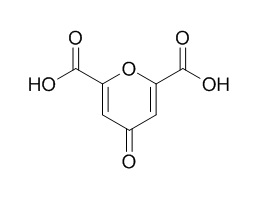
Chelidonic acid
Chelidonic acid is a component of Chelidonium majus L., used as a mild analgesic, an antimicrobial, an acentral nervous system sedative. Chelidonic acid also shows anti-inflammatory activity. Chelidonic acid has potential to inhibit IL-6 production by blocking NF-κB and caspase-1. Chelidonic acid is a glutamate decarboxylase inhibitor, with a Ki of 1.2 μM.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Braz J Biol.2023, 82:e266573.
VNU Journal of Science2023, 39(2):24-33.
Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology 2022, 34,53-62
Processes2020, 8(12),1540.
Front Plant Sci.2020, 11:630.
Food Chem.2024, 446:138870.
Pharm Biol.2022, 60(1):2040-2048.
Materials Today Communications2023, 37:107216
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2017, 494(3-4):587-593
Molecules.2024, 29(16):3976.
Related and Featured Products
Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:229-234.
Effects of chelidonic acid, a secondary plant metabolite, on mast cell degranulation and adaptive immunity in rats.[Pubmed:
27620504 ]
The present study evaluated the immunomodulatory effects of Chelidonic acid, a secondary plant metabolite, with therapeutic potential in allergic disorders, in experimental animals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In mast cell degranulation studies, ovalbumin immunized and challenged rats, Chelidonic acid (1, 3 and 10mg/kg, i.p.) dose relatedly prevented ovalbumin challenge induced mast cell degranulation by differing degrees when compared with vehicle treated group, and these effects were comparable with prednisolone (10mg/kg). A reduction in post-challenge mortality was also observed in all treated groups. Further, there were reductions in the blood eosinophil counts and serum IgE levels after Chelidonic acid treatment. Chelidonic acid also inhibited histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMC) in vitro, in a dose related manner. In tests for adaptive immunity, in rats immunized with sheep RBC, Chelidonic acid differentially suppressed the (a) plaque forming cell (PFC) count in rat splenic cells, (b) anti-SRBC antibody titre and serum IgG levels and (c) increases in foot pad thickness in the DTH assay - all of which were comparable with prednisolone.
CONCLUSIONS:
These experimental results are discussed in light of the possible therapeutic potential of Chelidonic acid in allergic disorders.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Aug;241(14):1559-67.
Chelidonic acid evokes antidepressant-like effect through the up-regulation of BDNF in forced swimming test.[Pubmed:
27037280 ]
Depression is usually accompanied by neuro-inflammatory reactions. Chelidonic acid, in particular, has shown anti-inflammatory effects.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the anti-depressant effects of Chelidonic acid and to discuss the potential mechanisms of a forced swimming test.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chelidonic acid was administered orally once a day for 14 days. On the 14th day, Chelidonic acid resulted in a significant decrease in immobility time during the forced swimming test without alteration of locomotor activity, in an open field test. Chelidonic acid also increased the number of nissl bodies in the hippocampus. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase phosphorylation in the hippocampus were up-regulated by the administration of Chelidonic acid. Chelidonic acid administration significantly increased the mRNA expression of hippocampal estrogen receptor-β. The levels of hippocampal interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α were effectively attenuated by the administration of Chelidonic acid. In addition, Chelidonic acid significantly increased the levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), dopamine, and norepinephrine compared with those levels for the mice that were administered distilled water in the hippocampus.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Chelidonic acid might serve as a new therapeutic strategy for the regulation of depression associated with inflammation.