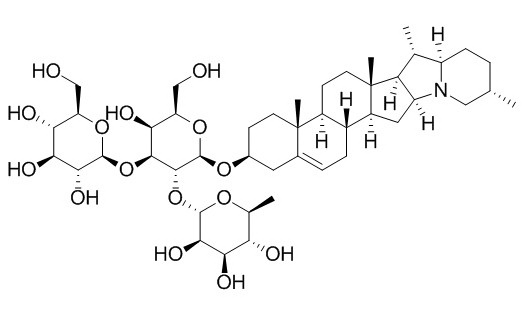
alpha-Solanine
Alpha-Solanine alters antioxidative enzyme activities and MDA and PCO concentrations and GST activity in fat body and midgut. Alpha-Solanine has proliferation-inhibiting and apoptosis-promoting effect on multiple cancer cells, such as clone, liver, melanoma cancer cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Agric Food Chem.2018, 66(1):351-358
Agriculture.2022, 12(3), 342.
Biomolecules.2024, 14(10):1257.
Pharmacol Rep.2018, 70(6):1195-1201
J Med Food.2020, 23(6):633-640.
J. Traditional Thai Medical Res. 2022,8(1):1-14.
J Ethnopharmacol.2018, 210:88-94
Molecules.2020, 25(9):2081.
Nutr Res Pract.2020, 14(3):203-217.
Molecules 2022, 27(3),960.
Related and Featured Products
PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e87868.
Antitumor efficacy of α-solanine against pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:
24505326]
alpha-Solanine, a steroidal glycoalkaloid in potato, was found to have proliferation-inhibiting and apoptosis-promoting effect on multiple cancer cells, such as clone, liver, melanoma cancer cells. However, the antitumor efficacy of alpha-Solanine on pancreatic cancer has not been fully evaluated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we inquired into the anti-carcinogenic effect of alpha-Solanine against human pancreatic cancer cells. In the present study, we investigated the anti-carcinogenic effect of alpha-Solanine against human pancreatic cancer cells. In vitro, alpha-Solanine inhibited proliferation of PANC-1, sw1990, MIA PaCa-2 cells in a dose-dependent manner, as well as cell migration and invasion with atoxic doses. The expression of MMP-2/9, extracellular inducer of matrix metalloproteinase (EMMPRIN), CD44, eNOS and E-cadherin were suppressed by alpha-Solanine in PANC-1 cells. Moreover, significantly decreased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and tube formation of endothelial cells were discerned following alpha-Solanine treatment. Suppressed phosphorylation of Akt, mTOR, and Stat3, and strengthen phosphorylation of β-catenin was found, along with markedly decreased tran-nuclear of NF-κB, β-catenin and TCF-1. Following the administration of alpha-Solanine (6 µg/g for 2 weeks) in xenograft model, tumor volume and weight were decreased by 61% and 43% (p<0.05) respectively, showing decreased MMP-2/9, PCNA and VEGF expression.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, alpha-Solanine showed beneficial effects on pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo, which may via suppressing the pathway proliferation, angiogenesis and metastasis.
Exp Ther Med . 2016 Sep;12(3):1525-1530.
Inhibitory effect of α-solanine on esophageal carcinoma in vitro[Pubmed:
27588073]
Abstract
α-solanine, a bioactive component and one of the major steroidal glycoalkaloids in potatoes, has been observed to inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in cancer cells. However, the antitumor efficacy of α-solanine on esophageal carcinoma has yet to be fully elucidated. In the present study, the antitumor efficacy of α-solanine against human esophageal carcinoma cells was investigated. It was determined that α-solanine inhibited the growth and proliferation of human esophageal EC9706 and Eca109 cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner, as well as the cell migration and invasion. In addition, the apoptotic rate was increased in the cancer cells treated with α-solanine in a dose-dependent manner, compared with that of the control group (P<0.05). The expression levels of tumor metastasis-related proteins, including matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, were reduced in the cells treated with α-solanine, as compared with the control group. Conversely, significantly higher expression levels of E-cadherin were detected in the α-solanine-treated groups, as compared with the control group (P<0.05). Therefore, the current results provide a novel insight into the anti-tumor mechanism of α-solanine, and suggest that α-solanine is a potential agent for the prevention and treatment of esophageal carcinoma.
Keywords: apoptosis; esophageal carcinoma; proliferation; tumor metastasis; α-solanine.
Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2014 Sep;87(1):26-39.
Potato leaf extract and its component, α-solanine, exert similar impacts on development and oxidative stress in Galleria mellonella L.[Pubmed:
25041927]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The glycoalkaloid alpha-Solanine. Wax moth larvae were reared from first instar on a diet supplemented with three concentrations of EPL or alpha-Solanine. Both EPL and alpha-Solanine affected survivorship, fecundity, and fertility of G. mellonella to approximately the same extent. We evaluated the effect of EPL and alpha-Solanine on oxidative stress in midgut and fat body by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl (PCO) contents, both biomarkers of oxidative damage. We evaluated glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity, a detoxifying enzyme acting in prevention of oxidative damage. EPL and alpha-Solanine altered MDA and PCO concentrations and GST activity in fat body and midgut.
