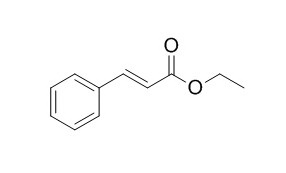
Ethyl cinnamate
Ethyl cinnamate has antifungal, and vasorelaxant effects, it can inhibit the tonic contractions induced by high K+ and phenylephrine (PE) in a concentration-dependent manner, with respective IC50 values of 0.30 +/- 0.05 mM and 0.38 +/- 0.04 mM. Ethyl cinnamate can lead to the damage of cell membrane system and metabolic disorder through inducing lipid peroxidation via initiating ROS overproduction.Ethyl cinnamate has acute inhibition to the maximum quantum yield and the potential activity of photosystem II of Chlorella pyrenoidosa.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Anal Methods Chem.2024, 2024:7703951.
J Microbiol Biotechnol.2020, 30(2):178-186.
Plant Sci.2020, 301:110656.
J Cell Mol Med . 2023, jcmm.17954.
LWT-Food Science and Technology2017, 75:488-496
Aquaculture2019, 510:392-399
Acta Chromatographica2016, 29(3)
Protoplasma.2024, 261(6):1267-1280.
Journal of Apicultural Research2021, 60(1).
Food Chem.2024, 460(Pt 1):140472.
Related and Featured Products
ScientificWorldJournal. 2015;2015:107823.
Toxic Effects of Ethyl Cinnamate on the Photosynthesis and Physiological Characteristics of Chlorella vulgaris Based on Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Flow Cytometry Analysis.[Pubmed:
26101784]
The toxic effects of Ethyl cinnamate on the photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Chlorella vulgaris were studied based on chlorophyll fluorescence and flow cytometry analysis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Parameters, including biomass, F(v)/F(m) (maximal photochemical efficiency of PSII), Ф(PSII) (actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light), FDA, and PI staining fluorescence, were measured.
The results showed the following: (1) The inhibition on biomass increased as the exposure concentration increased. 1 mg/L Ethyl cinnamate was sufficient to reduce the total biomass of C. vulgaris. The 48-h and 72-h EC50 values were 2.07 mg/L (1.94-2.20) and 1.89 mg/L (1.82-1.97). (2) After 24 h of exposure to 2-4 mg/L Ethyl cinnamate, the photosynthesis of C. vulgaris almost ceased, manifesting in Ф(PSII) being close to zero. After 72 h of exposure to 4 mg/L Ethyl cinnamate, the Fv /Fm of C. vulgaris dropped to zero. (3) Ethyl cinnamate also affected the cellular physiology of C. vulgaris, but these effects resulted in the inhibition of cell yield rather than cell death.
CONCLUSIONS:
Exposure to Ethyl cinnamate resulted in decreased esterase activities in C. vulgaris, increased average cell size, and altered intensities of chlorophyll a fluorescence. Overall, esterase activity was the most sensitive variable.
Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2013 Jan;34(1):156-62.
Effects of allelochemicals ethyl cinnamate on the growth and physiological characteristics of Chlorella pyrenoidosa.[Pubmed:
23487932]
The effects of Ethyl cinnamate on the growth and physiological characteristics of Chlorella pyrenoidosa were studied.
The allelopathic mechanisms were explored, from views of chlorophyll a content, antioxidant enzyme activities, reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, malondialdehyde (MDA) content and photosynthetic activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results revealed that Ethyl cinnamate had acute inhibitory effects on the growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa, and the inhibited degree tended to increase with increased concentrations. The effective concentration causing a 50% inhibition at 96 h was 5.45 mg c L(-1). Ethyl cinnamate induced the decrease of chlorophyll a, the over-accumulation of ROS and the increase of MDA. Therefore, it suggested that Ethyl cinnamate could lead to the damage of cell membrane system and metabolic disorder through inducing lipid peroxidation via initiating ROS overproduction. And for scavenging ROS, the algae cells were protected from oxidative damages through increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrated Ethyl cinnamate had acute inhibition to the maximum quantum yield and the potential activity of photosystem II of Chlorella pyrenoidosa, however, the photosynthetic activity could recover to some extent through self-regulation after some time.
Fitoterapia. 2000 Sep;71(5):567-9.
Antifungal properties of Ocimum gratissimum essential oil (ethyl cinnamate chemotype).[Pubmed:
11449510]
Largely widespread in tropical countries, Ocimum gratissimum has been claimed for many uses in folk medicine. Recent research on its essential oils showed five chemotypes.
CONCLUSIONS:
An Indian chemotype, with a high level of Ethyl cinnamate, presents, in vitro, an interesting spectrum of antifungal properties.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45 Suppl 1:S90-4.
Fragrance material review on ethyl cinnamate.[Pubmed:
18037216]
A toxicologic and dermatologic review of Ethyl cinnamate when used as a fragrance ingredient is presented.
Planta Med. 2002 Jul;68(7):655-7.
Vasorelaxant effects of ethyl cinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga on smooth muscles of the rat aorta.[Pubmed:
12143006]
From the rhizomes of Kaempferia galanga, Ethyl cinnamate (EC) was isolated and its vasorelaxant effect was examined on the rat aorta.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
EC inhibited the tonic contractions induced by high K+ and phenylephrine (PE) in a concentration-dependent manner, with respective IC50 values of 0.30 +/- 0.05 mM and 0.38 +/- 0.04 mM.
The relaxant effect against PE-induced contractions was greater in the presence of endothelium. Pre-treatment of the aorta with methylene blue and indomethacin significantly reduced the relaxant effect. These results suggest that the inhibitory effects of EC may involve inhibition of Ca2+ influx into vascular cells and release of nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin from the endothelial cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, the vasorelaxant effect of EC mediated through multiple pathways may explain the traditional use of the parent plant in treating hypertension.