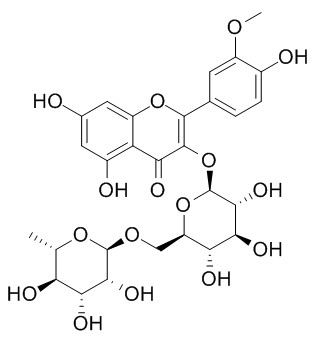
Narcissoside
Narcissoside is a good 15-LO and α-glucosidase inhibitor, it with synergism of B.flavum flavonoid and rutin, could be responsible for stronger protection against mitochondrial induced oxidative stress.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(8):951.
Nutrients.2023, 15(13):2960.
Advances in Traditional Medicine 2021, 21:779-789.
Br J Pharmacol.2024, 181(24):5009-5027.
Dicle Tip Dergisi2020, 47(2),423-430.
J. Essential Oil Research2024, 6:36:554-565.
Molecules.2024, 29(24):5983.
J Med Food.2022, 25(3):272-280.
Nutrients.2022, 14(23):4997.
Phytochem Anal.2023, pca.3305.
Related and Featured Products
Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 Jan-Mar;11(41):14-23.
Flavonoid profiles of three Bupleurum species and in vitro hepatoprotective of activity Bupleurum flavum Forsk.[Pubmed:
25709205]
Bupleurum L. (Aspiaceae) species are used as herbal remedy in Chinese traditional medicine. OBJECTIVE: The aim was to investigate the flavonoids in three annual European Bupleurum species, including B. baldense, B. affine and B. flavum, and to test their antioxidant and possible hepatoprotective effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Flavonoids from the methanol-aqueous extracts were quantified by solid-phase extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography. Bupleurum extracts (1-220 mg/ml) were tested for their antioxidant activity in DPPH and ABTS assays, as well as on isolated liver rat microsomes. In vitro hepatoprotective activity of B. flavum flavonoid (BFF) mixture and rutin, and Narcissoside, isolated from the same mixture, were evaluated on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BuOOH) toxicity models in isolated rat hepatocytes. Narcissoside was the dominant flavonol glycoside in B. flavum being present at 24.21 ± 0.19 mg/g, whilst the highest content of rutin (28.63 ± 1.57 mg/g) was found in B. baldense. B. flavum possessed the strongest DPPH (IC50 22.12 μg/ml) and ABTS (IC50 118.15 μg/ml) activity. At a concentration 1 mg/ml of BFF (rutin 197.58 mg/g, narcissin 75.74 mg/g), a stronger antioxidant effect in microsomes was evidenced in comparison with silymarin, rutin and Narcissoside. The hepatoprotective effect of BFF significantly reduced the elevated levels of lactate dehydrogenase and malondialdehyde, and ameliorated glutathione, being most active in t-BuOOH-induced injury model when compared with CCl4 toxicity (P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS:
In BFF, synergism of rutin and Narcissoside could be responsible for stronger protection against mitochondrial induced oxidative stress.
Pharm Biol. 2014 Sep;52(9):1166-9.
α-Glucosidase inhibition, 15-lipoxygenase inhibition, and brine shrimp toxicity of extracts and isolated compounds from Terminalia macroptera leaves.[Pubmed:
24635511]
Terminalia macroptera Guill. & Perr. (Combretaceae), a tree that grows in West Africa, has been used in traditional medicine against a variety of diseases such as hepatitis, gonorrhea, skin diseases, and diabetes. To investigate enzyme inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) and toxicity against brine shrimp of extracts and compounds from T. macroptera leaves.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Methanol extract, ethyl acetate, and butanol extracts obtained from the methanol extract, six isolated polyphenols (chebulagic acid, chebulic acid trimethyl ester, corilagin, methyl gallate, Narcissoside, and rutin), and shikimic acid were evaluated for enzyme inhibition and toxicity. In enzyme inhibition assays, all extracts showed high or very high activity. Chebulagic acid showed an IC50 value of 0.05 μM towards α-glucosidase and 24.9 ± 0.4 μM towards 15-LO, in contrast to positive controls (acarbose: IC50 201 ± 28 μM towards α-glucosidase, quercetin: 93 ± 3 μM towards 15-LO). Corilagin and Narcissoside were good 15-LO and α-glucosidase inhibitors, as well, while shikimic acid, methyl gallate, and chebulic acid trimethyl ester were less active or inactive. Rutin was a good α-glucosidase inhibitor (IC50 ca. 3 μM), but less active towards 15-LO. None of the extracts or the isolated compounds seemed to be very toxic in the brine shrimp assay compared with the positive control podophyllotoxin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Inhibition of α-glucosidase in the gastrointestinal tract may be a rationale for the medicinal use of T. macroptera leaves against diabetes in traditional medicine in Mali. The plant extracts and its constituents show strong inhibition of the peroxidative enzyme 15-LO.
J Sep Sci. 2014 Apr;37(8):957-65.
Extraction and isolation of flavonoid glycosides from Flos Sophorae Immaturus using ultrasonic-assisted extraction followed by high-speed countercurrent chromatography.[Pubmed:
24515421]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A method of ultrasonic-assisted extraction followed by high-speed countercurrent chromatography was established for the extraction and isolation of three flavonoid glycosides, i.e. rutin, Narcissoside, and nicotiflorin from Flos Sophorae Immaturus. The effects of ultrasonic-assisted extraction factors for the main flavonoid compound (rutin) from Flos Sophorae Immaturus were optimized using Box-Behnken design combined with response surface methodology. The optimum conditions were determined as ultrasonic power 83% (600 W), solvent-to-material ratio 56:1, methanol concentration 82% v/v, and extraction time 60 min. Three bioactive flavonol glucosides, rutin, Narcissoside, and nicotiflorin were isolated from Flos Sophorae Immaturus using high-speed countercurrent chromatography. The separation was performed with a two-phase solvent system containing ethyl acetate/n-butanol/methanol/water (4:0.9:0.2:5, v/v). Amounts of 87 mg of rutin, 10.8 mg of Narcissoside, and 1.8 mg of nicotiflorin were isolated from 302 mg of crude extract of Flos Sophorae Immaturus in a one-step separation within 160 min with purities of 99.3, 98.0, and 95.1%, respectively, as determined by HPLC with diode array detection. Their structures were characterized by UV, MS, and NMR spectroscopy.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was demonstrated that the established method was simple, fast, and convenient, which was feasible to extract and isolate active flavonoid glycosides from Flos Sophorae Immaturus.