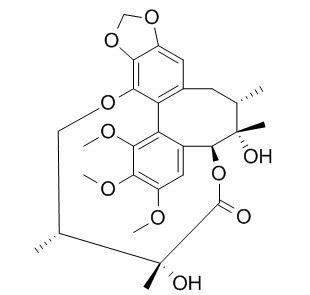
Gomisin D
Gomisin D is a natural product from Schizandra chinensis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 251:116444.
J of Health Science and Alternative Medicine2019, 1(1)
Molecules.2023, 28(5):2376.
Food Bioscience2023, 52:102412
Biomedicines.2020, 8(11):486.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(2): E119
Life (Basel).2022, 12(10):1630.
Phytomedicine.2023, 116:154841.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(23):E6071
Saudi Pharm J.2019, 27(1):145-153
Related and Featured Products
Planta Med. 2010 Oct;76(15):1672-7.
Evaluation of cytotoxic activity of Schisandra chinensis lignans.[Pubmed:
20458670]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using exhaustive chromatographic separation we have isolated (-)-tigloyl-deangeloyl-gomisin F as a novel dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan from schisandra chinensis. With the help of HPLC, we further isolated (+)-schisandrin, (+)-deoxyschisandrin, (+)-γ-schisandrin, (-)-gomisin J, (+)-gomisin A, (-)-gomisin N, (-)-tigloyl-gomisin P, (-)-wuweizisu C, (-)-Gomisin D, rubrisandrin A, (-)-gomisin G, (+)-gomisin K (3) and (-)-schisantherin C. A full NMR description of (-)-schisantherin C was carried out with the aim to confirm previous reports of its structure. Compounds isolated were identified on the basis of UV, IR, (1)H- and (13)C-NMR and MS. The cytotoxicity of lignans was tested for the BY-2 cell line alone and as a synergistic effect with the cytotoxic agent camptothecin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Lignans showed various toxicity and synergistic and antagonistic effects on camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity. Cytotoxicity against colon cancer cell line LoVo was also tested.
Phytother Res. 2015 Oct;29(10):1658-64.
Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) Activity by constituents of Schisandra chinensis.[Pubmed:
26084208]
Structure-activity relationship for the inhibition of Schisandra chinensis's ingredients toward (Uridine-Diphosphate) UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) activity was performed in the present study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vitro incubation system was employed to screen the inhibition capability of S. chinensis's ingredients, and in silico molecular docking method was carried out to explain possible mechanisms. At 100 μM of compounds, the activity of UGTs was inhibited by less than 90% by schisandrol A, schisandrol B, schisandrin, schisandrin C, schisantherin A, Gomisin D, and gomisin G. Schisandrin A exerted strong inhibition toward UGT1A1 and UGT1A3, with the residual activity to be 7.9% and 0% of control activity. Schisanhenol exhibited strong inhibition toward UGT2B7, with the residual activity to be 7.9% of control activity. Gomisin J of 100 μM inhibited 91.8% and 93.1% of activity of UGT1A1 and UGT1A9, respectively. Molecular docking prediction indicated different hydrogen bonds interaction resulted in the different inhibition potential induced by subtle structure alteration among schisandrin A, schisandrin, and schisandrin C toward UGT1A1 and UGT1A3: schisandrin A > schisandrin > schisandrin C. The detailed inhibition kinetic evaluation showed the strong inhibition of gomisin J toward UGT1A9 with the inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) to be 0.7 μM. Based on the concentrations of gomisin J in the plasma of the rats given with S. chinensis, high herb-drug interaction existed between S. chinensis and drugs mainly undergoing UGT1A9-mediated metabolism.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, in silico-in vitro method was used to give the inhibition information and possible inhibition mechanism for S. chinensis's components toward UGTs, which guide the clinical application of S. chinensis.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;39(15):2900-6.
Influlance of different drying methods on quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus[Pubmed:
25423829]
To study the influence of different drying methods on the quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus and thus provide useful reference for its proper drying methods.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus was processed by eight drying methods including vacuum freeze drying, natural drying in the shade, drying in the sun, oven drying and vacuum drying under different temperature. The contents of the functional ingredients includes chisandrin, Gomisin D, gomisin J, schisandrol B, angeloylgomisin H, angeloylgomisin Q, gomisin G, schisantherin A, deoxyschisandrin, schisandrin B, schisandrin C, 5-HMF, total aids and total sugars. The main components change after drying were analyzed by HPLC, ultraviolet spectrophotometry and potentiometric titration. Principal component analysis (PCA) was carried out by SPSS software to evaluate the quality of different processed products from Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus.
All these results are in accordance with the requirements of Chinese Pharmacopoeia published in 2010, the contents of schisandrin and total eleven lignans were the highest using vacuum drying, and 5-HMF were the lower, oven drying made little difference but with lower schisandrin and higher 5-HMF as the heat increased.
CONCLUSIONS:
Different drying methods have significant influence on the quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus. Oven drying under 5°C should be adopted to substitute drying in the sun according to the China Pharmacopoeia published in 2010 for Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus by comprehensive analysis of the cost, content and practicality.