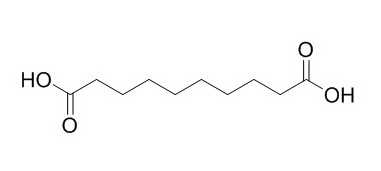
Decanedioic acid
Decanedioic acid is a saturated, straight-chain naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid, it exhibits significantly higher anti-HIV activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Institute of Food Science & Technology2021, 18 December.
Oncol Lett.2020, 20(4):122.
Foods.2021, 10(12):2929.
J Ginseng Res.2022, 46(1):104-114.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(4):462.
Molecules.2020, 25(21):5091.
Int. J. of Pha. and Phy. Res.2015, 7(1):144-149
Molecules.2020, 25(7):1625.
J.Food Processing & Preservation2022, jfpp.16666
Food Chem.2019, 274:345-350
Related and Featured Products
Tetrahedron Lett. 2014 Mar 19;55(12):1983-1986.
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 5'-O-Dicarboxylic Fatty Acyl Monoester Derivatives of Anti-HIV Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.[Pubmed:
24791029]
A number of 5'-O-dicarboxylic fatty acyl monoester derivatives of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (zidovudine, AZT), 2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (stavudine, d4T), and 3'-fluoro-3'-deoxythymidine (alovudine, FLT) were synthesized to improve the lipophilicity and potentially the cellular delivery of parent polar 2', 3'-dideoxynucleoside (ddN) analogues.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were evaluated for their anti-HIV activity. Three different fatty acids with varying chain length of suberic acid (octanedioic acid), sebacic acid (Decanedioic acid), and doDecanedioic acid were used for the conjugation with the nucleosides. The compounds were evaluated for anti-HIV activity and cytotoxicity. All dicarboxylic ester conjugates of nucleosides exhibited significantly higher anti-HIV activity than that of the corresponding parent nucleoside analogs.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among all the tested conjugates, 5'-O-suberate derivative of AZT (EC50 = 0.10 nM) was found to be the most potent compound and showed 80-fold higher anti-HIV activity than AZT without any significant toxicity (TC50 > 500 nM).
AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Feb;15(1):111-20.
Identification of unknown impurity of azelaic acid in liposomal formulation assessed by HPLC-ELSD, GC-FID, and GC-MS.[Pubmed:
24166667]
The identification of new contaminants is critical in the development of new medicinal products. Many impurities, such as pentanedioic acid, hexanedioic acid, heptanedioic acid, octanedioic acid, Decanedioic acid, unDecanedioic acid, doDecanedioic acid, triDecanedioic acid, and tetraDecanedioic acid, have been identified in samples of azelaic acid.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of this study was to identify impurities observed during the stability tests of a new liposomal dosage form of azelaic acid that is composed of phosphatidylcholine and a mixture of ethyl alcohol and water, using high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light-scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD), gas chromatography-flame ionisation detection (GC-FID), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) methods. During the research and development of a new liposomal formulation of azelaic acid, we developed a method for determining the contamination of azelaic acid using HPLC-ELSD. During our analytical tests, we identified a previously unknown impurity of a liposomal preparation of azelaic acid that appeared in the liposomal formulation of azelaic acid during preliminary stability studies. The procedure led to the conclusion that the impurity was caused by the reaction of azelaic acid with one of the excipients that was applied in the product. The impurity was finally identified as an ethyl monoester of azelaic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
The identification procedure of this compound was carried out in a series of experiments comparing the chromatograms that were obtained via the following chromatographic methods: HPLC-ELSD, GC-FID, and GC-MS. The final identification of the compound was carried out by GC with MS.