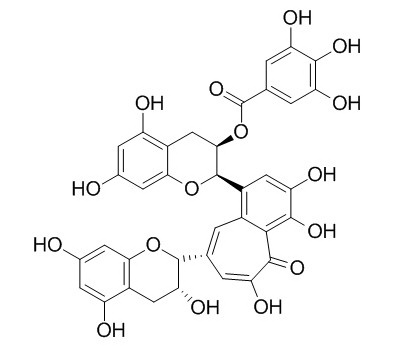
Theaflavin-3-gallate
Theaflavin-3-gallate has anticancer and apoptotic effects in non-small cell lung carcinoma, it acts as prooxidants and induce oxidative stress, with carcinoma cells more sensitive than normal fibroblasts. Theaflavin-3-gallate can play a role in decreased intestinal cholesterol absorption via inhibition of micelle formation.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Front. Physiol.2022, 790345.
ACS Omega.2024, 9(12):14356-14367.
Dent Mater J. 2024, dmj.2023-294.
Sci Rep.2025, 15(1):29590.
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020, 20(1):91.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(5):2796.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2023, 10.1002/kjm2.12764
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117395.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(10):5181.
Chem Biol Interact.2016, 258:59-68
Related and Featured Products
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 Jul;103(1):66-74.
Theaflavin-3-gallate and theaflavin-3'-gallate, polyphenols in black tea with prooxidant properties.[Pubmed:
18346048]
This study compared the in vitro responses of human gingival fibroblasts and of carcinoma cells derived from the tongue to Theaflavin-3-gallate (TF-2A) and theaflavin-3'-gallate (TF-2B), polyphenols in black tea.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of the theaflavin monomers were more pronounced to the carcinoma, than to the normal, cells. In phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, the theaflavins generated hydrogen peroxide and the superoxide anion, suggesting that their mode of toxicity may be due, in part, to the induction of oxidative stress. In a cell-free assay, Theaflavin-3-gallate and TF-2B reacted directly with reduced glutathione (GSH), in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Intracellular storages of GSH were depleted on treatment of the cells with the theaflavin monomers. Depletion of intracellular GSH was more extensive with Theaflavin-3-gallate than with TF-2B and was more pronounced in the carcinoma, than in the normal, cells. The toxicities of the theaflavins were potentiated when the cells were cotreated with the GSH depleter, d,l-buthionine-[S,R]-sulfoximine. In the presence of catalase, pyruvate and divalent cobalt, all scavengers of reactive oxygen species, the cytotoxicities of the theaflavins were lessened. Theaflavin-3-gallate and TF-2B induced lipid peroxidation in the carcinoma cells, whereas in the fibroblasts, peroxidation was evident upon exposure to Theaflavin-3-gallate, but not to TF-2B.
CONCLUSIONS:
These studies demonstrated that the black tea theaflavin monomers, Theaflavin-3-gallate and TF-2B, act as prooxidants and induce oxidative stress, with carcinoma cells more sensitive than normal fibroblasts.
Bangl. J. Pharmacol., 2015, 10(4):3047-53.
Anticancer and apoptotic effects of theaflavin-3-gallate in non-small cell lung carcinoma.[Reference:
WebLink]
The objective was to determine the antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of Theaflavin-3-gallate in human non-small cell lung cancer cells (A-549) along with determining the effect on cell cycle phase distribution, cell migration and invasion.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cell viability was determined by MTT assay while as phase contrast and fluorescence microscopies were involved to study apoptotic morphologi-cal features in these cells. Flow cytometry investigated the effect of Theaflavin-3-gallate on cell cycle phase distribution. Theaflavin-3-gallate treatment led to a substantial cytotoxic effect in A-549 cancer cells with IC50 values of 42.1 μM and 27.9 μM at 24 and 48 hours respectively. Further, 80 and 160 μM dose of Theaflavin-3-gallate induced apoptotic features including chromatin margina-tion and micronuclei presence. The population of cells in G2/M phase increased from 2.7% (control) to 6.8%, 17.2% and finally to 46.5% after treatment with 20, 80 and 160 μM concentration of Theaflavin-3-gallate respectively indicating G2/M phase cell cycle arrest.
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Dec 24;56(24):12031-6.
Theaflavins from black tea, especially theaflavin-3-gallate, reduce the incorporation of cholesterol into mixed micelles.[Pubmed:
19049290]
Tea is one of the most widely consumed beverages in the world and may be associated with reduced heart disease rates. Theaflavins, which are formed in the production of black tea, have been suggested being responsible for the blood-cholesterol-lowering (BCL) effects of tea.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We hypothesized that the effect of theaflavins on BCL could be through interference in the formation of dietary mixed micelles, which could result in reduced intestinal cholesterol absorption. Micelles were produced by mixing oleic acid, bile acids, lyso-phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol. Theaflavin-treated micelles/particles were analyzed using electron microscopy (cryo-TEM), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, and light-scattering particle size measurements. A dose-dependent inhibitory effect of theaflavins on the incorporation of (14)C-labeled cholesterol into micelles and a theaflavin-dependent increase in particle size was found. These particles consisted of insoluble large multilamellar vesicles with onion-like structures. Ultracentrifugation and HPLC analysis revealed that the pellets contained mainly Theaflavin-3-gallate, while the remaining theaflavins were found to be present in the supernatant. Using purified theaflavin subtypes confirmed that mainly Theaflavin-3-gallate is responsible for multilamellar vesicle formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results show that theaflavins can play a role in decreased intestinal cholesterol absorption via inhibition of micelle formation.