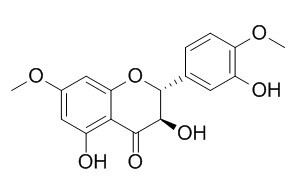
Blumeatin B
Blumeatin shows XO inhibitory activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):21690.
J Nat Med.2021, doi: 10.1007.
Chemistry of Plant Raw Materials2019, 4:135-147
Horticulturae2023, 9(2), 213.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2016, 2016:4357656
Front Aging Neurosci.2019, 11:230
Sci Rep.2017, 7(1):3249
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Journal of Functional Foods2022, 98:105271.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.2024, 108(1):207.
Related and Featured Products
Pharmaceutical Biology,2010,48(12):1405-1412.
Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of extracts and flavonoids of the leaves of Blumea balsamifera.[Reference:
WebLink]
Blumea balsamifera DC (Compositae) leaves have been recommended for use as a folk medicine in the treatment of various diseases related to urolithiasis in southeast Asia. Phytochemical studies of this plant revealed it contains four classes of flavonoids (e.g., flavonols, flavones, flavanones, and dihydroflavonol derivatives). In view of the broad pharmacological activity of flavonoids, this study was carried out to determine the xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory and enzymatically produced superoxide radical scavenging activity of different organic extracts and that of the isolated flavonoids from B. balsamifera leaves.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory activity of XO was assayed spectrophotometrically at 295 nm. The superoxide radicals scavenging activity was assessed by NBT reduction method, spectrophotometrically at 560 nm. A dose response curve was plotted for determining IC50 values.
The methanol extract (IC50 = 0.111 mg/mL) showed higher XO inhibitory activity than the chloroform (0.138 mg/mL) and pet-ether extracts (0.516 mg/mL). IC50 values of scavenging of superoxide radicals for extracts decreased in the order of: methanol (0.063 mg/mL) > chloroform (0.092 mg/mL) > pet-ether (0.321 mg/mL). The XO inhibitory activity of the isolated flavonoids and reference compounds tested decreased in the order of: allopurinol > luteolin > quercetin > tamarixetin > 5,7,3′,5′-tetrahydroxyflavanone > rhamnetin > luteolin-7-methyl ether > blumeatin > dihydroquercetin-4′-methyl ether > dihydroquercetin-7,4′-dimethyl ether > l-ascorbic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that the flavone derivatives were more active than the flavonol derivatives. The flavanone derivatives were moderately active and the dihydroflavonol derivatives were the least. The higher flavonoid content of extracts contributed to their higher XO inhibitory activity.