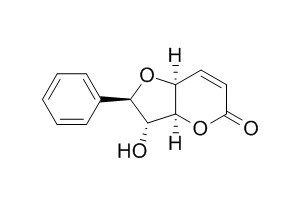
Altholactone
Altholactone may be a potential antimicrobial agent, particularly in ciprofloxacin-refractory S. aureus and E. faecalis infections. It can inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells through inducing apoptosis via oxidative stress, including bladder cancer, colon carcinoma cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Hanoi University of Pharmacy2023, 14(1):30-39.
Data Science for Genomics2023, 107-128.
Nat Prod Communications2018, 10.1177
Phytomedicine.2020, 79, 153351
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020, 21(4):935-941.
Agronomy2023, 13(6), 1435.
Pharmaceutics.2020, 12(9):882.
Free Radic Biol Med.2016, 97:307-319
Preprints2017, 2017120176
Viruses.2017, 9(10)
Related and Featured Products
Phytother Res. 2012 Jun;26(6):926-31.
Altholactone induces apoptotic cell death in human colorectal cancer cells.[Pubmed:
22105918]
Resistance of colorectal cancer (CRC) to the available chemotherapy reveals the demand for identification of new anticancer agents. We evaluated the antitumour potential of Altholactone, a naturally occurring bioactive compound isolated from Goniothalamus spp. (Annonaceae) hooks, against CRC cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antitumour activity of Altholactone was measured using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and the propidium iodide method. Apoptosis mediators involved were assessed using biochemical inhibitors and Western blotting analysis. Results revealed that Altholactone induced varying degrees of apoptosis in CRC cells but not in normal fibroblasts. Dissection of the Altholactone-induced apoptotic signalling pathway revealed that Altholactone activated caspase-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Activation of caspase-4 appeared to be the initiating event in the caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway. Pre-treatment of CRC cells with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) significantly inhibited activation of caspase-4 and Altholactone-induced apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Altholactone induces selective cytotoxicity against colon carcinoma cells and warrants further clinical evaluation.
Molecules. 2011 Jun 3;16(6):4560-6.
Altholactone displays promising antimicrobial activity.[Pubmed:
21642933]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antimicrobial activity of Altholactone, a naturally extracted styryllactone isolated from Goniothalamus malayanus, was determined against Gram positive (S. aureus ATTC 25923, S. aureus ATTC 25392, and E. faecalis ATTC 29212) and Gram negative (E. coli ATTC 35218, S. typhi ATTC 14023 and P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853) reference bacteria and against the fungus C. albicans ATTC 10231. Different concentrations of Altholactone (0, 12, 25, and 50 μg/mL) were used. Results revealed that Altholactone inhibited the growth of all tested microbes except P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 in a dose-dependent manner, with the highest cytotoxic effects occurring at 50 μg/mL. The average of the inhibition zones of the different concentrations was between 0-30 mm. Furthermore, Altholactone-induced antimicrobial activity against the more sensitive microbes was assessed by measuring the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC). Results indicated that Gram positive (S. aureus ATTC 25923, S. aureus ATTC 25392, and E. faecalis ATTC 29212) cells were more sensitive to Altholactone than Gram negative ones (E. coli ATTC 35218, S. typhi ATTC 14023). C. albicans showed moderate sensitivity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Altholactone might be a potential antimicrobial agent, particularly in ciprofloxacin-refractory S. aureus and E. faecalis infections. Further investigations are required to illustrate the mechanism(s) by which Altholactone produces its antimicrobial effects.
Oncol Rep. 2014 Jun;31(6):2769-75.
Altholactone induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in bladder cancer T24 cells through mitochondrial dysfunction, MAPK-p38 activation and Akt suppression.[Pubmed:
24700345]
Human bladder cancer is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy. Therefore, the search for new therapeutic agents is of great importance. Altholactone, isolated from Goniothalamus sp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Altholactone on bladder cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we characterized the effect of Altholactone on cell growth and apoptosis in bladder cancer T24 cells. Treatment with Altholactone resulted in a significant reduction in cell viability, induction of apoptosis and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in T24 cells. Furthermore, our results revealed that Altholactone-induced apoptosis was associated with decreased expression of Akt phosphorylation and activation of MAPK‑p38. Altholactone treatment was also found to result in a significant loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, Bcl-2 downregulation and caspase-3 activation. Pretreatment of T24 cells with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) significantly inhibited activation of caspase-3 and MAPK-p38 and prevented inactivation of Akt and Bcl-2.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data demonstrate that Altholactone induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in T24 cells via a novel mechanism involving inhibition of Akt and provide the rationale for further in vivo and preclinical investigation of Altholactone against bladder cancer.
Toxicol Lett. 2002 May 28;131(3):153-9.
Altholactone, a novel styryl-lactone induces apoptosis via oxidative stress in human HL-60 leukemia cells.[Pubmed:
11992734]
Plant styryl-lactone derivatives isolated from Goniothalamus sp. are potential compounds for cancer chemotherapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we have examined the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by Altholactone, a stryl-lactone isolated from the Malaysian plant G. malayanus on human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the externalization of phosphatidylserine (PS) using the annexin V/PI method on Altholactone treated HL-60 cells showed a concentration-dependent increase of apoptosis from concentrations ranging from 10.8 (2.5 microg/ml) to 172.4 microM (40 microg/ml). Pre-treatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (1 mM) completely abrogated apoptosis induced by Altholactone, suggesting for the involvement of oxidative stress. Further flow cytometric assessment of the level of intracellular peroxides using the fluorescent probe 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) confirmed that Altholactone induced an increase in cellular oxidative stress in HL-60 cells which was suppressed by N-acetylcysteine.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, our results demonstrate for the first time that Altholactone induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells occurs via oxidative stress.
Cell Biol Int. 2013 May;37(5):471-7.
Role of altholactone in inducing type II apoptosis signalling pathway and expression of cancer-related genes in cervical carcinoma HeLa cell line.[Pubmed:
23494867 ]
Goniothalamus species (Annonaceae) is a shrub that grows in the rainforest of tropical Asia. Several compounds have been isolated and exhibit the potential use for cancer treatment.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, Altholactone isolated from Goniothalamus macrophyllus was investigated for its cytotoxicity, apoptosis signalling and the expression of cancer-related genes in the cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Cytotoxicity was evaluated by MTT assay. Apoptotic characteristics were evaluated by morphological studies. Caspase-3 activity was detected using a fluorogenic substrate. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria and protein Bid were determined by Western blotting and cancer-related genes expression by RT-PCR.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrated that Altholactone was cytotoxic to HeLa (IC50 = 9.6 μg/mL), and apoptotic cell death was manifested by appearance of chromatin condensation and caspase-3 activation, which was inhibited by specific inhibitors of both caspase-8 and -9. Release into the cytosol of cytochrome and cleavage of Bid occurred. Altholactone also caused a decrease in bcl-2 and an increase in p53 expression. These unique properties of Altholactone suggest a potential for cancer chemotherapy.