mechanisms underlying their generation.
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem . 2022 Dec;37(1):768-780.
Positional scanning of natural product hispidol's ring-B: discovery of highly selective human monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor analogues downregulating neuroinflammation for management of neurodegenerative diseases[Pubmed:
35196956]
Multifunctional molecules might offer better treatment of complex multifactorial neurological diseases. Monoaminergic pathways dysregulation and neuroinflammation are common convergence points in diverse neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. Aiming to target these diseases, polypharmacological agents modulating both monoaminergic pathways and neuroinflammatory were addressed. A library of analogues of the natural product Hispidol was prepared and evaluated for inhibition of monoamine oxidases (MAOs) isoforms. Several molecules emerged as selective potential MAO B inhibitors. The most promising compounds were further evaluated in vitro for their impact on microglia viability, induced production of proinflammatory mediators and MAO-B inhibition mechanism. Amongst tested compounds, 1p was a safe potent competitive reversible MAO-B inhibitor and inhibitor of microglial production of neuroinflammatory mediators; NO and PGE2. In-silico study provided insights into molecular basis of the observed selective MAO B inhibition. This study presents compound 1p as a promising lead compound for management of neurodegenerative disease.
Z Naturforsch C J Biosci . Jul-Aug 2002;57(7-8):717-720.
Aurones interfere with Leishmania major mitochondrial fumarate reductase[Pubmed:
12241002]
A series of aurones was analyzed for the ability to inhibit respiratory functions of mitochondria of Leishmania parasites. The aim of this study was to find a rational explanation for the activity of certain aurones and auronols as novel antiprotozoal compounds of plant origin. In a cell-free assay mitochondrial fumarate reductase from L. donovani was inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner. The most active compounds were 4',6-dihydroxyaurone and 6-methoxyaurone which inhibited parasite enzyme activity at 25 nM by over ninety percent.
Biofactors . 2020 Nov;46(6):1041-1048
Longevity effects of hispidol in Caenorhabditis elegans[Pubmed:
33179346]
In this study, we investigated the longevity effects of Hispidol, a 6,4'-dihydroxyaurone, using the Caenorhabditis elegans model system. Our lifespan assay data revealed that Hispidol could prolong the lifespan of wild-type worms under normal culture condition. Moreover, Hispidol increased the survival rate of the worms against a heat stress condition through up-regulated expressions of HSP-16.2. Similarly, Hispidol protected worms from paraquat-induced oxidative stress. We also found that the Hispidol elevated the activities of antioxidant enzymes, thereby attenuating the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. These results suggest that the enhancement of lifespan and stress resistance by the Hispidol treatment might be attributed to its strong in vivo antioxidant capacity and regulation of stress proteins. Further tests on the aging-related factors revealed that Hispidol could regulate the speed of pharyngeal pumping, indicating the association of dietary restriction with the Hispidol-mediated longevity. However, there were no significant alterations in the body length of the worms between the groups. We then investigated the effects of Hispidol on body movement and lipofuscin accumulation in aged worms. Interestingly, these healthspan parameters were strongly improved by the Hispidol treatment. Our genetic studies showed no significant change in the lifespan of the daf-16 null mutants by Hispidol supplementation. In addition, enhanced nuclear translocation of DAF-16 was observed in the Hispidol-fed DAF-16::GFP fused transgenic mutants, suggesting the requirement of DAF-16/FOXO activation for the longevity effect of Hispidol.
Neurochem Res . 2020 Aug;45(8):1930-1940.
Antidepressant-Like Activities of Hispidol and Decursin in Mice and Analysis of Neurotransmitter Monoamines[Pubmed:
32440903]
The antidepressant activities of Hispidol and decursin (both potent monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) inhibitors) were evaluated using the forced swimming test (FST) and the tail suspension test (TST) in mice, and thereafter, levels of neurotransmitter monoamines and metabolites in brain tissues were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Hispidol (15 mg/kg) caused less or comparable immobility than fluoxetine (15 mg/kg; the positive control) in immobility time, as determined by FST (9.6 vs 32.0 s) and TST (53.1 vs 48.7 s), respectively, and its effects were dose-dependent and significant. Decursin (15 mg/kg) also produced immobility comparable to that of fluoxetine as determined by FST (47.0 vs 43.4 s) and TST (55.6 vs 63.4 s), and its effects were also dose-dependent and significant. LC-MS/MS analysis after FST showed that Hispidol (15 mg/kg) greatly increased dopamine (DA) and serotonin levels dose-dependently in brain tissues as compared with the positive control. Decursin (15 mg/kg) dose-dependently increased DA level after TST. Slight changes in norepinephrine and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid levels were observed after FST and TST in Hispidol- or decursin-treated animals. It was observed that Hispidol and decursin were effective and comparable to fluoxetine in immobility tests. These immobility and monoamine level results suggest that Hispidol and decursin are potential antidepressant agents for the treatment of depression, and that they act mainly through serotonergic and/or dopaminergic systems.
Biofactors . 2020 Nov;46(6):1041-1048.
Longevity effects of hispidol in Caenorhabditis elegans[Pubmed:
33179346]
In this study, we investigated the longevity effects of Hispidol, a 6,4'-dihydroxyaurone, using the Caenorhabditis elegans model system. Our lifespan assay data revealed that Hispidol could prolong the lifespan of wild-type worms under normal culture condition. Moreover, Hispidol increased the survival rate of the worms against a heat stress condition through up-regulated expressions of HSP-16.2. Similarly, Hispidol protected worms from paraquat-induced oxidative stress. We also found that the Hispidol elevated the activities of antioxidant enzymes, thereby attenuating the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. These results suggest that the enhancement of lifespan and stress resistance by the Hispidol treatment might be attributed to its strong in vivo antioxidant capacity and regulation of stress proteins. Further tests on the aging-related factors revealed that Hispidol could regulate the speed of pharyngeal pumping, indicating the association of dietary restriction with the Hispidol-mediated longevity. However, there were no significant alterations in the body length of the worms between the groups. We then investigated the effects of Hispidol on body movement and lipofuscin accumulation in aged worms. Interestingly, these healthspan parameters were strongly improved by the Hispidol treatment. Our genetic studies showed no significant change in the lifespan of the daf-16 null mutants by Hispidol supplementation. In addition, enhanced nuclear translocation of DAF-16 was observed in the Hispidol-fed DAF-16::GFP fused transgenic mutants, suggesting the requirement of DAF-16/FOXO activation for the longevity effect of Hispidol.