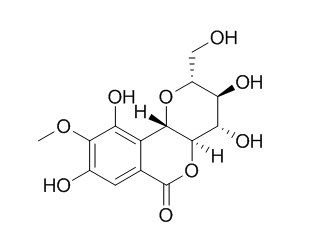
Bergenin
Bergenin is a potent antinarcotic agent, has antiviral ,antifungal, antiarrhythmic, antitumor, antiinflammatory, potent immunomodulatory, antitussive, antiulcerogenic,anti-plasmodial, anti-hepatotoxic and wound healing activities. Bergenin has antidiabetic activity, could be classified as a new group of α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bergenin reduces the expression of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways, and it may represent a novel treatment strategy for mastitis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Sustainability2021, 13(23),12981.
Industrial Crops and Products2022, 188:115638
J Chromatogr A.2024, 1714:464544.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(9):1435.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117395.
J of Health Science and Alternative Medicine2019, 1(1)
Molecules.2023, 28(10):4062.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117410.
J Food Sci Technol.2019, 56(5):2712-2720
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 320:117426.
Related and Featured Products
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1248-54.
Bergenin decreases the morphine-induced physical dependence via antioxidative activity in mice.[Pubmed:
25542428]
Oxidative stress plays a role in the development of physical dependence induced by morphine. Bergenin, a polyphenol found in many Asian, African, and South American medicinal plants, is a potent antinarcotic agent with wide spectrum of pharmacological activities including antioxidant action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we observed that Bergenin decreased the development of physical dependence induced by morphine in mice and the antioxidant activity of Bergenin plays a role in the antinarcotic effects through adapting to morphine-induced oxidative stress in the brain. The naloxone-precipitated withdrawal symptom (jumping frequency) was significantly ameliorated (50% of control group) by administration of Bergenin (20 mg/kg) in morphine-treated mice. Furthermore, morphine-induced down-regulation of glutathione (GSH) contents was reversed by Bergenin administration in the frontal cortex and liver. Bergenin had no effects on the increased levels of nfr2-dependent antioxidant enzyme HO1 and NQO1 in the frontal cortex, striatum, and liver of morphine-treated mice. However, the morphine-induced increase in nrf2 nuclear translocation in the frontal cortex and striatum was inhibited by Bergenin treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Bergenin has a potential antinarcotic effect via regulation of GSH contents and oxidative stress.
Fitoterapia. 2015 Mar;101:133-52.
Diversity, pharmacology and synthesis of bergenin and its derivatives: potential materials for therapeutic usages.[Pubmed:
25596093]
Bergenin, a natural secondary metabolite, has been isolated from different parts of a number of plants. It is one of active ingredients in herbal and Ayurvedic formulations. It exhibits antiviral, antifungal, antitussive, antiplasmodial, antiinflammatory, antihepatotoxic, antiarrhythmic, antitumor, antiulcerogenic, antidiabetic and wound healing properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It has been analyzed and estimated in different plant extracts, blood and drug samples using chromatographic techniques, and pharmacokinetic studies have been made. Several Bergenin derivatives were isolated and/or synthesized and were found to possess pharmacological activities. Total synthesis of Bergenin and its derivatives were reported. This review article covers literature on Bergenin and its derivatives until 2013. Ethnomedicinal value of Bergenin containing plant materials is also highlighted.
CONCLUSIONS:
This comprehensive review provides information on the potentiality of Bergenin and its derivatives for therapeutic usages.
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2013 Dec;28(6):1162-70.
Structure-activity relationships of bergenin derivatives effect on α-glucosidase inhibition.[Pubmed:
23009660 ]
The α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of Bergenin derivatives were evaluated. Bergenin derivatives were synthesized from Bergenin which is a characteristic compound of B. ligulata.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new Bergenin derivative, 11-O-(3',4'-dimethoxybenzoyl)-Bergenin showed the highest potent inhibitory activity among those of Bergenin derivatives. The presence of substituents at 3',4'-position in Bergenin derivatives altered the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. 11-O-(3',4'-dimethoxybenzoyl)-Bergenin was noncompetitive inhibitor for α-glucosidase.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study reveals that Bergenin derivatives could be classified as a new group of α-glucosidase inhibitors.
Inflammation. 2015 Jun;38(3):1142-50.
Bergenin Plays an Anti-Inflammatory Role via the Modulation of MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in a Mouse Model of LPS-Induced Mastitis.[Pubmed:
25487780]
Mastitis is a major disease in humans and other animals and is characterized by mammary gland inflammation. It is a major disease of the dairy industry.
Bergenin is an active constituent of the plants of genus Bergenia. Research indicates that Bergenin has multiple biological activities, including anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The objective of this study was to evaluate the protective effects and mechanism of Bergenin on the mammary glands during lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mastitis. In this study, mice were treated with LPS to induce mammary gland mastitis as a model for the disease. Bergenin treatment was initiated after LPS stimulation for 24 h. The results indicated that Bergenin attenuated inflammatory cell infiltration and decreased the concentration of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which were increased in LPS-induced mouse mastitis. Furthermore, Bergenin downregulated the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway proteins in mammary glands with mastitis.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Bergenin reduced the expression of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways, and it may represent a novel treatment strategy for mastitis.