CONCLUSIONS:
We infer that the influence of EPL on G. mellonella is not enhanced by synergistic effects of the totality of potato leaf components compared to alpha-Solanine alone.
Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013 May;83(1):15-24.
The influence of dietary α-solanine on the waxmoth Galleria mellonella L.[Pubmed:
23494897]
Plant allelochemicals are nonnutritional chemicals that interfere with the biology of herbivores.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We posed the hypothesis that ingestion of a glycoalkaloid allelochemical, α-solanine, impairs biological parameters of greater wax moths Galleria mellonella. To test this idea, we reared wax moths on artificial diets with 0.015, 0.15, or 1.5 mg/100 g diet of α-solanine. Addition of α-solanine to the diet affected survival of seventh-instar larvae, pupae, and adults; and female fecundity and fertility. The diet containing the highest α-solanine concentration led to decreased survivorship, fecundity, and fertility. The diets supplemented with α-solanine led to increased malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl contents in midgut and fat body and the effect was dose-dependent. Dietary α-solanine led to increased midgut glutathione S-transferase activity and to decreased fat body glutathione S-transferase activitiy.
CONCLUSIONS:
We infer from these findings that α-solanine influences life history parameters and antioxidative enzyme activities in the midgut and fat body of G. mellonella.
Molecules. 2014 Aug 11;19(8):11896-914.
α-Solanine inhibits invasion of human prostate cancer cell by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MMPs expression.[Pubmed:
2511680]
alpha-Solanine, a naturally occurring steroidal glycoalkaloid found in nightshade (Solanum nigrum Linn.), was found to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of tumor cells. However, the mechanism involved in suppression of cancer cell metastasis by alpha-Solanine remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study investigates the suppression mechanism of alpha-Solanine on motility of the human prostate cancer cell PC-3. Results show that alpha-Solanine reduces the viability of PC-3 cells. When treated with non-toxic doses of alpha-Solanine, cell invasion is markedly suppressed by alpha-Solanine. alpha-Solanine also significantly elevates epithelial marker E-cadherin expression, while it concomitantly decreases mesenchymal marker vimentin expression, suggesting it suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). alpha-Solanine reduces the mRNA level of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9 and extracellular inducer of matrix metalloproteinase (EMMPRIN), but increases the expression of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) and TIMP-2. Immunoblotting assays indicate alpha-Solanine is effective in suppressing the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositide-3 kinase (PI3K), Akt and ERK. Moreover, alpha-Solanine downregulates oncogenic microRNA-21 (miR-21) and upregulates tumor suppressor miR-138 expression.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results suggest that inhibition of PC-3 cell invasion by alpha-Solanine may be, at least in part, through blocking EMT and MMPs expression. alpha-Solanine also reduces ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and regulates expression of miR-21 and miR-138. These findings suggest an attractive therapeutic potential of alpha-Solanine for suppressing invasion of prostate cancer cell.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;718(1-3):1-9.
The protective and therapeutic effects of alpha-solanine on mice breast cancer.[Pubmed:
24051269]
alpha-Solanine, a naturally steroidal glycoalkaloid, is found in leaves and fruits of plants as a defensive agent against fungi, bacteria and insects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Herein, we investigated solanine toxicity in vitro and in vivo, and assessed its protective and the therapeutic effects on a typical animal model of breast cancer. The study conducted in three series of experiments to obtain (i) solanine effects on cell viability of mammary carcinoma cells, (ii) in vivo toxicity of solanine, and (iv) the protective and therapeutic effects of solanine on animal model of breast cancer. alpha-Solanine significantly suppressed proliferation of mouse mammary carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo (P<0.05). Under the dosing procedure, 5 mg/kg solanine has been chosen for assessing its protective and therapeutic effects in mice breast cancer. Tumor take rate in the solanine-treated group was zero compared with a 75% rate in its respective control group (P<0.05). The average tumor size and weight were significantly lower in solanine-treated animals than its respective control ones (P<0.05). Proapoptotic Bax protein expression increased in breast tumor by solanine compared with its respective control group (P<0.05). Antiapoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression found to be lower in solanine-treated animals (P<0.05). Proliferative and angiogenic parameters greatly decreased in solanine-treated mice (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
Data provide evidence that solanine exerts a significant chemoprotective and chemotherapeutic effects on an animal model of breast cancer through apoptosis induction, cell proliferation and angiogenesis inhibition. These findings reveal a new therapeutic potential for solanine in cancer.