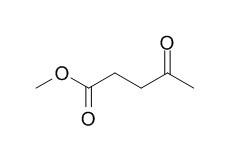
Methyl levulinate
Methyl levulinate is a natural product from Rauvolfia vomitoria.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Life Sci.2021, 286:120019.
Eur J Pharmacol.2021, 906:174220.
J Cell Mol Med.2023, jcmm.17968.
Food Chem.2024, 452:139555.
Life (Basel).2023, 13(2):457.
J Appl Biol Chem.2024, 67:33,238-244
Molecules.2019, 24(2):E343
Int Immunopharmacol.2023, 123:110572.
Foods.2022, 11(6):882.
J Control Release.2021, 336:159-168.
Related and Featured Products
ChemSusChem. 2015 May 11;8(9):1601-7.
In Situ Catalytic Hydrogenation of Biomass-Derived Methyl Levulinate to γ-Valerolactone in Methanol.[Pubmed:
25873556]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, the hydrocyclization of Methyl levulinate (ML) to γ-valerolactone (GVL) was performed in MeOH over an in situ prepared nanocopper catalyst without external H2 . This nanocopper catalyst served as a dual-functional catalyst for both hydrogen production by MeOH reforming and hydrogenation of ML. Nearly quantitative ML conversion with a GVL selectivity of 87.6 % was achieved at 240 °C in 1 h in MeOH under a nitrogen atmosphere. ML in the methanolysis products of cellulose also could be hydrogenated effectively to GVL over this nanocopper catalyst even in the presence of humins to give an ML conversion of 94.1 % and a GVL selectivity of 73.2 % at 240 °C in 4 h.
CONCLUSIONS:
The absorption behavior of humins on the surface of the nanocopper catalyst was observed, which resulted in a pronounced increase in the acidic sites of the nanocopper catalyst that facilitate ring-opening and the hydrocarboxylation/alkoxycarbonylation of GVL to byproducts.
Carbohydr Res. 2012 Sep 1;358:37-9.
One-pot preparation of methyl levulinate from catalytic alcoholysis of cellulose in near-critical methanol.[Pubmed:
22841826]
One-pot preparation of Methyl levulinate (MLA) from cellulose in near-critical methanol was studied.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Acids containing SO(3)H group were proven to be effective catalysts for the production of MLA from cellulose's catalytic alcoholysis. The effects of different reaction conditions, such as an initial cellulose concentration of 10-30 g/L, a temperature range from 170 to 190°C, and a sulfuric acid concentration of 0.01-0.03 mol/L, on the production of MLA were investigated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results showed the reaction temperature and acid concentration significantly affected the process of cellulose alcoholysis and the yield of MLA. A high yield of up to 55% MLA was achieved at 190°C for 5h, using 0.02 mol/L H(2)SO(4) as a catalyst.