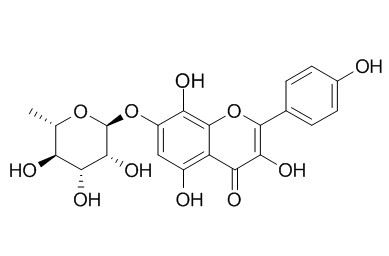
Rhodionin
Rhodionin and rhodionin can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with high specificity which could have implications for interactions with co-administered drugs; they can significantly suppress the elevation of the postprandial blood triglyceride level, suggests that they may be to the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and to health foods. Rhodionin has antioxidant activity, it exhibits potent 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging activities, with IC50 values of 19.49 ± 0.21 uM.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2023, 28(19):6775.
Tokyo Pharmaceutical University2020, 500001431953.
Journal of Ginseng Research2019, 10.1016
Molecules2022, 27(3),1140.
ACS Chem Biol.2019, 14(5):873-881
Molecules.2020, 25(23):5636.
Molecules.2018, 23(3):E615
The Korea Journal of Herbology2016, 29-35
Histol Histopathol.2022, 18518.
Saudi Pharm J.2019, 27(1):145-153
Related and Featured Products
Molecules. 2012 Sep 27;17(10):11484-94.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. BOR.[Pubmed:
23018923]
Isolation of compounds from the root of Rhodiola sachalinensis (RRS) yielded tyrosol (1), salidroside (2), multiflorin B (3), kaempferol-3,4'-di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), afzelin (5), kaempferol (6), Rhodionin (7), and rhodiosin (8).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Quantification of these compounds was performed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). To investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the compounds, DPPH radical scavenging, NBT superoxide scavenging and nitric oxide production inhibitory activities were examined in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells. We suggest that the major active components of RRS are herbacetin glycosides, exhibiting antioxidant activity, and kaempferol, exhibiting anti-inflammatory activity.In this study, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity and nitrotetrazolium blue chloride (NBT) superoxide scavenging activity were measured to assess the antioxidant activity of the components from RRS. DPPH has the ability to easily accept hydrogen atoms because it contains an unstable element, the hydrazyl nitrogen, therefore, antioxidant activity can be measured because DPPH loses its violet color when it receives hydrogens from antioxidants [18]. Additionally, NBT has the ability to easily receive superoxide because it contains unstable anions. Therefore, antioxidant activity may be measured when NBT loses its yellow color upon reaction with abundant superoxide [19]. Among the compounds from RRS, 7(Rhodionin) and 8 exhibited the most potent DPPH free radical scavenging activities, with IC50 values of 19.49 ± 0.21 and 27.77 ± 0.61 μM, respectively, compared to the positive control, L-ascorbic acid (IC50 = 32.89 ± 0.70 μM). The other compounds did not exhibit activities in this assay up to 100 μM (Table 2).
Planta Med. 2008 Nov;74(14):1716-9.
Constituents of Rhodiola rosea showing inhibitory effect on lipase activity in mouse plasma and alimentary canal.[Pubmed:
18982538 ]
As a methanol extract of the rhizome of Rhodiola rosea inhibits the activity of lipase in isolated mouse plasma in vitro and in the mouse gastrointestinal tube in vivo, the active components in this plant were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After fractionation and separation processes, Rhodionin and rhodiosin were isolated as active ingredients. Their IC50 values were 0.093 mM and 0.133 mM in vitro, respectively. Both compounds significantly suppressed the elevation of the postprandial blood triglyceride level, e.g., by 45.6 % (150 mg/kg, 60 min after oral administration) and 57.6 % (200 mg/kg, 180 min after oral administration), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Consequently, we anticipate the application of this plant and its constituents to the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hyperlipidemia and exogeneous obesity and to health foods.
Pharmazie. 2013 Dec;68(12):974-6.
Two potent cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors found in Rhodiola rosea.[Pubmed:
24400445]
Throughout the world, in particular in Russia, Northern Europe and China, Rhodiola species are used as herb supplements. Previously, we found that the extract of Rhodiola rosea, one of the most widely used Rhodiola species, had an inhibitory effect on the catalytic activity of cytochrome P450 2D6. Here, its inhibitory components were identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A human liver microsomal in vitro system was used with dextromethorphan as substrate. The production rate of destrorphan, a metabolite of dextromethorphan, was used to measure enzyme activity. The concentration of destrorphan in the samples was measured using LC-MS/MS. Inhibitory activity of eight main components from Rhodiola rosea was evaluated.
Rhodiosin and Rhodionin showed inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.761 microM and 0.420 microM, respectively. The other components showed no obvious inhibition (with a residual enzyme activity of more than 90%). Both rhodiosin and Rhodionin were determined to be non-competitive inhibitors with Ki values of 0.769 microM and 0.535 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
Two of the main Rhodiola rosea compounds, rhodiosin and Rhodionin, can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 non-competitively with high specificity which could have implications for interactions with co-administered drugs.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Jun;56(6):807-14.
Identification and comparative determination of rhodionin in traditional tibetan medicinal plants of fourteen Rhodiola species by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:
18520085]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using the HPLC/PDA/ESI/MS method, a comparative analysis of Rhodionin (RH) was undertaken in order to conduct a qualitative and quantitative study in 38 batches of fourteen species of Rhodiola for quality control purposes. Alongside of this RH analysis, a simultaneous determination of salidroside (SA), tyrosol (TY), and gallic acid (GA) was carried out. Rhodiola plants are a popularly used ethnodrug from the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau of China. The identity of RH was unambiguously determined based on the quasimolecular ions in negative ESI-MS mode. This method was validated in respect to sensitivity, linearity, precision, repeatability and recovery using optimized chromatographic conditions. The linear calibration curve was acquired with R(2)>0.999, and the limit of detection (S/N=3) was estimated to be 43.75 microg/g. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of the intra- and inter-day precisions were 0.75% and 0.50%, respectively. The repeatability was evaluated by a replicated analysis of samples with the RSD value found within 0.67%. The recovery rates varied within the range of 98.79-100.08% with RSD less than 1.10%. In the present study, the content of RH was quantified within 0.4192-4.7260 mg/g for 16 batches of R. crenulata. It was also found in eight other species plants.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrated that RH is a useful characteristic standard compound for quality evaluation and chemical differentiation among species of Rhodiola. The study also indicated that the analytical procedure is precise, reproducible and a potential tool for both quality assessment and species identification.
J Sep Sci. 2014 Sep;37(17):2314-21.
Application and recovery of ionic liquids in the preparative separation of four flavonoids from Rhodiola rosea by on-line three-dimensional liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:
24916654]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A novel on-line three-dimensional liquid chromatography method was developed to separate four main flavonoids from Rhodiola rosea. Ethyl acetate/0.5 mol/L ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride aqueous solution was selected as the solvent system. In the first-dimension separation, the target flavonoids were entrapped and subsequently desorbed into the second-dimension high-speed countercurrent chromatographic column for separation. In the third-dimension chromatography, the residual ionic liquid in the four separated flavonoids was removed and the used ionic liquid was recovered. As a result, 35.1 mg of compound 1, 20.4 mg of compound 2, 8.5 mg of compound 3, and 10.6 mg of compound 4 were obtained from 1.53 g R. rosea extract. They were identified as rhodiosin, Rhodionin, herbacetin, and kaempferol, respectively. The recovery of ionic liquid reached 99.1% of the initial amount.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results showed that this method is a powerful technology for the separation of R. rosea flavonoids and that the ionic-liquid-based solvent system has advantages over traditional solvent systems in renewable and environmentally friendly properties.