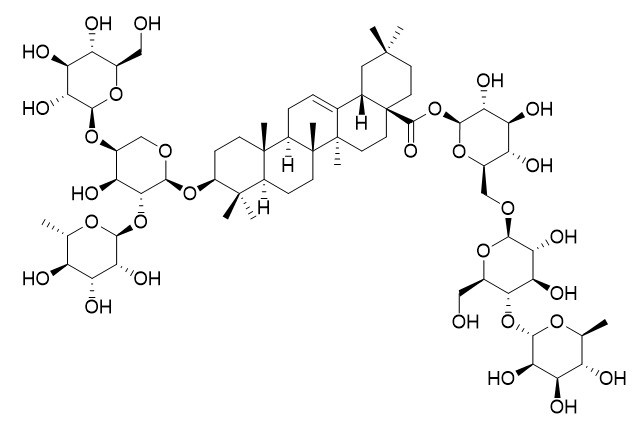
Hederacolchiside E
Hederacolchiside E has antioxidant activity, it shows inhibition on lipid peroxidation of linoleic acid emulsion; it may exert its anti-inflammatory effects by blocking bradykinin or other inflammation mediators. Hederacolchiside E shows neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer's disease (AD) models via modulating oxidative stress.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(4):284.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(3),1696.
Molecules.2024, 29(6):1240.
Food Sci Biotechnol.2016, 25(5):1437-1442
Journal of Third Military Medical University2019, 41(2):110-115
J Agric Food Chem.2018, 66(1):351-358
Int J Mol Sci.2018, 19(9):E2825
LWT2024, v208:116677
J Food Compos Anal2017, 62:197-204
Ind Crops Prod.2015, 67:185-191
Related and Featured Products
Planta Med. 2004 Jun;70(6):561-3.
Antioxidant activity of saponins isolated from ivy: alpha-hederin, hederasaponin-C, hederacolchiside-E and hederacolchiside-F.[Pubmed:
15241892]
The antioxidant activities of alpha-hederin and hederasaponin C from Hedera helix, and Hederacolchiside E and hederacolchiside F from Hedera colchica were investigated, in this study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidant properties of the saponins were evaluated using different antioxidant tests: 1,1-di-phenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH.) free radical scavenging, total antioxidant activity, reducing power, superoxide anion radical scavenging, hydrogen peroxide scavenging, and metal chelating activities. Alpha-hederin, hederasaponin C, as well as Hederacolchiside E and hederacolchiside F exhibited a strong total antioxidant activity. At the concentration of 75 pg/mL, these saponins showed 94, 86, 88 and 75% inhibition on lipid peroxidation of linoleic acid emulsion,respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These various antioxidant activities were compared with model antioxidants such as a-tocopherol, butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT).
Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:376-389.
Synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship studies of hederacolchiside E and its derivatives as potential anti-Alzheimer agents.[Pubmed:
29202401 ]
Inspired by the previously reported neuroprotective activity of Hederacolchiside E (1), we synthesized Hederacolchiside E for the first time along with eleven of its derivatives.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The neuroprotective effects of these compounds were further evaluated against H2O2- and Aβ1-42-induced injury using cell-based assays. The derivatives showed obvious differences in activity due to structural variations, and two of them exhibited better neuroprotective effects than 1 in the Aβ1-42-induced injury model. Compound 7 was the most active derivative and had a relatively simple chemical structure. Moreover, 1 and 7 can significantly reduce the release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and extent of malondialdehyde (MDA) increase resulting from Aβ1-42 treatment, which demonstrated that these kinds of compounds show neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer's disease (AD) models via modulating oxidative stress.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 7 could be used as promising lead for the development of a new type of neuroprotective agent against AD.
Phytomedicine. 2005 Jun;12(6-7):440-4.
Acute anti-inflammatory activity of four saponins isolated from ivy: alpha-hederin, hederasaponin-C, hederacolchiside-E and hederacolchiside-F in carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.[Pubmed:
16008120 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anti-inflammatory potential of alpha-hederin (monodesmoside) and hederasaponin C from Hedera helix, and Hederacolchiside E and hederacolchiside F (bidesmosides) from H. colchica was investigated in carrageenan-induced acute paw edema in rats. Saponins and indomethacin were given orally in concentrations of 0.02 and 20mg/kg body wt. For the first phase of acute inflammation, indomethacin was found as the most potent drug. Alpha-hederin and hederasaponin C were found ineffective, while Hederacolchiside E and hederacolchiside F showed slight anti-inflammatory effects on the first phase. For the second phase of acute inflammation, indomethacin and hederacolchiside F were determined as very potent compounds. alpha-hederin was found ineffective for the second phase, either. Despite hederasaponin C and Hederacolchiside E were found effective in the second phase of inflammation, they were not found as effective as indomethacin and hederacolchiside F.
CONCLUSIONS:
As a conclusion, hederasaponin C, Hederacolchiside E and hederacolchiside F, may exert their anti-inflammatory effects by blocking bradykinin or other inflammation mediators. The latter affect may occur via affecting prostaglandin pathways.
Regarding the structure activity relationship, it is likely that sugars at C3 position and Rha7-Glcl-6Glc moiety at C28 position are essential for the acute anti-inflammatory effect.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Dec 15;48(5):1425-9.
LC-MS/MS method for determination of hederacolchiside E, a neuroactive saponin from Pulsatilla koreana extract in rat plasma for pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:
18947958 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A simple, rapid, and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method was applied to pharmacokinetic study of a neuroactive oleanolic-glycoside saponin, Hederacolchiside E from SK-PC-B70M, a standardized extract of Pulsatilla koreana in rat. Rat plasma samples were pretreated by protein precipitation with acetonitrile, eluted from C(18) column, and analyzed using electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS/MS in negative ion mode. Digoxin was used as an internal standard. The standard curves were linear (r>0.997) over the concentration ranges of 2-500 ng/mL. The intra- and inter-day precisions were measured to be below 9% and accuracy between 90 and 111% for all quality control samples at 2, 20, 100, and 500 ng/mL (n=5). The lower limits of quantification (LLOQ) for Hederacolchiside E was 2 ng/mL and the limit of detection (LOD) 0.5 ng/mL using 20 microL of plasma sample. Subsequently, Hederacolchiside E was determined in rat plasma samples after oral administration of SK-PC-B70M. The mean maximum plasma concentrations of Hederacolchiside E were 0.07, 0.13, and 0.36 microg/mL and the mean areas under the plasma concentration versus time curve 0.56, 1.27, and 6.46 microg h/mL at doses of 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg, respectively, which indicated non-linear pharmacokinetic pattern.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, this method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of Hederacolchiside E after an oral administration of SK-PC-B70M to rats.