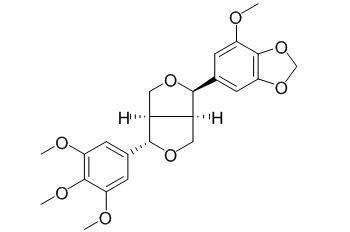
Episesartemin A
Episesartemin A is a natural product from Artemisia absinthium.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2024, 29(6):1392.
Plants (Basel).2023, 12(5):1120.
Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation2024, 024-00662-1.
Pharmacol Rep.2022, 74(1):175-188.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(6):3390.
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 145:112474.
Green Chemistry2021, ISSUE 2.
Food and Chemical Toxicology2020, 111221
BMC Plant Biol.2018, 18(1):122
Foods.2023, 12(19):3647.
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry. 2017 Mar;135:181-190.
Sensory active piperine analogues from Macropiper excelsum and their effects on intestinal nutrient uptake in Caco-2 cells.[Pubmed:
28065397]
The phytochemical profile of Macropiper excelsum (G.Forst.) Miq. subsp. excelsum (Piperaceae), a shrub which is widespread in New Zealand, was investigated by LC-MS-guided isolation and characterization via HR-ESI-TOF-MS and NMR spectroscopy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The isolated compounds were sensorily evaluated to identify their contribution to the overall taste of the crude extract with sweet, bitter, herbal and trigeminal impressions. Besides the known non-volatile Macropiper compounds, the lignans (+)-diayangambin and (+)-excelsin, four further excelsin isomers, (+)-diasesartemin, (+)-sesartemin, (+)-Episesartemin A and episesartemin B were newly characterized. Moreover, piperine and a number of piperine analogues as well as trans-pellitorine and two homologues, kalecide and (2E,4E)-tetradecadienoic acid N-isobutyl amide were identified in M. excelsum, some of them for the first time.
Tetrahedron, 1980, 36(24):3551-3558.
New unsymmetrically substituted tetrahydrofurofuran lignans from artemisia absinthium: Assignment of the relative stereochemistry by lanthanide induced chemical shifts.[Reference:
WebLink]
The isolation of thirteen tetrahydrofurofuran lignans from the roots of A. absinthium and six closely related species is reported.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new group of four lignans, all stereoisomers of 1- [(3,4-methylenedioxy-5-methoxy) phenyl]-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-tetrahydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan, was found. The compounds, named sesartemin, Episesartemin A, episesartemin B, and diasesartemin, were characterized by 1H NMR (including lanthanide induced shifts), UV, IR and MS.
CONCLUSIONS:
A fifth new lignan of the sesamin type (the eq/eq isomer of fargesin) could be identified as a minor constituent.
The relative configurations of two further products (fargesin and epiashantin) could be confirmed by the lanthanide induced shift technique.