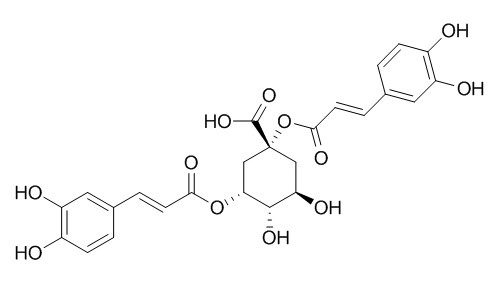
1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid
1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid has neuroprotective, and antioxidant effects, it can prevent Aβ(42)-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt followed by the stimulation of Trk A, then the inhibition of GSK3β as well as the modulation of Bcl-2/Bax. 1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid has protective effects against MPP~+ induces neurotoxicity of PC12 Cells, it (50 umol/L) pretreatment can inhibit the MPP+-induced up-regulation of the expression of α-synuclein mRNA and protein.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(21):E5488
Toxicol Rep.2021, 8:1131-1142.
Horticulturae2021, 7(1),5.
PLoS One.2020, 15(2):e0220084.
Br J Pharmacol.2024, 181(24):5009-5027.
Food Res Int.2021, 148:110607.
Nutrients.2020, 12(3):595.
J Pharmaceutical Research Int.2021, 33(41A):275-284.
JEJU National University2022, 24032.
BMC Complement Med Ther.2023, 23(1):264.
Related and Featured Products
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;39(12):2275-80.
Regulation of syringin, chlorogenic acid and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of Saussurea involucrata.[Pubmed:
25244758]
Syringin, chlorogenic acid and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid are three main bioactive ingredients in herbs of Saussurea involucrata with various pharmacological properties, while their contents are very low.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the biosynthesis of syringin, chlorogenic acid and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid in the cell suspension cultures of S. involucrata were regulated by feeding carbon sources and precursors, which resulted in a great increase of the contents and yields of the above three bioactive ingredients. After 16 days of fermentation, the yields of syringin, chlorogenic acid and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid reached 339.0, 225.3, 512.7 mg x L(-1), respectively. Meanwhile, their contents increased up to 67.9, 1.9, 10.6 times of wild medicinal material, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results provided a solid basis for further studies on application of cell suspension cultures of S. involucrata for large-scale production of bioactive compounds syringin, chlorogenic acid and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid.
Organic. Chem., 1999, 72.
1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid, an antioxidant component of Cynara cardunculus leaves[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study describes the isolation, identification and some antioxidant properties of 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid. This compound was isolated from a methanolic extract of Cynara cardunculus leaves. The isolation was based on a selective extraction of 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid with diethylether from a weak acidic water-methanolic solution and on column chromatography. The compound structure was determined by 1D and 2D H-NMR spectroscopy. Inhibition of hemolysis induced by hydrogen peroxide and the anti-radical effect of both 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid and cynarin (1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid) were studied. Cynarin was formed from 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid by trans-esterification during solvent extraction.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antioxidant activity of dicaffeoylquinic acids in both systems was found to be stronger than that of ascorbic acid.
Brain Res. 2010 Aug 6;1347:142-8.
1, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid-mediated glutathione synthesis through activation of Nrf2 protects against OGD/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in astrocytes.[Pubmed:
20513363 ]
Oxidative stress plays an important role in pathological processes of cerebral ischemia followed by reperfusion.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (1, 5-diCQA) on primary culture rat cortical astrocytes induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)/reperfusion was evaluated in this study. Appropriate concentration of 1, 5-diCQA pretreatment significantly suppressed cell death, reduced the production of reactive oxygen species, prevented glutathione (GSH) depletion, increased the activity of glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), and triggered Nrf2 nuclear translocation in astrocytes induced by 4h of OGD and 20 h of reperfusion. Interestingly, these protective effects were greatly attenuated in Nrf2 siRNA-transfected cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that 1, 5-diCQA has antioxidant signaling properties that upregulate GSH synthesis by stimulating the Nrf2 pathway in astrocytes and protects them from cell death in an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion.
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem . 2016;31(2):266-75.
Antioxidant, antiradical, and anticholinergic properties of cynarin purified from the Illyrian thistle (Onopordum illyricum L.)[Pubmed:
25792498]
Abstract
Cynarin is a derivative of hydroxycinnamic acid and it has biologically active functional groups constituent of some plants and food. We elucidated the antioxidant activity of cynarin by using different in vitro condition bioanalytical antioxidant assays like DMPD(•+), ABTS(•+), O2(•-), DPPH(•) and H2O2 scavenging effects, the total antioxidant influence, reducing capabilities, Fe(2+) chelating and anticholinergic activities. Cynarin demonstrated 87.72% inhibition of linoleic acid lipid peroxidation at 30 μg/mL concentration. Conversely, some standard antioxidants like trolox, α-tocopherol, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) exhibited inhibitions of 90.32, 75.26, 97.61, 87.30%, and opponent peroxidation of linoleic acid emulsion at the identical concentration, seriatim. Also, cynarin exhibited effective DMPD(•+), ABTS(•+), O2(•-), DPPH(•), and H2O2 scavenging effects, reducing capabilities and Fe(2+) chelating effects. On the contrary, IC50 and K(i) parameters of cynarin for acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibition were determined as 243.67 nM (r(2): 0.9444) and 39.34 ± 13.88 nM, respectively. This study clearly showed that cynarin had marked antioxidant, anticholinergic, reducing ability, radical-scavenging, and metal-binding activities.
