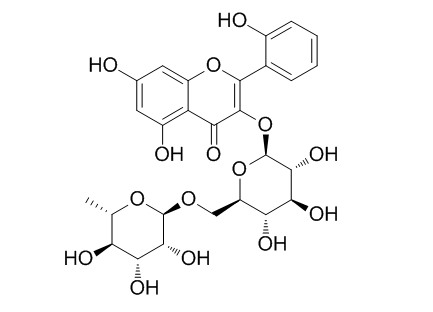
Datiscin
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(8):951.
Chinese J of Tissue Engineering Res.2022, 26(17): 2636-2641.
Food Funct.2022, 13(14):7638-7649.
Biotechnol Bioeng.2020, 117(7):2198-2208.
Talanta.2022, 249:123645.
Molecules.2023, 28(9):3685.
BMC Microbiol.2019, 19(1):78
Horticulturae2023, 9(2), 213.
Nutrients.2020, 12(12):3607.
Elife.2021, 10:e68058.
Related and Featured Products
Planta,2010,231:507–521.
Two novel disaccharides, rutinose and methylrutinose, are involved in carbon metabolism in Datisca glomerata.[Reference:
WebLink]
Datisca glomerata forms nitrogen-fixing root nodules in symbiosis with soil actinomycetes from the genus Frankia. Analysis of sugars in roots, nodules and leaves of D. glomerata revealed the presence of two novel compounds that were identified as α-L-rhamnopyranoside-(1 → 6)-D-glucose (rutinose) and α-L-rhamnopyranoside-(1 → 6)-1-O-β-D-methylglucose (methylrutinose). Rutinose has been found previously as a/the glycoside part of several flavonoid glycosides, e.g. rutin, also of Datiscin, the main flavonoid of Datisca cannabina, but had not been reported as free sugar.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Time course analyses suggest that both rutinose and methylrutinose might play a role in transient carbon storage in sink organs and, to a lesser extent, in source leaves. Their concentrations show that they can accumulate in the vacuole. Rutinose, but not methylrutinose, was accepted as a substrate by the tonoplast disaccharide transporter SUT4 from Arabidopsis.
CONCLUSIONS:
In vivo 14C-labeling and the study of uptake of exogenous sucrose and rutinose from the leaf apoplast showed that neither rutinose nor methylrutinose appreciably participate in phloem translocation of carbon from source to sink organs, despite rutinose being found in the apoplast at significant levels. A model for sugar metabolism in D. glomerata is presented.