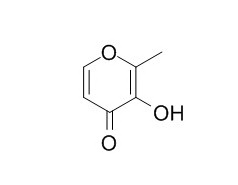
Maltol
Maltol is a naturally occurring organic compound that is flavour enhancer and flavouring agent. Maltol has neuroprotective effects against hypoxia-induced neuroretinal cell damage in R28 cells, and it has potential as a new neuroprotective therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related ocular diseases, including glaucoma.Maltol exhibits hepatoprotective effect on alcohol-induced liver oxidative injury, may due to its potent antioxidant properties.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J of the Korean Society of Cosmetics and Cosmetology2019, 225-231
Mol Pharm.2017, 14(9):3164-3177
Molecules.2023, 28(10):4121.
Molecules.2017, 22(12)
Food Res Int.2022, 157:111397.
J AOAC Int.2024, qsae028.
Phytochem Anal.2022, doi: 10.1002
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2093.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(9):1435.
Pest Manag Sci.2019, 75(9):2530-2541
Related and Featured Products
Mol Vis. 2014 Oct 17;20:1456-62.
Neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth effects of maltol on retinal ganglion cells under oxidative stress.[Pubmed:
25352751]
To evaluate the neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth effects of Maltol, a natural aroma compound, on retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) under oxidative stress in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Mouse primary RGCs were isolated using immunopanning-magnetic separation and exposed to H2O2 in the presence of Maltol. The cell viability and apoptosis were determined by using adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) assay and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end labeling (TUNEL), respectively. Neurite outgrowth was assessed by immunofluorescence for α-tubulin. The activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) was also evaluated using immunofluorescence. When the RGCs were exposed to 20 μM of H2O2 for 16 h, their viability dropped to 40.3±3.4%. However, the Maltol treatment restored the cells in a dose-dependent manner. The viability recovered to 73.9±5.1% with 10 μM of Maltol and even reached 175.1±11.3% with 2 mM of Maltol, as measured by ATP assay. This oxidative stress significantly increased the number of TUNEL-positive RGCs, but the Maltol drastically reduced the proportion of those apoptotic cells. The oxidative stress hampered the neurite outgrowth of the RGCs, whereas Maltol restored their ability to sprout neurites. Regarding NF-κB, the active form of phosphorylated NF-κB (pNF-κB) increased the oxidative stress level but the Maltol treatment again reduced it to an unstressful level.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data revealed that Maltol attenuated the oxidative stress-induced injury in the primary mouse RGCs. Its neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth effects seemed to be related to NF-κB signaling. Maltol has potential as a new neuroprotective therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related ocular diseases, including glaucoma.
Nutrients. 2015 Jan 20;7(1):682-96.
Maltol, a food flavoring agent, attenuates acute alcohol-induced oxidative damage in mice.[Pubmed:
25608939]
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of Maltol, a food-flavoring agent, on alcohol-induced acute oxidative damage in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Maltol used in this study was isolated from red ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A Meyer) and analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry. For hepatoprotective activity in vivo, pretreatment with Maltol (12.5, 25 and 50 mg/kg; 15 days) drastically prevented the elevated activities of aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and triglyceride (TG) in serum and the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in liver tissue (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the levels of hepatic antioxidant, such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) were elevated by Maltol pretreatment, compared to the alcohol group (p < 0.05). Histopathological examination revealed that Maltol pretreatment significantly inhibited alcohol-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and fatty degeneration. Interestingly, pretreatment of Maltol effectively relieved alcohol-induced oxidative damage in a dose-dependent manner. Maltol appeared to possess promising anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacities.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was suggested that the hepatoprotective effect exhibited by Maltol on alcohol-induced liver oxidative injury may be due to its potent antioxidant properties.
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb;29(1):58-65.
The neuroprotective effect of maltol against oxidative stress on rat retinal neuronal cells.[Pubmed:
25646062]
Maltol (3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone), formed by the thermal degradation of starch, is found in coffee, caramelized foods, and Korean ginseng root. This study investigated whether Maltol could rescue neuroretinal cells from oxidative injury in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
R28 cells, which are rat embryonic precursor neuroretinal cells, were exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 0.0 to 1.5 mM) as an oxidative stress with or without Maltol (0.0 to 1.0 mM). Cell viability was monitored with the lactate dehydrogenase assay and apoptosis was examined by the terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated terminal uridine deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method. To investigate the neuroprotective mechanism of Maltol, the expression and phosphorylation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 were evaluated by Western immunoblot analysis. R28 cells exposed to H2O2 were found to have decreased viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. However, H2O2-induced cytotoxicity was decreased with the addition of Maltol. When R28 cells were exposed to 1.0 mM H2O2 for 24 hours, the cytotoxicity was 60.69 ± 5.71%. However, the cytotoxicity was reduced in the presence of 1.0 mM Maltol. This H2O2-induced cytotoxicity caused apoptosis of R28 cells, characterized by DNA fragmentation. Apoptosis of oxidatively-stressed R28 cells with 1.0 mM H2O2 was decreased with 1.0 mM Maltol, as determined by the TUNEL method. Western blot analysis showed that treatment with Maltol reduced phosphorylation of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK, but not p38. The neuroprotective effects of Maltol seemed to be related to attenuated expression of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK.
CONCLUSIONS:
Maltol not only increased cell viability but also attenuated DNA fragmentation. The results obtained here show that Maltol has neuroprotective effects against hypoxia-induced neuroretinal cell damage in R28 cells, and its effects may act through the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
Food Chem. 2012 Jul 15;133(2):264-70.
Multispectroscopic studies on the interaction of maltol, a food additive, with bovine serum albumin.[Pubmed:
25683394]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The interaction between Maltol, a food additive, and bovine serum albumin (BSA) under simulated physiological conditions was investigated by fluorescence, UV-Vis absorption, circular dichroism (CD) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. The results suggested that the fluorescence quenching of BSA by Maltol was a static procedure forming a Maltol-BSA complex. The positive values of enthalpy change and entropy change indicated that hydrophobic interactions played a predominant role in the interaction of Maltol with BSA. The competitive experiments of site markers revealed that the binding of Maltol to BSA mainly took place in subdomain IIA (Sudlow site I). The binding distance between Maltol and BSA was 3.01 nm based on the Förster theory of non-radioactive energy transfer. The interaction between Maltol, a food additive, and bovine serum albumin (BSA) under simulated physiological conditions was investigated by fluorescence, UV-Vis absorption, circular dichroism (CD) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. The results suggested that the fluorescence quenching of BSA by Maltol was a static procedure forming a Maltol-BSA complex.
CONCLUSIONS:
The positive values of enthalpy change and entropy change indicated that hydrophobic interactions played a predominant role in the interaction of Maltol with BSA. The competitive experiments of site markers revealed that the binding of Maltol to BSA mainly took place in subdomain IIA (Sudlow site I). The binding distance between Maltol and BSA was 3.01 nm based on the Förster theory of non-radioactive energy transfer. Moreover, the results of UV-Vis, synchronous fluorescence, CD and FT-IR spectra demonstrated that the microenvironment and the secondary structure of BSA were changed in the presence of Maltol.Moreover, the results of UV-Vis, synchronous fluorescence, CD and FT-IR spectra demonstrated that the microenvironment and the secondary structure of BSA were changed in the presence of Maltol.