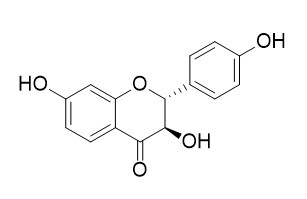
Garbanzol
Garbanzol is a natural product from Cicer arietinum.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Appl Pharm Sci.2022, 12(04):044-053
Anat Rec2018, 24264
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(3):379.
Cell Death Discov.2023, 9(1):350.
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):13610.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 320:117426.
Phytomedicine.2021, 93:153789.
mBio.2020, 11(3):e00686-20.
Int Immunopharmacol.2019, 71:361-371
Molecules.2019, 24(16):E3003
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Res. 2017 Jul;31(13):1573-1577.
Antioxidant capacity and identification of the constituents of ethyl acetate fraction from Rhus verniciflua Stokes by HPLC-MS.[Pubmed:
28100074 ]
Ethyl acetate fraction (EAF) from Rhus verniciflua Stokes is an important source of bioactive compounds. The aim of this study was the tentative identification and quantification of phenolic compounds, comparison of the phenolic structure-antioxidant activity relationships.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Twelve compounds of EAF belonging to polyphenol types were detected by high performance liquid chromatography and analysed on line with negative ion electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry, which were ethoxy 3-hydroxy benzoic acid, gallic acid (GA), 3,4-dihydroxy amygdalic acid, gallic acid cetyl ester, protocatechuic acid (PA), fustin, ethyl gallate (EG), Garbanzol, fisetin, sulfuretin, butin and 3,7-dihydroxyflavanone-4'-rhamnoside. The antioxidant activity were evaluated based on the different types of radical scavenging capacities, i.e. DPPH·, ABTS·+ and OH.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antioxidant capacity of EAF mainly depended on the GA, EG, PA, fisetin, sulfuretin and butin. The phenolics exhibited a dose-dependent behaviour and high antioxidant ability.
Metab Eng. 2015 Sep;31:84-93.
Assembly of a novel biosynthetic pathway for production of the plant flavonoid fisetin in Escherichia coli.[Pubmed:
26192693 ]
Plant secondary metabolites are an underutilized pool of bioactive molecules for applications in the food, pharma and nutritional industries. One such molecule is fisetin, which is present in many fruits and vegetables and has several potential health benefits, including anti-cancer, anti-viral and anti-aging activity. Moreover, fisetin has recently been shown to prevent Alzheimer's disease in mice and to prevent complications associated with diabetes type I. Thus far the biosynthetic pathway of fisetin in plants remains elusive.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we present the heterologous assembly of a novel fisetin pathway in Escherichia coli. We propose a novel biosynthetic pathway from the amino acid, tyrosine, utilizing nine heterologous enzymes. The pathway proceeds via the synthesis of two flavanones never produced in microorganisms before--Garbanzol and resokaempferol.
CONCLUSIONS:
We show for the first time a functional biosynthetic pathway and establish E. coli as a microbial platform strain for the production of fisetin and related flavonols.
Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(12):1177-9.
Radical scavenging activities of flavonoids from roots of Akschindlium godefroyanum.[Pubmed:
25426867 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chemical constituents of crude ethyl acetate extract of roots of Akschindlium godefroyanum (Kuntze) H. Ohashi were investigated and seven flavonoids were isolated. Their structures were identified based on spectroscopic methods as well as by comparison with spectral data reported in the literature as six flavanonols and a flavonol including 7,4'-dihydroxy-5,3'-dimethoxyflavanonol (1), neophellamuretin (2), taxifolin (3), erycibenin D (4), geraldol (5), fustin (6) and Garbanzol (7). Compounds 2, 4 and 7 were found in the genus Akschindlium for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 3, 5 and 6 appeared to have free radical scavenging activities using DPPH assay with IC50 of 21, 40 and 15 μg/mL, respectively.