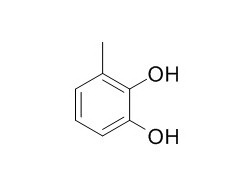
3-Methylcatechol
3-Methylcatechol is a natural product from Phellinus igniarius.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.2024, 108(1):207.
Journal of Ginseng Research2023, 12.004.
Molecules.2022, 27(2):451.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2019, 50(4):285-290
Foods.2023, 12(7):1355.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol.2020, 190(2):732-744
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(3):352.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2022, 44(10):5106-5116.
Talanta Open2023, 7:100227
J Ethnopharmacol.2017, 198:205-213
Related and Featured Products
J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2014;60(5):183-90.
Enhanced 3-methylcatechol production by Pseudomonas putida TODE1 in a two-phase biotransformation system.[Pubmed:
25420423]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, genetically engineered Pseudomonas putida TODE1 served as a biocatalyst for the bioproduction of valuable 3-Methylcatechol (3MC) from toluene in an aqueous-organic two-phase system. The two-phase system was used as an approach to increase the biocatalyst efficiency.Among the organic solvent tested, n-decanol offered several benefits including having the highest partitioning of 3MC, with a high 3MC yield and low cell toxicity. The effect of media supplementation with carbon/energy sources (glucose, glycerol, acetate and succinate), divalent metal cations (Mg(2+), Ca(2+), Mn(2+) and Fe(2+)), and short-chain alcohols (ethanol, n-propanol and n-butanol) as a cofactor regeneration system on the toluene dioxygenase (TDO) activity, cell viability, and overall 3MC yield were evaluated. Along with the two-step cell preparation protocol, supplementation of the medium with 4 mM glycerol as a carbon/energy source, and 0.4 mM Fe(2+) as a cofactor for TDO significantly enhanced the 3MC production level.
When in combination with the use of n-decanol and n-butanol as the organic phase, a maximum overall 3MC concentration of 31.8 mM (166 mM in the organic phase) was obtained in a small-scale production, while it was at 160.5 mM (333.2 mM in the organic phase) in a 2-L scale.
CONCLUSIONS:
To our knowledge, this is the highest 3MC yield obtained from a TDO-based system so far.
BMC Biotechnol. 2010 Jun 30;10:49.
A process optimization for bio-catalytic production of substituted catechols (3-nitrocatechol and 3-methylcatechol.[Pubmed:
20587073]
Substituted catechols are important precursors for large-scale synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other industrial products. Most of the reported chemical synthesis methods are expensive and insufficient at industrial level. However, biological processes for production of substituted catechols could be highly selective and suitable for industrial purposes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We have optimized a process for bio-catalytic production of 3-substituted catechols viz. 3-nitrocatechol (3-NC) and 3-Methylcatechol (3-MC) at pilot scale. Amongst the screened strains, two strains viz. Pseudomonas putida strain (F1) and recombinant Escherichia coli expression clone (pDTG602) harboring first two genes of toluene degradation pathway were found to accumulate 3-NC and 3-MC respectively. Various parameters such as amount of nutrients, pH, temperature, substrate concentration, aeration, inoculums size, culture volume, toxicity of substrate and product, down stream extraction, single step and two-step biotransformation were optimized at laboratory scale to obtain high yields of 3-substituted catechols. Subsequently, pilot scale studies were performed in 2.5 liter bioreactor. The rate of product accumulation at pilot scale significantly increased up to approximately 90-95% with time and high yields of 3-NC (10 mM) and 3-MC (12 mM) were obtained.
CONCLUSIONS:
The biocatalytic production of 3-substituted catechols viz. 3-NC and 3-MC depend on some crucial parameters to obtain maximum yields of the product at pilot scale. The process optimized for production of 3-substituted catechols by using the organisms P. putida (F1) and recombinant E. coli expression clone (pDTG602) may be useful for industrial application.