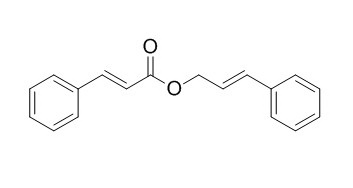
Cinnamyl cinnamate
Cinnamyl cinnamate is used as a fragrance ingredient.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Hum Exp Toxicol.2023, 42:9603271231171642.
Academic J of Second Military Medical University2018, 39(11)
J. of The Korean Society of Food Culture2017, 144-149
Nutrients.2019, 11(11):E2694
Mol Pharmacol.2021, 99(2):163-174.
Nutr Metab (Lond).2019, 16:31
Cell Rep.2022, 39(1):110643.
Medicina (Kaunas).2020, 56(12):685.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2022, 30(2):124-133
Microb Pathog.2019, 131:128-134
Related and Featured Products
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2007;45(1):S66–S69.
Fragrance material review on cinnamyl cinnamate.[Reference:
WebLink]
A toxicologic and dermatologic review of Cinnamyl cinnamate when used as a fragrance ingredient is presented.
Phytomedicine. 2005 Mar;12(3):221-8.
Antibacterial activity of Turkish propolis and its qualitative and quantitative chemical composition.[Pubmed:
15830845]
The antibacterial activity of propolis from different regions of Turkey was studied, accompanied by TLC and GC-MS analyses of its chemical composition and spectrophotometric quantification of the most important active principles.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All six samples were active against the bacterial test strains used; however, samples 1 (Yozgat), 2 (Izmir) and 3 (Kayseri) were more active than samples 4 (Adana), 5 (Erzurum) and 6 (Artvin). By TLC comparison all samples were found to contain poplar taxonomic markers but in samples 4 (Adana), 5 (Erzurum) and 6 (Artvin), different substances were observed, which were not present in P. nigra L. bud exudate. The typical poplar samples 1 (Yozgat), 2 (Izmir) and 3 (Kayseri) displayed very similar phenolic and flavonoid content. Samples 4 (Adana), 5 (Erzurum) and 6 (Artvin) were characterized by low phenolic and very low flavonoid concentrations. Qualitative analysis by GC-MS revealed that sample 4 (Adana) contained diterpenic acids and high percent of Cinnamyl cinnamate, sample 5 (Erzurum)-significant amounts of hydroxy fatty acids and triterpenic alcohoLs, and sample 6 (Artvin)-phenolic glycerides, characteristic for the bud exudate of Populus euphratica Oliv.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results confirm the importance of phenolics for propolis antibacterial activity, and the significance of P. nigra L. as a propolis source, which provides the hive with the best defense against microorganisms.