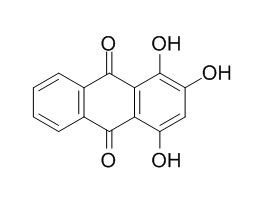
Purpurin
Purpurin is one of the natural colorants extracted from madder roots and other Rubiaceae family plants. Purpurin is a novel specific inhibitor of Adipocyte-derived leucine aminopeptidase, it exhibits anti-angiogenic, antifungal, antibiotic, and antioxidative activities.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biomolecules.2022, 12(12):1754.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 326:117902.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(17):9673.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:5319584.
Biomolecules.2019, 9(11):E696
Phytomedicine.2018, 38:12-23
Prev Nutr Food Sci.2024, 29(4):563-571.
J Agric Food Chem.2020, 68(51):15164-15175
Asian J Beauty Cosmetol2024, 22(1): 103-112.
Journal of Functional Foods2019, 52:430-441
Related and Featured Products
Chin J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;11(4):396-400.
Effects of lovastatin, clomazone and methyl jasmonate treatment on the accumulation of purpurin and mollugin in cell suspension cultures of Rubia cordifolia.[Pubmed:
23845549]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Content determination of Purpurin (AQs) and mollugin (NQs) were carried out using RP-HPLC. The yield of the two compounds was compared with the DMSO-supplied group and the possible mechanism was discussed. Lovastatin treatment increased the yield of Purpurin and mollugin significantly. Clomazone treatment resulted in a remarkable decrease of both compounds. In the MeJA-treated cells, the Purpurin yield increased, meanwhile, the mollugin yield decreased compared with control.
CONCLUSIONS:
The IPP origin of mollugin in R. cordifolia cell suspension cultures was likely from the MEP pathway. To explain the different effects of MeJA on Purpurin and NQs accumulation, studies on the regulation and expression of the genes, especially after prenylation of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid should be conducted.
PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50866.
Purpurin suppresses Candida albicans biofilm formation and hyphal development.[Pubmed:
23226409]
We have previously demonstrated the novel antifungal activity of Purpurin against Candida fungi.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we extended our investigation by examining the in vitro effect of Purpurin on C. albicans morphogenesis and biofilms. The susceptibility of C. albicans biofilms to Purpurin was examined quantitatively by 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfo-phenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide reduction assay. Hyphal formation and biofilm ultrastructure were examined qualitatively by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to evaluate the expression of hypha-specific genes and hyphal regulator in Purpurin-treated fungal cells. The results showed that, at sub-lethal concentration (3 μg/ml), Purpurin blocked the yeast-to-hypha transition under hypha-inducing conditions. Purpurin also inhibited C. albicans biofilm formation and reduced the metabolic activity of mature biofilms in a concentration-dependent manner. SEM images showed that Purpurin-treated C. albicans biofilms were scanty and exclusively consisted of aggregates of blastospores. qRT-PCR analyses indicated that Purpurin downregulated the expression of hypha-specific genes (ALS3, ECE1, HWP1, HYR1) and the hyphal regulator RAS1. The data strongly suggested that Purpurin suppressed C. albicans morphogenesis and caused distorted biofilm formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
By virtue of the ability to block these two virulence traits in C. albicans, Purpurin may represent a potential candidate that deserves further investigations in the development of antifungal strategies against this notorious human fungal pathogen in vivo.
Psychopharmacology (Berl) . 2020 Mar;237(3):887-899.
Purpurin exerted antidepressant-like effects on behavior and stress axis reactivity: evidence of serotonergic engagement[Pubmed:
31900524]
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Major depression represents a significant public health problem worldwide, and effective regimen is lacking. The present study investigated the antidepressant-like effects of Purpurin, a natural anthraquinone compound from Rubia tinctorum L., and explored the underlying mechanism(s).
Methods: Forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) were used to assess antidepressant-like effects of Purpurin in mice. Effects of Purpurin on neuroendocrine responsivity were evaluated at the level of corticosterone and ACTH following acute restraint stress and intracerebroventricular injection of corticotrophin-releasing-factor (CRF). Serotonergic mechanisms underlying Purpurin antidepressant effect were explored using biochemical, neurochemical, and pharmacological paradigms.
Results: Chronic Purpurin treatment exerted in mice dose-dependently antidepressant-like effects on behavior and stress axis reactivity (n = 9-11 per group). The Purpurin-triggered antidepressant-like effects are serotonergically dependent, since Purpurin-treated mice showed escalated levels of brain serotonin and suppressed monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity (n = 8-11 per group). Consistently, chemical depletion of brain serotonin by p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA) abolished the antidepressant-like effects of Purpurin on behavior and stress axis responsivity (n = 9-10 per group). Moreover, the antidepressant effect by Purpurin was preferentially counteracted by 1A-selective 5-HT receptor antagonist WAY-100635, but potentiated by 1A-selective agonist 8-OH-DPAT and sub-effective dose of serotonergic antidepressant fluoxetine (n = 9-11 per group), suggesting a crucial role for 5-HT1A related serotonergic system in mediating such Purpurin antidepressant effect.
Conclusion: We have revealed the antidepressant-like effects of Purpurin on both behavior and stress axis reactivity in mice, with serotonergic system that preferentially couples with 5-HT1A receptors being critically engaged.
Keywords: Antidepressant-like effect; Purpurin; Serotonin; Stress.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jul 18;450(1):561-7.
Purpurin inhibits adipocyte-derived leucine aminopeptidase and angiogenesis in a zebrafish model.[Pubmed:
24928393]
A natural product Purpurin was identified as one of the most potent inhibitors of A-LAP from the screening.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vitro enzymatic analyses demonstrated that Purpurin inhibited A-LAP activity in a non-competitive manner with a Ki value of 20 M. In addition, Purpurin showed a strong selectivity toward A-LAP versus another member of M1 family of zinc metallopeptidase, aminopeptidase N (APN). In angiogenesis assays, Purpurin inhibited the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced invasion and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Moreover, Purpurin inhibited in vivo angiogenesis in zebrafish embryo without toxicity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data demonstrate that Purpurin is a novel specific inhibitor of A-LAP and could be developed as a new anti-angiogenic agent.
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015 Apr 24.
Structural and optical properties of Purpurin for dye-sensitized solar cells.[Pubmed:
26037779]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, we reported a combined experimental and theoretical study on molecular structure, vibrational spectra and Homo-Lumo analysis of Purpurin and TiO2/Purpurin. The geometries, electronic structures, molecular orbital analysis of natural dye sensitizer Purpurin were studied based on density functional theory (DFT) using the hybrid functional B3LYP. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and FT-Raman spectra have been recorded and extensive spectroscopic investigations have been carried out on Purpurin. The optimized geometries, wave number and intensity of the vibrational bands of Purpurin have been calculated using density functional level of theory (DFT/B3LYP) employing 6-311G (d,p) basis set. Based on the comparison between calculated and experimental results, assignments of the fundamental vibrational modes are examined. Interaction between HOMO and LUMO of Purpurin are investigated to understand the recombination process and charge transfer process involving these dyes.
CONCLUSIONS:
We also performed analysis of I-V characteristics to investigate the role of charge transfer and the stability of the dye molecule.