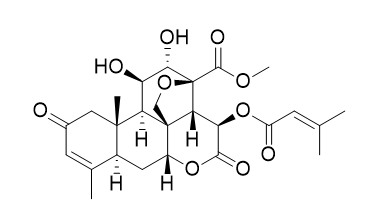
Brusatol
Brusatol, a Nrf2 inhibitor, has dual anti-hepatitis C virus and anticancer effects and can enhance the comparable effects of sorafenib. Brusatol-mediated inhibition of c-Myc/ROS signaling pathway increases HIF-1α degradation by promoting PHD activity and induces cell death in colorectal cancer under hypoxia. It inhibits the response of cultured beta-cells to pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro. Brusatol also shows antitrypanosomal activity against trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma evansi.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Arch Biochem Biophys.2024, 759:110111.
Phytomedicine.2018, 47:48-57
J Sep Sci.2020, 201901140
J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea2016, 163-171
Hum Exp Toxicol.2023, 42:9603271221145386.
Biochem Pharmacol.2023, 211:115502.
Exp Parasitol.2018, 194:67-78
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):13072.
Neurochem Int.2018, 121:114-124
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(22), 10552
Related and Featured Products
BMC Cancer. 2018 Jun 25;18(1):680.
Dual effects of the Nrf2 inhibitor for inhibition of hepatitis C virus and hepatic cancer cells.[Pubmed:
29940898 ]
We previously showed that knockdown of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) resulted in suppression of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. In this study, whether Brusatol, an Nrf2 inhibitor, has dual anti-HCV and anticancer effects was explored.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anti-HCV effect of Brusatol was investigated by analyzing HCV RNA and proteins in a hepatic cell line persistently-infected with HCV, HPI cells, and by analyzing HCV replication in a replicon-replicating hepatic cell line, OR6 cells. Then, dual anti-HCV and anticancer effects of Brusatol and enhancement of the effects by the combination of Brusatol with anticancer drugs including sorafenib, which has been reported to have the dual effects, were then investigated.
Brusatol suppressed the persistent HCV infection at both the RNA and protein levels in association with a reduction in Nrf2 protein in the HPI cells. Analysis of the OR6 cells treated with Brusatol indicated that Brusatol inhibited HCV persistence by inhibiting HCV replication. Combination of Brusatol with an anticancer drug not only enhanced the anticancer effect but also, in the case of the combination with sorafenib, strongly suppressed HCV infection.
CONCLUSIONS:
Brusatol has dual anti-HCV and anticancer effects and can enhance the comparable effects of sorafenib. There is therefore the potential for combination therapy of Brusatol and sorafenib for HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Feb 18;2018:9742154.
UVA Irradiation Enhances Brusatol-Mediated Inhibition of Melanoma Growth by Downregulation of the Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response.[Pubmed:
29670684 ]
Brusatol (BR) is a potent inhibitor of Nrf2, a transcription factor that is highly expressed in cancer tissues and confers chemoresistance. UVA-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS) can damage both normal and cancer cells and may be of potential use in phototherapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to provide an alternative method to treat the aggressive melanoma, we sought to investigate whether low-dose UVA with BR is more effective in eliminating melanoma cells than the respective single treatments. We found that BR combined with UVA led to inhibition of A375 melanoma cell proliferation by cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase and triggers cell apoptosis. Furthermore, inhibition of Nrf2 expression attenuated colony formation and tumor development from A375 cells in heterotopic mouse models. In addition, cotreatment of UVA and BR partially suppressed Nrf2 and its downstream target genes such as HO-1 along with the PI3K/AKT pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
We propose that cotreatment increased ROS-induced cell cycle arrest and cellular apoptosis and inhibits melanoma growth by regulating the AKT-Nrf2 pathway in A375 cells which offers a possible therapeutic intervention strategy for the treatment of human melanoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 May 8;460(3):868-72.
Brusatol inhibits the response of cultured beta-cells to pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro.[Pubmed:
25824046]
Brusatol is a natural terpenoid that is capable of inducing a variety of biological effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We presently report that this substance dramatically improves beta-cell survival when exposed to pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IFNγ) in vitro. This was observed in insulin producing rat (RIN-5AH), mouse (βTC6) and human (EndoC-βH1) beta-cell lines. Brusatol prevented beta-cell oxidative stress in response to cytokines and counteracted induction of iNOS on the protein level. Brusatol, however, block neither the cytokine-induced increase of iNOS mRNA, nor NF-κB activation, suggesting that inhibition of iNOS protein expression relies on posttranscriptional mechanism.
CONCLUSIONS:
This indicates that Brusatol acts via a novel protective pathway, which may represent a more promising way of improving beta-cell function and survival.
Vet Parasitol. 2008 Dec 20;158(4):288-94.
In vitro antitrypanosomal activities of quassinoid compounds from the fruits of a medicinal plant, Brucea javanica.[Pubmed:
18986767 ]
The medicinal plant Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae) is widely distributed throughout Asia where its bitter fruits have been used in traditional medicine for various ailments.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fifteen C-20 quassinoids were isolated from the fruits of B. javanica and examined for their in vitro antitrypanosomal activities against trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma evansi. Bruceine A, bruceantinol, bruceine C, Brusatol, and bruceine B showed strong antitrypanosomal activities with IC(50) values in the range of 2.9-17.8nM, which compared well with the standard trypanocidal drugs diminazene aceturate (IC(50)=8.8nM) and suramin (IC(50)=43.2nM). However, dehydrobruceine A, dehydrobruceine B, and dehydroBrusatol were about 2100, 900, and 1200 times less active, respectively, than bruceine A, bruceine B, and Brusatol.
