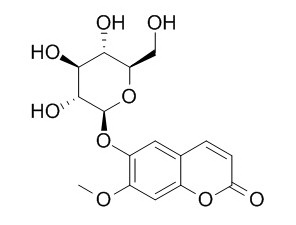
Magnolioside
Magnolioside has anti-plasmodial activity, shows notable growth inhibitory activity against chloroquine-sensitive strains of P. falciparum. It also shows a moderate antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus CIP 53.154.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176749.
J Chromatogr A.2022, 1685:463640.
Molecules2022, 27(9):2827.
J Nat Med.2018, 72(3):734-744
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(10):5813.
Materials Today Communications2023, 37:107216
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2018, 151:32-41
Food Funct.2022, 13(23):12105-12120.
Adv Healthc Mater.2024, 13(13):e2303276.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(7):6360.
Related and Featured Products
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2011 Dec;33(4):663-6.
Antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activity of coumarin derivatives from dried roots of Angelica gigas Nakai in vitro.[Pubmed:
21428713]
The butanol-soluble fraction of the dried root of Angelica gigas exhibited significant protection against chloroquine-sensitive strains of Plasmodium falciparum using the parasite lactate dehydrogenase assay method.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using antiplasmodial activity-guided fractionation, five coumarins, marmesinin (1), nodakenin (2), skimmin (3), apiosylskimmin (4), and Magnolioside (5), were isolated and evaluated for in vitro antiplasmodial activity, as well as for their cytotoxic potential on SK-OV-3 cancer cell lines. Compounds 1 and 5 showed notable growth inhibitory activity against chloroquine-sensitive strains of P. falciparum with IC(50) values of 5.3 and 8.2 μM. The compounds showed no significant cytotoxicity (IC(50) > 100 μM) toward the SK-OV-3 cancer cell line.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report on the antiplasmodial activity of these coumarin derivatives from the dried root of A. gigas.
Phytochemistry Letters, 2016 , 18 :23-28.
Chemical composition, antibacterial, antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of glycosides from aerial parts of Eryngium tricuspidatum L.[Reference:
WebLink]
Two new phenolic glucosides, together with six known compounds, were isolated from the aerial part of Eryngium tricuspidatum L. (Apiaceae).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of the new compounds were established as 2-hydroxy- 3,5-dimethyl-acetophenon-4-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (1) and 2,3-dimethyl-4-hydroxymethylphenyl-1-hydroxymethyl-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (2) on the basis of detailed spectroscopic data including MS, 1D, and 2D NMR. The antibacterial, tyrosinase inhibitory and DPPH radical scavenging activities of hydromethanolic extract, fractions, and the eight isolated compounds were evaluated. The antibacterial assay showed a moderate activity for Magnolioside (4) against Staphylococcus aureus CIP 53.154. Compound 7 (quercetin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 6)-O-β-d-galactopyranoside) had moderate DPPH radical scavenging activity whereas compounds 2 exhibited good inhibitory effect against mushroom tyrosinase.
Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Nov;30(11):1368-73.
Neuroprotective coumarins from the root of Angelica gigas: structure-activity relationships.[Pubmed:
18087802]
An n-butanol-soluble fraction of the root of Angelica gigas Nakai (Umbelliferae) exhibited significant protection against glutamate-induced toxicity in primary cultured rat cortical cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using neuroprotective activity-guided fractionation, nine coumarins; marmesinin (1), nodakenin (2), columbianetin-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), (S)-peucedanol-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4), (S)-peucedanol-3'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), skimmin (6), apiosylskimmin (7), isoapiosylskimmin (8) and Magnolioside (9), were isolated from the n-butanol fraction. Of these nine coumarins, three dihydrofuranocoumarins; 1, 2 and 3, exhibited significant neuroprotective activities against glutamate-induced toxicity, exhibiting cell viabilities of about 50% at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 microM. To explore the structure-activity relationships of coumarins, sixteen previously isolated compounds; 10-25, were simultaneously evaluated in the same system.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results revealed that cyclization of the isoprenyl group, such as dihydropyran or dihydrofuran, or the furan ring at the C-6 position of coumarin, as well as lipophilicity played an important role in the neuroprotective activity of coumarins.