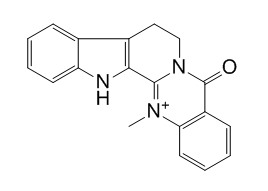
Dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride
Dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride has novel anti-cholinesterase and antiamnesic activities, it inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity in a dose-dependent and non-competitive manner(IC50=37.8 microM); its potent antiamnesic effect is thought to be due to the combined effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibition and the known cerebral blood flow enhancement. Dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride (0.1-0.3 mg/kg iv) can increase the cerebral blood flow recorded from the surface of the supra-sylvian gyrus in anesthetized cats, suggest that it selectively increases cerebral blood flow.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
National Natural Science Foundation of China2024, pages 33.
Nutrients.2017, 10(1)
J Biotechnol.2020, 318:10-19.
Bulletin of Health Research2016, 44(4):279-286
Drug Dev Ind Pharm.2024, 50(11):938-951.
Foods.2021, 10(11):2754.
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):117.
Molecules.2021, 26(3):695.
Redox Rep.2024, 29(1):2392329.
J Herbmed Pharmacol.2018, 7(4):280-286
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 1994 Mar;57(3):387-9.
Increased feline cerebral blood flow induced by dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride from Evodia rutaecarpa.[Pubmed:
8201313]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride (0.1-0.3 mg/kg iv), which was isolated from the leaves of Evodia rutaecarpa, increased the cerebral blood flow recorded from the surface of the supra-sylvian gyrus in anesthetized cats. This action reached a maximum 1-4 min after injection and continued for 10 min. However, the compound had negligible effects on other cardiorespiratory functions at the doses examined.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the compound selectively increases cerebral blood flow.
Planta Med. 1996 Oct;62(5):405-9.
Novel anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities of dehydroevodiamine, a constituent of Evodia rutaecarpa.[Pubmed:
8923803 ]
To find a new compound with antiamnesic activity, we screened 29 natural products for their abilities to inhibit acetylcholinesterase and reverse scopolamine-induced amnesia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among the plants tested Evodia rutaecarpa Bentham showed a strong inhibitory effect on acetylcholinesterase in vitro and an anti-amnesic effect in vivo. By sequential fractionation of E. rutaecarpa, the active component was finally identified as Dehydroevodiamine hydrochloride (DHED). DHED inhibited acetylcholinesterase activity in a dose-dependent and non-competitive manner. The IC50 value of DHED is 37.8 microM. A single administration of DHED to rats (6.25 mg/kg) significantly reversed the scopolamine-induced memory impairment in a passive avoidance test. The antiamnesic effect of DHED was more potent than that of tacrine which is the only drug for Alzheimer's disease approved by FDA. This potent antiamnesic effect of DHED was thought to be due to the combined effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibition and the known cerebral blood flow enhancement.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that DHED has novel anti-cholinesterase and antiamnesic activities and might have therapeutic potential in various disorders including Alzheimer's disease.