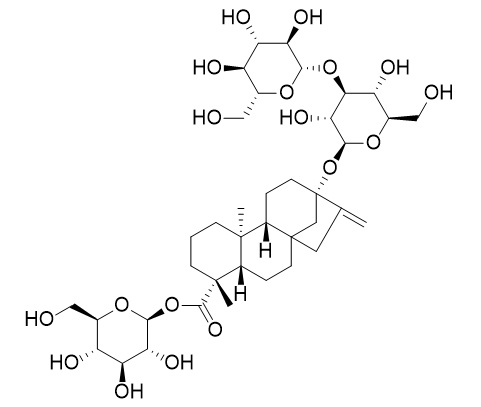
Rebaudioside G
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Vet Sci.2020, 21(3):e39.
Drug Des Devel Ther.2020, 14:5189-5204.
Journal of Functional Foods2017, 30:30-38
Eur J Pharmacol.2022, 917:174744.
J Anal Toxicol.2021, bkab015.
J Control Release.2024, 375:300-315.
Foods2023, 12(23), 4342.
Food Quality and Safety2018, 2:213-219
Int J Cosmet Sci.2019, 41(1):12-20
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 18(12)
Related and Featured Products
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 403(9):2683-2690.
Shafii B , Vismeh R , Randy Beaudry…. Large-scale profiling of diterpenoid glycosides fromStevia rebaudianausing ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.[Reference:
WebLink]
The plant Stevia rebaudiana accumulates a suite of diterpenoid metabolites that are natural sweeteners finding increased use as sugar substitutes. To guide breeding of stevia plants that accumulate substances with desirable flavor in high yield, rapid and accurate methods are needed to profile these substances in plant populations.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This report describes an 8-min ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for separation and quantification of seven stevia glycosides including steviolbioside; stevioside; rebaudioside A, rebaudioside B, and rebaudioside C; rubusoside; and dulcoside as well as aglycones steviol and isosteviol. This negative mode electrospray ionization/multiple reaction monitoring method yielded low limits of detection <1 ng/mL for steviol, 6 ng/mL for isosteviol, and <15 ng/mL for all stevia glycosides. Stevioside and Reb A, B, and C were quantified in more than 1,100 extracts from stevia leaves as part of a large-scale profiling exercise. Leaf tissue levels in this population spanned about two orders of magnitude for stevioside (2–125 mg/g dry weight), Reb A (2.5–164 mg/g), Reb B (0.5–50 mg/g), and Reb C (1.5–125 mg/g), but levels of individual metabolites exhibited independent variation.
CONCLUSIONS:
The wide spread of metabolite levels highlights the utility and importance of performing targeted metabolic profiling for large plant populations.