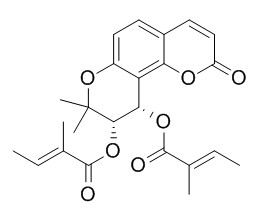
Praeruptorin D
Praeruptorin D exhibits antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities, it protects mice from hydrochloric acid (HCl)-induced lung injury by inhibiting PMNs influx, IL-6 release and protein exudation. Praeruptorin D can significantly up-regulate CYP3A4 expression and activity via the Pregnane X receptor (PXR)-mediated pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Heliyon.2023, 9(11):e21944.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 335:118628.
Plants (Basel).2023, 12(6):1259.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2014, 14:242
Molecules.2020, 25(21):5091.
J Ethnopharmacol.2018, 210:88-94
Food Addit Contam Part A.2021, 38(12):1985-1994.
J Biomol Struct Dyn.2024, 1-12.
Phytomedicine.2022, 100:154085.
Pharmacogn Mag.2015, 11(43):562-6
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 9;148(2):596-602.
Up-regulatation of CYP3A expression through pregnent X receptor by praeruptorin D isolated from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn.[Pubmed:
23702042 ]
Qianhu, the dried roots of Peucedanum praeruptorum DUNN (Umbelliferae), is a well-known traditional Chinese medicinal herb which was officially listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Praeruptorin D (PD) is one of the major active constituents of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn (Qianhu). The Pregnane X receptor (PXR) is an orphan nuclear receptor and plays a pivotal role in the activation of human cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) gene.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of PD on the PXR-mediated transactivation of CYP3A4, and thus to predict potential herb-drug interactions between PD, Qianhu, and the other co-administered drugs that metabolized by CYP3A4.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of PD on the Cyp3a11, mPXR mRNA expression in mice primary hepatocytes was measured using real-time PCR. The gene expression, protein expression, and catalytic activity of CYP3A4 in the LS174T cells after transfected with PXR expression plasmids were determined by real-time PCR, Western blot analysis, and LC-MS/MS based CYP3A4 substrate assay.
The results revealed that the level of Cyp3a11 gene expression in mice primary hepatocytes was significantly increased by PD, but PD cannot induce the mPXR gene expression. On the other hand, CYP3A4 mRNA, protein expression and functional activity in PXR-over-expression LS174T cells were significantly increased by PD through PXR-mediated pathway; conversely, no significant change was found in the untransfected cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that PD can significantly up-regulate CYP3A4 expression and activity via the PXR-mediated pathway and this should be taken into consideration to predict any potential herb-drug interactions when PD and Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn are co-administered with other drugs.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jun 15;710(1-3):39-48.
Praeruptorin D and E attenuate lipopolysaccharide/hydrochloric acid induced acute lung injury in mice.[Pubmed:
23588118]
Acute lung injury is a life-threatening syndrome characterized by overwhelming lung inflammation and increased microvascular permeability, which causes a high mortality rate worldwide. The dry root of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn has been long used to treat respiratory diseases in China.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, Praeruptorin A, C, Praeruptorin D and E (PA, PC, PD and PE), four pyranocoumarins extracted from this herb, have been investigated for the pharmacological effects in experimental lung injury mouse models. Praeruptorin D and PE significantly inhibited the infiltration of activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and decreased the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid at the same dose. There was no statistically significant difference between Praeruptorin D and PE group. Further study demonstrated that Praeruptorin D and PE suppressed protein extravasations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, attenuated myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and the pathological changes in the lung. Both Praeruptorin D and PE suppressed LPS induced Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway activation in the lung by decreasing the cytoplasmic loss of Inhibitor κB-α (IκB-α) protein and inhibiting the translocation of p65 from cytoplasm to nucleus.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggested that Praeruptorin D and PE might be useful in the therapy of lung injury.
Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(7):9129-41.
Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of Praeruptorin D from Radix peucedani in rats by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).[Pubmed:
22942756 ]
Praeruptorin D (PD), a major pyranocoumarin isolated from Radix Peucedani, exhibited antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities. The aim of this study was to investigate the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of PD in rats following intravenous (i.v.) administration.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The levels of PD in plasma and tissues were measured by a simple and sensitive reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. The biosamples were treated by liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) with methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and osthole was used as the internal standard (IS). The chromatographic separation was accomplished on a reversed-phase C(18) column using methanol-water (75:25, v/v) as mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min and ultraviolet detection wave length was set at 323 nm.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrate that this method has excellent specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy and recovery. The pharmacokinetic study found that PD fitted well into a two-compartment model with a fast distribution phase and a relative slow elimination phase. Tissue distribution showed that the highest concentration was observed in the lung, followed by heart, liver and kidney. Furthermore, PD can also be detected in the brain, which indicated that PD could cross the blood-brain barrier after i.v. administration.