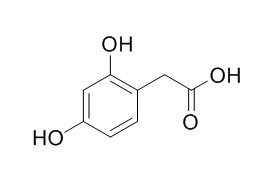
2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is a functional moiety in the toxin molecule and the biological action of spider toxin is explained by direct interaction with an Fe-S center which is known to play an important role for the glutamate binding.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(6):526.
FASEB J.2019, 33(2):2026-2036
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).2017, 65(9):826-832
Food Sci Biotechnol.2024, 33(15):3629-3637.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2019, 50(4):285-290
Korean Journal of Medicinal Crop Science2018, 26(5):382-390
Environ Toxicol.2023, 23929.
Fitoterapia.2022, 157:105130.
J AOAC Int.2024, qsae028.
Food Funct.2022, 13(14):7638-7649.
Related and Featured Products
Brain Res. 1987 Aug 18;418(1):198-200.
Molecular action mechanism of spider toxin on glutamate receptor: role of 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in toxin molecule.[Pubmed:
2889509]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Joro spider toxin (JSTX) isolated from Nephila clavata was shown to inhibit L-glutamate binding to rat brain synaptic membranes in a dose-dependent manner. 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (2,4-DHPA), a common moiety of spider toxins, also inhibited specifically L-glutamate binding at a concentration similar to that of the toxin. The binding activity inhibited by 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid or JSTX was recoverable on addition of ferric compound.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is a functional moiety in the toxin molecule and the biological action of spider toxin is explained by direct interaction with an Fe-S center which is known to play an important role for the glutamate binding.