CONCLUSIONS:
The relationship of the structure and antitrypanosomal activity of these quassinoid compounds suggested that the presence of a diosphenol moiety in ring A and the nature of the C-15 side chain are important for their activities against T. evansi. This is the first report on the antitrypanosomal activity of isolated quassinoids.
J Med Chem. 2014 Sep 25;57(18):7600-12.
Novel nitric oxide-releasing derivatives of brusatol as anti-inflammatory agents: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and nitric oxide release studies.[Pubmed:
25179783 ]
Brusatol, a biologically active natural product, was modified in four distinct positions through the covalent attachment of a furoxan moiety, which acts as a nitric oxide (NO) donor.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Forty derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their inhibitory effects on excess NO biosynthesis in activated macrophages. Among them, compound 75 demonstrated inhibition (IC50 = 0.067 μM) comparable to that of Brusatol but were less cytotoxic. More importantly, even at very low doses (2 μmol/kg/day), compound 75 also showed substantial inhibitory efficacy against chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)-like inflammation in the mouse model induced by cigarette smoke (CS) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Particularly, this compound was over 100-fold less toxic (LD50 > 3852 μmol/kg) than Brusatol and could be a promising lead for further studies. Notably, the improved properties of this derivative are associated with its NO-releasing capability.
Theranostics. 2017 Aug 11;7(14):3415-3431.
Brusatol-Mediated Inhibition of c-Myc Increases HIF-1α Degradation and Causes Cell Death in Colorectal Cancer under Hypoxia.[Pubmed:
28912885 ]
HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor-1) regulates the expression of ~100 genes involved in angiogenesis, metastasis, tumor growth, chemoresistance and radioresistance, underscoring the growing interest in targeting HIF-1 for cancer control.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying Brusatol-induced HIF-1α degradation and cell death in colorectal cancer under hypoxia (0.5% O2). Under hypoxia, pretreatment of cancer cells with Brusatol increased HIF-1α degradation and cancer cell death in a dose-dependent manner. This effect was mediated by activation of prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs), as evidenced by the block of Brusatol-induced HIF-1α degradation and cancer cell death by both pharmacological inhibition and siRNA-mediated knockdown of PHDs. In addition, a ferrous iron chelator (2,2'-bypyridyl) blocked Brusatol-induced degradation of HIF-1α and cancer cell death in hypoxia by inhibiting PHD activation. We further found that Brusatol inhibited c-Myc expression, and showed that overexpression of c-Myc prevented Brusatol-induced degradation of HIF-1α and cancer cell death by increasing mitochondrial ROS production and subsequent ROS-mediated transition of ferrous iron to ferric iron. Consistent with these results, treatment of tumor-bearing mice with Brusatol significantly suppressed tumor growth by promoting PHD-mediated HIF-1α degradation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively, our results suggest that Brusatol-mediated inhibition of c-Myc/ROS signaling pathway increases HIF-1α degradation by promoting PHD activity and induces cell death in colorectal cancer under hypoxia.
Oncotarget. 2017 May 10;8(49):84974-84985.
Exploring brusatol as a new anti-pancreatic cancer adjuvant: biological evaluation and mechanistic studies.[Pubmed:
29156697]
Pancreatic cancer is highly resistant to chemotherapeutic agents and is known to have a poor prognosis. The development of new therapeutic entities is badly needed for this deadly malignancy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we demonstrated for the first time that Brusatol, a natural quassinoid isolated from a Chinese herbal medicine named Bruceae Fructus, possessed potent cytotoxic effect against different pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. Its anti-pancreatic cancer effect was comparable to that of the first-line chemotherapeutic agents such as gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil, with a more favorable safety profile. In addition, Brusatol showed a synergistic anti-proliferative effect toward PANC-1 and Capan-2 cell lines when combined with gemcitabine or 5-fluorouracil. The results of flow cytometry suggested that Brusatol combination treatment with gemcitabine or 5-fluorouracil was able to cause cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase, and accentuate apoptosis in PANC-1 cells. Moreover, Brusatol deactivated gemcitabine/5-fluorouracil-induced NF-κB activation. Western blot analysis and qRT-PCR results showed that Brusatol significantly down-regulated the expression of vimentin and Twist, and markedly stimulated the expression of E-cadherin, the key regulatory factors of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. Furthermore, treatment with combination of Brusatol and gemcitabine or 5-fluorouracil significantly reduced in vivo tumor growth when compared with treatment of either Brusatol or gemcitabine/5-fluorouracil alone.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results have amply demonstrated that Brusatol is a potent anti-pancreatic cancer natural compound, and the synergistic anti-pancreatic cancer effects of Brusatol and gemcitabine/5-fluorouracil observed both in vitro and in vivo are associated with the suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, indicating that Brusatol is a promising adjunct to the current chemotherapeutic regimen.