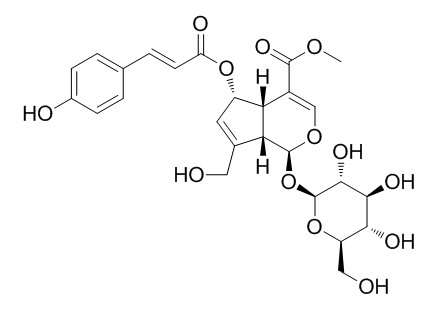
(E)-6-O-(p-coumaroyl)scandoside methyl ester
(E)-6-O-(p-coumaroyl)scandoside methyl ester shows moderate anti-proliferation effect on PC3 human androgen-independent prostate cancer cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Oncol Rep.2016, 35(3):1356-64
Pharmaceutics2022, 14(2),376.
Int J Biol Macromol.2020, 169:342-351
Planta Med.2018, 84(15):1101-1109
Molecules. 2013, 18(7):7376-88
Arch Biochem Biophys.2020, 687:108384.
J Chromatogr A.2022, 1685:463640.
Anal Bioanal Chem.2023, 415(9):1641-1655.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(1):538.
J Adv Res.2021, 35:245-257.
Related and Featured Products
Food Chemistry, 2010, 119(3):1239-1245.
Authentication of the anti-tumor herb Baihuasheshecao with bioactive marker compounds and molecular sequences.[Reference:
WebLink]
Baihuasheshecao (Hedyotis diffusa), a Chinese herb for cancer treatment, is frequently adulterated by a related species Hedyotis corymbosa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
DNA sequencing of the complete internal transcribed spacer region was applied to differentiate H. diffusa from H. corymbosa and other closely related species. The molecular data showed that four out of seven herb samples of Baihuasheshecao were adulterants. Chemical analyses by TLC and HPLC were used to authenticate H. diffusa and H. corymbosa. Two marker compounds were identified exclusively in H. diffusa: 6-O-(E)-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester ((E)-6-O-(p-coumaroyl)scandoside methyl ester
, compound 1) and 10(S)-hydroxypheophytin a (compound 2). Both compounds showed moderate anti-proliferation effect on PC3 human androgen-independent prostate cancer cells, while compound 2 also showed strong anti-proliferation effect on LNCaP human androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Accordingly, these bioactive marker compounds could be applied to verify the authenticity and assess the quality of Baihuasheshecao.
Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul; 19(7): 2027.
Asperuloside and Asperulosidic Acid Exert an Anti-Inflammatory Effect via Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages.[Pubmed:
30002289]
Hedyotis diffusa is a folk herb that is used for treating inflammation-related diseases in Asia. Previous studies have found that iridoids in H. diffusa play an important role in its anti-inflammatory activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect and potential mechanism of five iridoids (asperuloside (ASP), asperulosidic acid (ASPA), desacetyl asperulosidic acid (DAA), scandoside methyl ester (SME), and (E)-6-O-(p-coumaroyl)scandoside methyl ester (CSME)) that are presented in H. diffusa using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)—induced RAW 264.7 cells. ASP and ASPA significantly decreased the production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in parallel with the inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), TNF-α, and IL-6 mRNA expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. ASP treatment suppressed the phosphorylation of the inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappaB alpha (IκB-α), p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The inhibitory effect of ASPA was similar to that of ASP, except for p38 phosphorylation.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, the anti-inflammatory effects of ASP and ASPA are related to the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and mediators via suppression of the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, which provides scientific evidence for the potential application of H. diffusa.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006 Feb 2;831(1-2):303-6.
Estimation of p-coumaric acid as metabolite of E-6-O-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester in rat plasma by HPLC and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:
16388996 ]
CONCLUSIONS:
A rapid and simple high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method has been developed for the determination of p-coumaric acid in rat plasma and applied to a pharmacokinetic study in rats after administration of a prodrug, (E)-6-O-(p-coumaroyl)scandoside methyl ester, isolated from Hedyotis diffusa (Willd.). Sample preparation involved protein precipitation with acetonitrile. The supernatant was then injected onto a Diamonsil C(18) column (250 mm x 4.6mm i.d., 5 microm). The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile-water (21:79, v/v) with 1% glacial acetic acid. The UV detector was set at 310 nm. The lower limit of quantification of p-coumaric acid in rat plasma was 0.02 microg/mL. The calibration curves were linear over the concentration range 0.02-5 microg/mL with correlations greater than 0.999.
CONCLUSIONS:
The assay procedure was applied to the study of the metabolite pharmacokinetics of E-6-O-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester in rat.
Gancaonin N
Catalog No: CFN95066
CAS No: 129145-52-4
Price: $463/5mg
Patulitrin
Catalog No: CFN95153
CAS No: 19833-25-1
Price: $318/10mg
19-O-beta-D-carboxyglucopyranosyl-12-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-11,16-dihydroxyabieta-8,11,13-triene
Catalog No: CFN95217
CAS No: 1011714-20-7
Price: $318/5mg
Gypenoside XIII
Catalog No: CFN95239
CAS No: 80325-22-0
Price: $288/10mg
3'-Hydroxy-5,7,4',5'-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN95397
CAS No: 29976-51-0
Price: $318/5mg
Tumulosic acid
Catalog No: CFN95399
CAS No: 508-24-7
Price: $368/5mg
Quercetin 3,7-diglucoside
Catalog No: CFN95408
CAS No: 6892-74-6
Price: $318/10mg
12beta-Acetoxy-7beta-hydroxy-3,11,15,23-tetraoxo-5alpha-lanosta-8,20-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No: CFN95515
CAS No: 1245946-62-6
Price: $318/5mg
Nomilinic acid
Catalog No: CFN95559
CAS No: 35930-20-2
Price: $318/5mg
Iristectorin A-6''-O-glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95597
CAS No: 86849-71-0
Price: $413/5mg