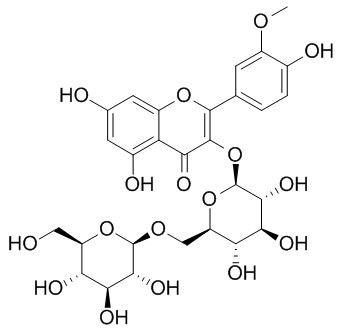
Astragaloside
Astragaloside may protect against brain contusion and neuronal apoptosis after TBI by attenuating microglia activation in male rats. Astragalosides-induced apoptosis in NB4 cells may be associated with down-regulation of the expression of BCL-2 and NF-κB, finally the relative activity of caspase-3 activated. Astragaloside has several pharmacological actions on cardiovascular system, including positive inotropic, anti-arrhythmia and anti-oxidant activities; it also has anti-apoptotic activity, which may contribute to the improvement of clinical outcomes in treating myocarditis with pharmaceutics of Astragalus membranaceus.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2020, AAC.01921-20.
J Liq Chromatogr R T2018, 41(12):761-769
Food Chem.2016, 191:81-90
Molecules.2021, 26(4):1084.
LWT2020, 110397
Molecules.2019, 24(10):E1930
Cytotechnology.2017, 69(5):765-773
Horticulture Research2022, uhac276.
PLoS One.2021, 16(6):e0248479.
Int J Mol Sci.2018, 19(2)
Related and Featured Products
Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(3):517-27.
Protective effect of astragaloside on focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed:
20503469 ]
This study was to observe the neurological protective effects of Astragalosides (AST) on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats and to explore its possible mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Male SD rats received right middle cerebral artery occlusion for 120 min and AST (40 mg/kg) was orally administered. The rats were decapitated 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after reperfusion. The neurological deficit score, infarct volume and water content of brain were measured; the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS), and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA), lactate (LD) and nitric oxide (NO) of brain tissue were detected too. The expression of inducible nitric synthase (iNOS), nerve growth factor (NGF) and tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) mRNA were measured by RT-PCR or real-time PCR. AST could significantly reduce the neurological deficit score; infract volume and water content, increase SOD and LDH activities, decrease NOS activity and MDA, LD and NO content. AST treatment could down-regulate expression of iNOS mRNA, while, NGF and TrkA mRNA were up-regulated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggest that AST have the protective effects on focal cerebral ischemia in rats at the different reperfusion time points, the mechanism may be related to the antioxidation, regulated the expressions of iNOS, NGF and TrkA mRNA.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;22(3):703-6.
Role of BCL-2, caspase-3 and NF-κB in astragaloside inducing apoptosis of human NB4 cells.[Pubmed:
24989280]
This study was purposed to investigate the apoptosis-inducing effect of Astragalosides on acute promyelocytic leukemia(APL) cell line NB4 and its mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
NB4 cells were treated with different concentrations (200, 300, 400 µg /ml) of Astragalosides for 48 h. The cell proliferation was assayed by using CCK-8 method; the cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITE/PI double staining. The mRNA expression of BCL-2 and the relative activity of BCL-2, NF-κB and caspase-3 were detected by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. The results showed that after treated with Astragalosides for 48 h, Astragalosides inhibited NB4 cell proliferation in concentration-dependent way, the apoptosis rate of NB4 cells gradually elevated from 4.69% to 40.85% with the increasing of Astragalosides concentration. Simultaneously, the mRNA expression of BCL-2 was down-regulated, Western blot analysis showed that the protein expression levels of BCL-2 and NF-κB decreased after Astragalosides treatment, while caspase-3 protein expression level increased.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is concluded that the molecular mechanism of the Astragalosides-induced apoptosis in NB4 cells may be associated with down-regulation of the expression of BCL-2 and NF-κB, finally the relative activity of caspase-3 activated.
Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(6):1357-70.
Astragaloside improves outcomes of traumatic brain injury in rats by reducing microglia activation.[Pubmed:
25384449]
Astragaloside (AST) is traditionally prescribed for the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We directly tested the therapeutic effects of Astragaloside in a rat model of traumatic brain injury (TBI). One hour after the onset of TBI rats were given Saline (1 ml/kg) or Astragaloside (20-80 mg/kg) via i.p. injection. Astragaloside causes the attenuation of TBI-induced cerebral contusion, neuronal apoptosis, and neurological motor dysfunction. TBI-induced microglial activation evidenced by the morphological transformation of microglia (or ameboid microglia) and the microglial overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha was reduced by Astragaloside .
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicate that Astragaloside may protect against brain contusion and neuronal apoptosis after TBI by attenuating microglia activation in male rats.