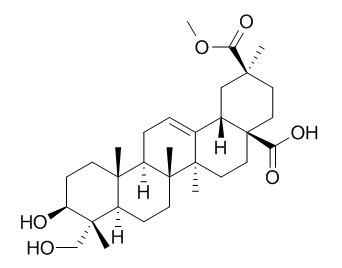
Phytolaccagenic acid
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Curr Eye Res.2018, 43(1):27-34
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(22):12152.
Eur J Pharmacol.2018, 832:96-103
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(22), 10552
Protoplasma.2024, 261(6):1267-1280.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(2):764.
JABS2020, 14:2(2020)
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 321:117501.
Sci Rep.2019, 9:19059
Molecules.2024, 29(17):4034.
Related and Featured Products
J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Nov 16;64(45):8583-8591.
GC-MS Profiling of Triterpenoid Saponins from 28 Quinoa Varieties (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Grown in Washington State.[Pubmed:
27525448]
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) contains 2 to 5% saponins in the form of oleanane-type triterpenoid glycosides or sapogenins found in the external layers of the seeds. These saponins confer an undesirable bitter flavor.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study maps the content and profile of glycoside-free sapogenins from 22 quinoa varieties and 6 original breeding lines grown in North America under similar agronomical conditions.
Saponins were recovered using a novel extraction protocol and quantified by GC-MS. Oleanolic acid (OA), hederagenin (HD), serjanic acid (SA), and Phytolaccagenic acid (PA) were identified by their mass spectra. Total saponin content ranged from 3.81 to 27.1 mg/g among the varieties studied. The most predominant sapogenin was Phytolaccagenic acid with 16.72 mg/g followed by hederagenin at 4.22 mg/g representing the ~70% and 30% of the total sapogenin content. Phytolaccagenic acid and the total sapogenin content had a positive correlation of r2 = 0.88 (p < 0.05). Results showed that none of the varieties we studied can be classified as "sweet". Nine varieties were classified as "low-sapogenin". We recommend six of the varieties be subjected to saponin removal process before consumption.
CONCLUSIONS:
A multivariate analysis was conducted to evaluate and cluster the different genotypes according their sapogenin profile as a way of predicting the possible utility of separate quinoa in food products. The multivariate analysis showed no correlations between origin of seeds and saponin profile and/or content.