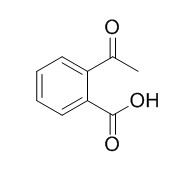
2-Acetylbenzoic acid
2-Acetylbenzoic acid is more potent than 2-propionyloxybenzoic acid in inhibiting platelet function and platelet prostaglandin (PG) synthesis although the potencies of these agents were comparable in inhibiting prostacyclin (PGI2) synthesis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharmacognosy Journal.2022, 14,4,327-337.
J Appl Biol Chem.2022, 65(4):pp.463-469.
Acta Edulis Fungi2020, 27(02):63-76.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(9):1130.
Cell Rep.2020, 32(11):108158.
Molecules.2022, 27(13):4227.
Microb Pathog.2019, 131:128-134
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(77).
VNU J Sci: Med. Pharm. Sci.2024, 40(2):21-30.
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(9):3392.
Related and Featured Products
Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1982 Jul;9(1):9-23.
Structure-activity studies of aspirin and related compounds on platelet aggregation, arachidonic acid metabolism in platelets and artery, and arterial prostacyclin activity.[Pubmed:
6813878 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A series of benzoic acid derivatives was tested for specificity of action on human platelet function and platelet prostaglandin (PG) synthesis versus prostacyclin (PGI2) production by rat and rabbit aorta rings. None of the agents tested was more specific for one system than the other. ASA was more potent than 2-propionyloxybenzoic acid (2-PBA) in inhibiting platelet function and platelet PG synthesis although the potencies of these agents were comparable in inhibiting PGI2 synthesis. 3-Propionyloxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) caused increased activity in both systems while 2-Acetylbenzoic acid (ABA) had only minor effects. A cyclical derivative, 3-methylphthalide (3-MP), inhibited both platelet function and PGI2 synthesis although it did not inhibit cyclo-oxygenase activity, suggesting a novel mechanism of action.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus only minor changes in the ASA molecule could be effected without significant changes in pharmacological activity. The investigation of novel agents such as 3-MP may lead to a better understanding of arachidonate metabolism in different tissues and possibly to the development of more tissue-specific drugs.
Agents Actions. 1981 May;11(3):281-6.
Relationship of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in platelets to anti-aggregatory and anti-inflammatory activity of some benzoic acid derivatives.[Pubmed:
7257955]
The relationships between inhibition of platelet prostaglandin (PG) synthesis and aggregation, and suppression inflammation were investigated with a number of benzoic acid (aspirin-like) chemicals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds studied were 2-Acetylbenzoic acid (ABA), 3-methylphthalide (3-MP), 3-propionyloxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) and 2-propionyloxybenzoic acid (2-PBA). At 0.5--0.6 mM, 3-MP inhibited the second phase of ADP-induced aggregation in human platelets, and reduced collagen-induced aggregation by 50%. Previous studies have shown 2-PBA to inhibit aggregation at similar concentrations. In contrast, ABA required 10 times higher concentrations, and low concentrations actually potentiated aggregation. Inhibition of PG synthesis from 14C-arachidonic acid (AA) by human platelets was shown for 2-PBA, but not to 3-BPA, or ABA. At high concentration (1 mM), 3-MP showed modest inhibitory activity. Significant inhibition of AA aggregation was produced by ASA (83%), 2-PBA (76%) and 3-MP (69%), an order reflecting their inhibition of PG synthesis, where ABA and 3-PBA did not inhibit AA aggregation. Carrageenin-induced edema of the rat paw was suppressed by 3-MP, ABA and 2-PBA; all being roughly equipotent with aspirin. In contrast, 3-PBA did not suppress edema. Following oral administration of the drugs to rats, PG synthesis from labeled AA by rat platelets showed similar profiles to effects of the drugs on PG synthesis in human platelets.
CONCLUSIONS:
This suggests that biotransformation or species differences are not explanations for the observed differences in activity in the various test systems. The results indicate that, in a related series of chemicals there is not a good correlation between ability to inhibit platelet PG synthesis, anti-aggregatory activity and anti-inflammatory activity. Multiple mechanisms of action, differing sensitivities of various tissue PG synthetases, or unidentified factors could be involved.