Keywords: Antiacetylcholinesterase; Onopordum illyricum; anticholinergic; antioxidant activity; cynarin; radical scavenging.
Chin Med J (Engl). 2011 Sep;124(17):2628-35.
1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid protects primary neurons from amyloid β 1-42-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.[Pubmed:
22040415]
Recently, 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (1,5-DQA), a caffeoylquinic acid derivative isolated from Aster scaber, was found to have neuroprotective effects. However, the protective mechanisms of 1,5-DQA have not yet been clearly identified. The purpose of this study was to explore the protective mechanisms of 1,5-DQA on neuronal culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the neuroprotective effects of 1,5-DQA against amyloid β(1-42) (Aβ(42))-induced neurotoxicity in primary neuronal culture. To evaluate the neuroprotective effects of 1,5-DQA, primary cultured cortical neurons from neonate rats were pretreated with 1,5-DQA for 2 hours and then treated with 40 µmol/L Aβ(42) for 6 hours. Cell counting kit-8, Hoechst staining and Western blotting were used for detecting the protective mechanism. Comparisons between two groups were evaluated by independent t test, and multiple comparisons were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
1,5-DQA treated neurons showed increased neuronal cell viability against Aβ(42) toxicity in a concentration-dependent manner, both phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2) were activated by 1,5-DQA with stimulating their upstream tyrosine kinase A (Trk A). However, the neuroprotective effects of 1,5-DQA were blocked by LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, but not by PD98059, an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Furthermore, 1,5-DQA's anti-apoptotic potential was related to the enhanced inactivating phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and the modulation of expression of apoptosis-related protein Bcl-2/Bax.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that 1,5-DQA prevents Aβ(42)-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt followed by the stimulation of Trk A, then the inhibition of GSK3β as well as the modulation of Bcl-2/Bax.
Acta Med. Universit. Sci. Et. Technol. Huazhong, 2010, 39(4): 435-38.
Protective Effects of 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid against MPP~+ Induced Neurotoxicity of PC12 Cells[Reference:
WebLink]
To investigate the protective effects of 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid(1,5-diCQA)preconditioning on the injury of PC12 cells induced by MPP+ and the possible mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
MPP+ was added to make a model of Parkinson disease in rat pheochromocytoma(PC12)cells.PC12 cells were divided into three groups randomly:control group,MPP+ group,1,5-diCQA+MPP+ group.Cell viability was determined by MTT assay.Cellular ROS and GSH were observed by a spectrophotometer.The expression of α-synuclein mRNA and protein was detected by using RT-PCR and Western blot respectively. ①The cell viability in MPP+ group was obviously less than in control group and 1,5-diCQA pretreatment+MPP+ group.②The ROS production and cellular depletion was lessened by pretreatment of 1,5-diCQA in a dose-dependent manner.③1,5-diCQA(50 μmol/L)pretreatment could inhibit the MPP+-induced up-regulation of the expression of α-synuclein mRNA and protein.
CONCLUSIONS:
1,5-diCQA may have a neuroprotective potential for it could attenuate the oxidative stress and α-synuclein overexpression in the PC12 cells induced by MPP+.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:280351.
Inulae Flos and Its Compounds Inhibit TNF-α- and IFN-γ-Induced Chemokine Production in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes.[Pubmed:
22919411]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study is to investigate which kinds of solvent extracts of Inulae Flos inhibit the chemokine productions in HaCaT cell and whether the inhibitory capacity of Inulae Flos is related with constitutional compounds. The 70% methanol extract showed comparatively higher inhibition of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) in HaCaT cells, therefore this extract was further partitioned with n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, butanol, and water. The ethyl acetate fraction inhibited TARC, macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC/CCL22), and regulated on activation of normal T-cell-expressed and -secreted (RANTES/CCL5) production in HaCaT cells better than the other fractions. The compounds of Inulae Flos, such as 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and luteolin, inhibited TARC, MDC, and RANTES production in HaCaT cells. 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid was contained at the highest concentrations both in the 70% methanol extract and ethyl acetate fraction and inhibited the secretion of chemokines dose-dependently more than the other compounds. Luteolin also represented dose-dependent inhibition on chemokine productions although it was contained at lower levels in 70% methanol extract and solvent fractions.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the inhibitory effects of Inulae Flos on chemokine production in HaCaT cell could be related with constituent compounds contained, especially 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and luteolin.