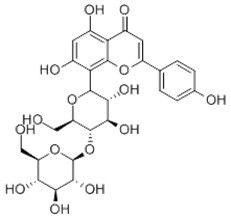
Glucosylvitexin
Glucosylvitexin can inhibit thyroid peroxidase (TPO) activity, thus it can produce goitrogenic and antithyroid effects similar to those of certain other antithyroid agents and small doses of methimazole (MMI).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Cells.2024, 13(14):1229.
LWT2021, 147:111620.
Rec. Nat. Prod.2024, 18:4,405-418.
Separations2021, 8(6),80.
Molecules2022, 27(3),1140.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2021, 29(1):45-50.
Phytother Res.2018, 32(5):923-932
LWT2024, 200:116184.
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine2015, 36(4):486-497
Nutrients.2018, 10(7)
Related and Featured Products
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Apr;68(4):707-14.
Antithyroid and goitrogenic effects of millet: role of C-glycosylflavones.[Pubmed:
2921306]
Pearl millet [Pennisetum millet (L.) leeke] is the main source of food energy for the rural poor in many areas of the semiarid tropics. Epidemiological evidence suggests that millet may play a role in the genesis of endemic goiter in these areas, and sparse experimental data in rats support this suspicion.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study was undertaken to determine in vivo in rats and in vitro using porcine thyroid slices and a thyroid peroxidase (TPO) assay the goitrogenic and antithyroid effects of millet diets, extracts of millet, and certain pure compounds contained therein. For use in these studies, whole grain millet was progressively dehulled to yield successively four bran and four flour fractions in which direct analyses revealed progressively lower concentrations of C-glycosylflavones. In vivo feeding of bran fraction 1, that richest in C-glycosylflavones, led to a significant increase in thyroid weight and antithyroid effects. Feeding of bran fraction 2, the next richest in C-glycosylflavones, produced similar, but less marked, changes. In vitro studies of 125I metabolism using porcine thyroid slices indicated that extracts of bran fractions 1 and 2 were most potent, producing changes similar to those produced by methimazole (MMI). At a concentration of 60 mumol/L, Glucosylvitexin, the major C-glycosylflavone present in millet, had effects comparable to those of 1 mumol/L MMI. Similarly, in studies of porcine TPO, extracts of bran fraction 1 caused pronounced (85%) inhibition of enzyme activity, and progressively less inhibition was induced by extracts of bran fractions 2, 3, and 4. Overall, the TPO-inhibiting activities of the various millet fractions closely correlated with their C-glycosylflavone concentrations. Three C-glycosylflavones present concentrations. Three C-glycosylflavones present in millet, Glucosylvitexin, glycosylorientin, and vitexin, also inhibited TPO activity. Thus, in vivo and in vitro studies revealed that millet diets rich in C-glycosylflavones produce goitrogenic and antithyroid effects similar to those of certain other antithyroid agents and small doses of MMI.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that in areas of iodine deficiency in which millet is a major component of the diet, its ingestion may contribute to the genesis of endemic goiter.
(3E,5E,11E)-tridecatriene-7,9-diyne-1,2-diacetate
Catalog No: CFN95191
CAS No: 94753-06-7
Price: $318/5mg
[(1(10)E,2R,4R)]-2-Methoxy-8,12-epoxygemacra-1(10),7,11-trien-6-one
Catalog No: CFN95198
CAS No: 75412-95-2
Price: $318/10mg
Isovalerylshikonin
Catalog No: CFN95222
CAS No: 52387-14-1
Price: $318/10mg
Pieceid-2''-O-gallate
Catalog No: CFN95226
CAS No: 105304-51-6
Price: $318/10mg
2-Methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
Catalog No: CFN95269
CAS No: 2348-82-5
Price: $70/20mg
Sibiricose A4
Catalog No: CFN95298
CAS No: 241125-73-5
Price: $318/5mg
4'-O-Methyllucenin II (Diosmetin 6,8-di-C-glucoside)
Catalog No: CFN95344
CAS No: 98813-28-6
Price: $318/10mg
Cuneataside C
Catalog No: CFN95368
CAS No: 871720-16-0
Price: $318/10mg
Hosenkoside L
Catalog No: CFN95520
CAS No: 161016-50-8
Price: $318/10mg
Methyl lucidenate A
Catalog No: CFN95583
CAS No: 105742-79-8
Price: $318/5mg