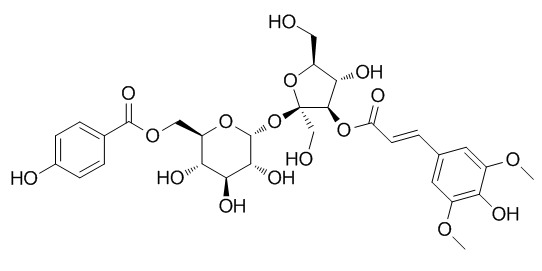
Tenuifoliside B
Tenuifoliside B is a target lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor. Tenuifoliside B has cognitive improving and cerebral protective effects. it can inhibit potassium cyanide (KCN)-induced hypoxia and scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
ACS Pharmacol.Transl.Sci.2024, 4c00003.
J Cell Physiol.2020, 10.1002
Phytother Res.2022, 35844057.
Molecules.2021, 26(4):1084.
J Liq Chromatogr R T2025, 2505536.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(5):2799.
Cytotechnology2022, s10616
Vietnam Journal of Food Control.2022, 5(2): 115-128.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(8):7300.
Molecules.2023, 28(3):1313.
Related and Featured Products
J Sep Sci. 2017 Mar;40(6):1385-1395.
Bioactivity screening, extraction, and separation of lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors from Polygala tenuifolia Willd. based on a hyphenated strategy.[Pubmed:
28134488]
Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors are currently widely used in the treatment of ischemic stroke, and natural products are considered promising sources of lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, ultrafiltration liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry was used for the screening and identification of lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors from Polygala tenuifolia. Furthermore, five lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors, sibiricose A5, 3,6'-di-O-sinapoyl-sucrose, glomeratose A, Tenuifoliside B, and tenuifoliside C, were selected as target lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors. In addition, the five target compounds with purities of 96.45, 97.65, 96.38, 94.34, and 93.29% were extracted and isolated using a new hyphenated strategy of microwave-assisted extraction coupled with countercurrent chromatography with a two-phase solvent system of n-hexane/n-butanol/ethanol/water (5.321:1.00:1.664:6.647). The bioactivities of the isolated compounds were analyzed using PC12 cells and the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results also demonstrated that microwave-assisted extraction coupled with countercurrent chromatography is an efficient method of isolating chemical constituents from medicinal herbs. Moreover, the research route consisting of activity screening, extraction, separation, and activity verification of the compounds has the advantages of being efficient, orientated, and objective.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 Jul;27(7):1081-5.
Cognitive improving and cerebral protective effects of acylated oligosaccharides in Polygala tenuifolia.[Pubmed:
15256744]
We studied the cognitive improving and cerebral protective constituents in the roots of Polygala tenuifolia Willdenow, a well-known Chinese traditional medicine prescribed for amnesia, neurasthenia, palpitation, noctural emission and insomnia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Tenuifoliside B (1), which is one of the acylated oligosaccharides in the roots of P. tenuifolia, showed the cerebral protective effect on potassium cyanide (KCN)-induced anoxia in mice, widely used as an animal model for cerebrovascular disease, and also had an ameliorative effect on the scopolamine-induced impairment of performance in passive avoidance task in rats. Compound 1 significantly enhanced oxotremorine-induced tremors in mice, suggesting that it ameliorated the scopolamine-induced impairment of passive avoidance response by enhancing the cholinergic system.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings show that compound 1 has cognitive improving and cerebral protective effects.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Mar;30(3):514-9.
Cerebral protective and cognition-improving effects of sinapic acid in rodents.[Pubmed:
17329848]
We previously demonstrated that Tenuifoliside B and 3,6'-disinapoylsucrose in Polygalae Radix, the root of Polygala tenuifolia WILLDENOW, inhibited potassium cyanide (KCN)-induced hypoxia and scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Because both ingredients have a common sinapoyl moiety in their structure, we inferred that the sinapoyl moiety could inhibit hypoxia and memory impairment.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study to clarify the hypothesis, sinapic acid inhibited KCN-induced hypoxia and scopolamine-induced memory impairment as well as Tenuifoliside B and 3,6'-disinapoylsucrose did. In addition, sinapic acid inhibited decompression- or bilateral carotid artery ligation-induced hypoxia (or mortality) and CO2-induced impairment in mice, and basal forebrain lesion-induced cerebral cholinergic dysfunction (decreases in acetylcholine concentration and choline acetyltransferase activity) in rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results, taken together, suggest the possibilities that sinapic acid is not only a very important moiety in the pharmacological activities of Tenuifoliside B and 3,6'-disinapoylsucrose but also a candidate for a cerebral protective and cognition-improving medicine.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Aug;42(16):3167-3177.
Analysis of influencing factors of secondary metabolites contents in cultivated Polygala tenuifolia.[Pubmed:
29171237]
This work was launched to explore the effect of habitat and growth year on the secondary metabolites contents of cultivated Polygala tenuifolia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The samples of cultivated P. tenuifolia were analyzed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography(UPLC)-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry(Q-TOF MS), and the obtained data were analyzed using multiple statistical analysis and cluster analysis. The results showed that compared with growth year, habitat is a main influencing factor which affected the secondary metabolites contents of P. tenuifolia. The contents of sucrose esters and oligosacchride multi-esters are greatly dependent on the habitat (the sample-AG with high levels of components of Tenuifoliside B and tenuifoliside C, and the sample-FY with high levels of 3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose, tenuifoliose S, tenuifoliose L, and tenuifoliose V). There is no obvious effect of habitat and growth year on xanthone. The contents of triterpene saponins are greatly dependent on the growth year, and the content of parts of triterpene saponins increased as time goes on.
CONCLUSIONS:
The result indicated that the effect of habitat and growth year on different types of secondary metabolites is not completely equivalent. This study will contribute to the breeding of P. tenuifolia and amendment of current commodity criteria.